Divisions in Society: A Narrative of 1980s Britain
The poem "Divisions" by Tony Harrison explores the societal divisions in 1980s Britain, touching on class, economic disparities, gender roles, educational differences, regional disparities, and psychological divisions. Through its structure, diction, and themes, the poem delves into the complexities
0 views • 7 slides
Overview of Poetry Genres and Elements for English Students
Explore different genres of poetry including narrative, epic, dramatic, satirical, elegy, fable, and prose poetry. Delve into the unique elements of poetry such as diction and figurative devices like simile and metaphor. Engage with various examples from renowned poets and learn about the aesthetic
1 views • 25 slides
Understanding the Five Parts of a Classical Argument
The classical argument is composed of five main parts: Introduction, Narration, Confirmation, Refutation and Concession, and Summation. Each part plays a crucial role in presenting a well-structured and persuasive argument, with devices and strategies such as diction, syntax, and figurative language
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding the Functions and Elements of Drama in Year 7 Curriculum
Explore the functions and elements of drama with Year 7 students in this engaging lesson. Understand how drama educates, informs, entertains, promotes tolerance, and more. Dive into the key elements like script, plot, diction, characterization, actors, and stage. Learn about playwrights and categori
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Rhetoric: Ethos, Pathos, Logos
Rhetoric is the art of persuasive communication in various contexts. It involves utilizing ethos (credibility), pathos (emotions), and logos (logic) to influence the audience. Distinguishing between argument and persuasion, this communication form employs elements such as organization patterns, appe
4 views • 18 slides
Understanding Aristotle's Poetics: A Critique of the Classic Age
Aristotle, a tutor to Alexander the Great, delves into fundamental concepts in his work "Poetics." He challenges Plato's view of imitation, emphasizing creativity. Focusing on Mimesis, Katharsis, Hamartia, and Spoudaios, he explores the essence of art and tragedy, highlighting noble character and tr
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Micromessaging: Hidden Impact of Subtle Behaviors
Micromessaging refers to the subtle, semi-conscious messages we send through our behaviors, both verbal and physical, that influence our interactions with others. These messages, categorized as micro-affirmations and micro-inequities, can have a significant impact on individuals. The concept delves
1 views • 17 slides
Exploring Diction in Writing: Connotation, Denotation, and Formality
Diction, the author's choice of words, is foundational in shaping voice. This content delves into diction elements such as connotation, denotation, and formality. It analyzes how words like "thirsting" and "prowling" evoke specific feelings and attitudes, giving examples from literature to illustrat
0 views • 8 slides
Analyzing Themes and Symbolism in Literature
Authors often use symbols to convey themes in their works. This analysis delves into how authors like William Golding in "Lord of the Flies" and Charles Dickens in his novels use symbols, settings, and diction to create mood, highlight societal issues, and develop characters like Pip and Estella. Th
0 views • 18 slides
Common Mistakes in Literary Double-Entry Journals
Diction analysis in double-entry journals often involves discussing the author's word choice and its impact on the overall meaning. Examples from various literary works, such as Bradbury's "Fahrenheit 451," demonstrate how specific words contribute to characterization and thematic development. Under
1 views • 25 slides
Mastering Diction: Lead/Led and Loose/Lose
Understand the differences between lead/led and loose/lose with clear explanations and examples. Learn how to use these words correctly in sentences to improve your writing skills. Explore the nuances of pronunciation and usage to avoid common mistakes. Practice exercises included for reinforcement.
