Non-Standard Errors in Research Methods
Research teams conducting experiments using the same data show large variations in results, termed as non-standard errors (NSE). Peer feedback helps reduce NSE, but factors like vague hypotheses and test statistic definitions can lead to result discrepancies. Addressing issues like multiple hypothes
2 views • 12 slides
Skin Cancer Cases Surge in France Due
This alarming statistic comes as skin cancer cases have seen a significant rise over the past five decades.
0 views • 6 slides
Educational Statistics: Key Concepts and Calculations
Statistics is the science of collecting, describing, and interpreting data. It involves two main areas - Descriptive Statistics for organizing and presenting data and Inferential Statistics for drawing conclusions about populations. An example scenario demonstrates the terms like population, sample,
1 views • 35 slides
Chi-Square Tests in Statistics
Chi-square tests in statistics are used to examine the relationship between categorical variables or test claims about categorical variable distributions in populations. The Chi-square test statistic measures the discrepancy between observed and expected counts, with the Chi-square distribution help
1 views • 16 slides
Health and Inequality in Ghana
This exploration delves into health and inequality issues, focusing on maternal health in Ghana. It discusses maternal health goals, a comparison between Ghana and the UK, and profiles of mothers from both the southern and northern regions of Ghana. The content emphasizes the importance of free heal
0 views • 13 slides
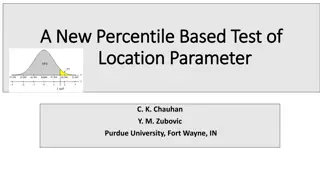
Percentile Based Test of Location Parameter & Unbiased Estimates
Proposing a new percentile-based test for determining the true mean of a normal distribution when two symmetric sample percentile values are known. The test statistic is explored for its distribution properties and performance through simulation. Additionally, investigating unbiased estimates and id
1 views • 22 slides
Cambodian National ID Program Overview
The General Department of Identification (GDI) in the Kingdom of Cambodia oversees various departments such as Civil Registration, People Statistic, Khmer ID Card, Passport, and Nationality. Their scope includes managing identity issues for the population, supervising administration services, issuin
0 views • 13 slides
Central Tendency and Variability in Distributions
Central tendency and variability are fundamental features of statistical distributions. Central tendency, encompassing mean, median, and mode, represents the middle of a distribution, while variability describes the spread of data points. Knowing the effect of distribution shape on these measures he
1 views • 25 slides
Vital Statistics Registration Process and Data Collection Overview
This content provides detailed information on the vital statistics registration process, including live birth characteristics, data collection procedures, and coverage of items such as date of occurrence, registration, place of birth, mother and father characteristics. It also outlines the central s
1 views • 15 slides
Regression Analysis in Statistical Research
Regression analysis, specifically focusing on the R2 statistic, is a method used to examine the relationship between two variables at an interval/ratio level. It evaluates how well a line fits the data and measures the strength of the relationship between independent and dependent variables. Being s
1 views • 5 slides
Exploring Word Embeddings and Syntax Encoding
Word embeddings play a crucial role in natural language processing, offering insights into syntax encoding. Jacob Andreas and Dan Klein from UC Berkeley delve into the impact of embeddings on various linguistic aspects like vocabulary expansion and statistic pooling. Through different hypotheses, th
0 views • 26 slides
One Factor Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
One Factor Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) is a statistical method used to compare means of three or more groups. This method involves defining factors, measuring responses, examining assumptions, utilizing the F-distribution, and formulating hypothesis tests. ANOVA requires that populations are normal
0 views • 23 slides
Confidence Limits in Statistical Analysis
Confidence limits are a crucial concept in statistical analysis, representing the upper and lower boundaries of confidence intervals. They provide a range of values around a sample statistic within which the true parameter is expected to lie with a certain probability. By calculating these limits, r
1 views • 4 slides
Introduction to Independent Sample Means T-Test in Educational and Psychological Research
Independent Sample Means T-Test is a statistical analysis used to compare the means of two independent groups to determine if there is a significant difference between them. This test is commonly used in educational and psychological research to assess the effectiveness of interventions or treatment
2 views • 21 slides
Permutation Tests and False Detection Rate in HPV Vaccine Trial
Permutation tests are computer-intensive methods used for hypothesis testing when the distribution of the test statistic is unknown. In a hypothetical HPV vaccine trial with 200 women, the scientific question revolves around comparing infection risks in groups receiving the vaccine and placebo. The
0 views • 19 slides
Civil Registration and Vital Statistics System in Viet Nam
The Civil Registration and Vital Statistics System in Viet Nam plays a crucial role in gathering population data for various governmental purposes. The General Statistic Office, along with other ministries, oversees the legal framework and data collection processes to ensure accurate information for
0 views • 18 slides
Big Data Modernization in Colombia: Experiences & Innovations
Since 2014, Colombia's National Statistic System (NSS) has been undergoing modernization and innovation to enhance the generation, production, and dissemination of statistics. The incorporation of non-traditional data sources, such as Big Data, has revolutionized the statistical process, emphasizing
0 views • 13 slides
Measures of Model Goodness in Classification
In this learning material, metrics for classifiers are explored, focusing on the accuracy measure as a common but limited metric. The concept of accuracy is discussed alongside its drawbacks when there is uneven assignment to categories, leading to a presentation of the Kappa statistic as a more nua
0 views • 39 slides
Understanding Medical Errors: Causes and Impact
Medical errors are a critical issue often overshadowed in healthcare. This content delves into the root causes, including communication problems, staffing issues, and technical failures. It highlights the alarming statistic that medical errors are the third leading cause of death in the U.S. Researc
0 views • 9 slides
METAL Practical
Learn how to run a meta-analysis using METAL software to combine results files from genetic association studies. Follow steps for file preparation, driver file creation, and executing the meta-analysis based on effect size and test statistic.
0 views • 17 slides
Intraclass Kappa for Test-Retest Reliability Measurement
Learn about the importance of establishing reliability in structured interview and questionnaire instruments for valid measurement. Discover how the Intraclass Kappa statistic can address rater bias in test-retest reliability assessments. Find out how to calculate and interpret the Intraclass Kappa
0 views • 16 slides
Permutation Tests and False Detection Rate in Research
Explore the concept of permutation tests and the importance of maintaining the Type I error level without large sample approximations. Using the example of an HPV vaccine trial, learn how to restate scientific questions as statistical hypotheses and analyze the differences in infection probabilities
0 views • 19 slides
Introduction to Statistical Analysis: Types of Statistics & Calculations
Explore the basics of statistical analysis, including descriptive and inferential statistics, population vs. sample, variables, data types, and key terms like parameter and statistic. Learn through exercises on school supplies spending and malpractice insurance studies.
0 views • 10 slides