0 views • 9 slides
Language Arts Class Agenda for January 12, 2016
Independent reading and in-class assignment on similes and poetry with a focus on denotation and connotation. Learning targets include writing similes, deciphering a poem's message, and understanding the difference between denotation and connotation. Success criteria involve completing pages 4 and 5
0 views • 13 slides
Exploring the Depths of a Poem: Uncovering Hidden Meanings
Dive deep into the essence of a poem, analyzing visual elements, content, and temporal aspects. Unravel the tones of both the speaker and the poet, examining diction, setting, syntax, form, and more. Discover the universal, psychological, theological, and social implications on human existence woven
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Colloquialisms and Diction in Language Usage
Colloquialisms are informal expressions commonly used in spoken language, while diction refers to the selection of words to express ideas effectively. Learn about common colloquialisms like "could of" and "be sure and" to avoid using them in formal writing. Enhance your understanding of proper usage
0 views • 40 slides
Literary Analysis: Imagery, Syntax, Diction, and Detail in Voice Lessons
Explore the use of auditory and olfactory imagery in Kate Chopin's "The Awakening," analyze the syntactic structure in Edgar Allan Poe's "The Black Cat," understand the nuances of diction, and delve into Winston Churchill's portrayal of King Henry VIII through contrasting details. Engage with questi
0 views • 22 slides
Mastering Diction: Imply vs. Infer, Irregardless, and In Regards To
Explore the nuances of diction with a focus on common pitfalls such as using "hopefully" incorrectly, distinguishing between "imply" and "infer," understanding why "irregardless" is not considered good usage, and learning the preferred usage of "in regards to." Enhance your writing skills by avoidin
0 views • 9 slides
Essential Music Terminology Explained
Learn about key music terms such as Pitch, Dynamics, Tempo, Composer, and more in this comprehensive guide. Understand concepts like Interval, Crescendo, Diction, and how they contribute to the world of music. Explore elements like Bar Line, Arranger, Phrases, and the different vocal parts like Alto
0 views • 35 slides
Diction: Understanding the Difference Between "All Together" and "Altogether"; "All Ready" and "Already
Understand the nuances between "all together" and "altogether," as well as "all ready" and "already." Learn how to use these phrases correctly through examples and clear explanations.
0 views • 5 slides
Effective Writing Tips for Academic Tone and Diction
Enhance your writing skills with tips on academic tone and diction. Learn to avoid contractions, abbreviate appropriately, and steer clear of clichés and regionalisms. Improve your communication by following these guidelines.
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Tone and Mood in Literature
Tone refers to the author's attitude towards the subject, while mood is the emotional atmosphere of the text. The difference lies in how the author feels versus how the reader feels. Understanding and analyzing tone involves considering aspects like diction, imagery, figurative language, and syntax.
0 views • 14 slides
The Professor Nissim Ezekiel - A Satirical Poem on Indian Professors
The Professor is a satirical poem written by Nissim Ezekiel that humorously portrays a typical Indian professor named Professor Seth boasting about his family and mispronouncing words. Ezekiel's subtle and well-crafted diction shines through this dramatic monologue. The poem, awarded the Sahitya Aka
0 views • 7 slides
Contrasting Perspectives on Death: Kooser's A Death in the Office vs. Keats' The Human Seasons
Ted Kooser's "A Death in the Office" and John Keats' "The Human Seasons" present differing views on mortality. Kooser portrays death as a routine process, while Keats sees it as a natural phase of life. Despite not explicitly mentioning death, both poems evoke contemplation on the inevitability of o
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Poetic Form and Meaning in English Poetry
Explore the intricate elements of poetic form, such as rhyme, meter, stanzas, and refrains, in popular English forms like ballads, sonnets, odes, and free verse. Delve into the significance of traditional ballads like "La Belle Dame sans Merci" and "The Tyger," discovering how these poems subvert ex
0 views • 22 slides
Diction in Grammar: Accept vs. Except, Advice vs. Advise
Understand the distinctions between commonly confused word pairs in English grammar: "accept" vs. "except" and "advice" vs. "advise." Practice examples provided to enhance comprehension and usage accuracy.
0 views • 6 slides
5th Grade Music Curriculum Overview
Students in 5th grade music cover various elements such as identifying instruments, learning chordal accompaniments, performing blues progressions, reading melodies, singing with clear diction, and composing music. Each marking period focuses on different aspects like tone color, vocal expression, m
0 views • 4 slides
Common Diction Errors: Their, There, They're; To, Too, Two; Your, You're
Exploring common diction errors such as confusing "their, there, they're" and "to, too, two," along with "your, you're." This mini-lesson clarifies their differences and provides examples for better understanding.
0 views • 9 slides
Literary Terms Guide for Academic Year
In preparation for the upcoming school year, familiarize yourself with key literary terms such as Character, Diction, Imagery, Exposition, and more. Understand the roles of Antagonists and Protagonists, learn about Diction, Denotation, Connotation, and how they shape writing. Enhance your understand
0 views • 31 slides
Mastering Voice in Writing: Diction, Detail, Imagery, Syntax, and Tone
Enhance your writing by mastering the elements of voice - diction, detail, imagery, syntax, and tone. Discover how word choice shapes effective communication and learn the importance of clarity and precision in creating impactful writing.
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Tragedy in English Literature: An Overview
Tragedy, as defined by Aristotle, is the imitation of a serious action complete in itself, depicted through language and incidents that evoke pity and fear. This introduction delves into the key elements of tragedy, such as plot, character, thought, diction, song, and spectacle, with a focus on Thom
0 views • 13 slides
Humour in RC Sherriff's Journey's End: A Reflection on War
RC Sherriff's play "Journey's End" delves into the experiences of soldiers during World War I, portraying a mix of fear, camaraderie, and subtle humour as coping mechanisms. The use of humour, particularly through character interactions, provides relief from the harsh realities of war and adds a hum
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Author's Style: Language, Diction, and Voice
Author's style encompasses various elements like syntax, diction, tone, and perspective. By analyzing how language is used, dialogue realism, sentence structure, tone, and word choice, one can determine the unique voice of the author. This guide explains how to identify and evaluate an author's styl
0 views • 17 slides
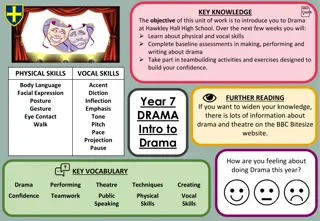
Drama Introduction at Hawkley Hall High School
Introduction to Drama at Hawkley Hall High School focuses on exploring physical and vocal skills, participating in team-building activities, and developing confidence in drama. Students will learn about body language, facial expression, posture, gesture, accent, diction, tone, pitch, projection, and
0 views • 5 slides
Analysis of "The Highwayman" Poem by Alfred Noyes
The analysis delves into the themes, characters, setting, diction, figures of speech, and overall message of Alfred Noyes' famous poem "The Highwayman." It explores the tragic love story between the highwayman and Bess, highlighting the evocative language and vivid imagery used to convey a tale of r
0 views • 14 slides
Insights into Elizabethan Poetry: A Glance at the Golden Age
The Elizabethan Age, also known as the Age of Shakespeare, during Queen Elizabeth I's reign from 1558 to 1603, marked a golden era in English poetry. This period saw a flourishing of poetic forms influenced by Greek and Italian poetry. Major poets like Edmund Spenser, Sir Philip Sidney, and William
0 views • 6 slides
Rhetorical Devices in Speeches of Elizabeth I and Abraham Lincoln
Explore the use of various rhetorical devices such as imagery, diction, connotation, denotation, metaphor, analogy, juxtaposition, antithesis, parallelism, repetition, and polysyndeton in the speeches of Queen Elizabeth I and President Abraham Lincoln. Witness how these rhetorical techniques enhance
0 views • 12 slides
Literary Analysis of "The Catcher in the Rye": Themes, Characters, and Devices
Explore the coming-of-age theme, first-person point of view, diction, motifs, hyperbole, and symbols in J.D. Salinger's novel "The Catcher in the Rye." Delve into the societal and literary implications of Holden Caulfield's journey from innocence to experience, analyzing the characters, themes, and
0 views • 13 slides
Mastering Diction: A Lot vs. Alot and All Right
Understand the nuances of diction with a focus on common errors like "a lot" vs. "alot" and "all right" vs. "alright." Dive into the correct usage of these terms, learn informal vs. formal language distinctions, and challenge your understanding with practice exercises.
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Diction and Denotation in Literature
Explore the concepts of diction, denotation, and connotation in English literature through an analysis of "My Papa's Waltz." Delve into the nuances of word choice, emotional coloration, and childhood experiences portrayed in the poem, questioning the expectations versus the reality portrayed. Uncove
0 views • 10 slides
Exploring Elements of Poetry: Diction, Rhythm, Stanza, Lines, Theme
Delve into the nuances of poetry with a focus on diction, rhythm, stanza formation, line arrangement, and thematic exploration. Understand how these elements contribute to the mood and meaning of a poem through insightful analysis and review questions.
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Diction, Connotation, Denotation, and Syntax in Writing
Explore the nuances of diction, connotation, denotation, and syntax in writing through examples and explanations. Discover how word choice, emotional undertones, literal meanings, and sentence structure impact the effectiveness and perception of written work. Enhance your understanding of these key
0 views • 10 slides