Projectile Motion: Characteristics, Examples, and Formulas
Projectile motion involves the motion of objects under the influence of gravity, with both vertical and horizontal components. This type of motion is seen in activities such as throwing a ball, kicking a football, or dropping objects. The motion is described by specific formulas, including calculati
19 views • 19 slides
Motion: Frames of Reference and Relative Motion
Motion is defined as a change in position over time. To describe motion accurately, one needs to understand frames of reference and relative motion. Frames of reference are systems of objects used to determine if something is in motion, while relative motion involves movement in relation to a refere
9 views • 14 slides
Motion: Concepts and Definitions in Physics
Motion in physics is defined as the change in position of an object over time. It involves concepts like rest, motion, distance, displacement, rate of motion, and types of motion. Rest and motion are relative to a reference point, while distance and displacement differ in their scalar and vector nat
5 views • 25 slides
Motion Planning in Klamp't: Overview and Key Concepts
Motion Planning in Klamp't covers key concepts such as C-Space and robot-level abstractions, planning algorithms, toolkit components, and the kinematic planning pipeline. It compares to other packages like OMPL, MoveIt!, and OpenRAVE, offering PRM-style planners at the C-Space level and support for
1 views • 26 slides
Autonomous Obstacle Avoidance Robot Using ROS, Lidar, and Raspberry Pi with Matlab Path Planning
Obstacle avoidance in robotics has evolved from basic collision avoidance to autonomous path planning with the use of Lidar and ROS. This project involves mapping the environment using Lidar scans and implementing a path planning algorithm in Matlab to navigate around obstacles. By utilizing a Raspb
17 views • 15 slides
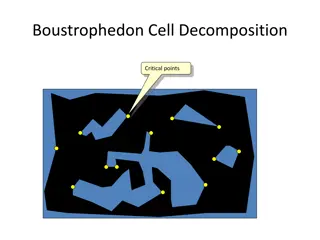
Robot Motion Planning Algorithms Overview
Explore Boustrophedon Cell Decomposition, Probabilistic Road Maps, and RRT Algorithm for robot motion planning. Learn how PRMs perform in practice but can face challenges in narrow passages leading to disconnected graphs.
5 views • 5 slides
Circular Motion in Physics
Circular motion involves objects moving in a circular path at a constant speed, experiencing acceleration and centripetal force. This motion is characterized by angular speed, centripetal acceleration, and the necessary centripetal force. The concept of uniform circular motion and angular displaceme
4 views • 38 slides
Robotic Motion Planning: Approaches and Research Issues
This content delves into various aspects of robot motion planning, covering topics such as problem-solving in mobile robotics, strategic planning, obstacle avoidance, control, base algorithms like graph search, pros and cons of different approaches, research issues, and objectives related to travel.
3 views • 26 slides
Joint Motion: Osteokinematic and Arthrokinematic Movements
Joint motion involves osteokinematic movements, which are under voluntary control and include flexion, extension, and more. End-feel sensations like bony, capsular, and springy block indicate different joint conditions. Arthrokinematic motion refers to how joint surfaces move during osteokinematic m
1 views • 17 slides
Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion explain the relationship between forces and motion. The first law states that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a net force, while the second law describes how force is related to an object's mass and acceleration. The third law states that for every ac
2 views • 21 slides
Mind Controlled Robot Project by Adithya Kumar - Eighth Grade
Adithya Kumar, an eighth-grade student, has designed a groundbreaking Mind Controlled Robot project that allows users to control a robot using brain waves. The project utilizes a Mindwave EEG headset, Arduino Uno motherboard kit, and various materials. Adithya's detailed experimental design and proc
1 views • 11 slides
ROBOSYNTH: SMT-Based Synthesis of Integrated Task and Motion Plans
The ROBOSYNTH system aims to facilitate the creation of task plans that are feasible at the motion level by integrating task and motion planning. It provides a structured approach to generating plans, considering constraints on robot paths. The system employs a C program with defined actions and con
3 views • 25 slides
Mobile Robot Kinematics for Navigation
Exploring the kinematics of wheeled locomotion in mobile robots, this content covers forward and inverse kinematics, instantaneous center of curvature, and the use of kinematics for robot navigation. Highlighting the challenges of measuring robot position and the integration of wheel velocities for
5 views • 52 slides
Robot Localization Using Kalman Filters
Robot localization in a hallway is achieved through Kalman-like filters that use sensor data to estimate the robot's position based on a map of the environment. This process involves incorporating measurements, updating state estimates, and relying on Gaussian assumptions for accuracy. The robot's u
9 views • 26 slides
Shy Robot Programming Challenge: Logic-Based Autonomous Robot
The Shy Robot is an autonomous robot equipped with two IR sensors to avoid obstacles. Its behavior is determined by a logical control system - moving backward if both sensors detect an object, turning right if only the left sensor detects an object, turning left if only the right sensor detects an o
9 views • 5 slides
Installation of Robot-Mounted Detector on DIAD Beamline
Installing a robot-mounted detector on the DIAD beamline for the 2021 MOCRAF Workshop at the ICALEPCS conference. The robot arm holds a diffraction detector for dual imaging and diffraction purposes, ensuring safety for personnel, equipment, and integration into EPICS and GDA systems. Functionality
0 views • 28 slides
Motion and Newton's Laws
Explore the concepts of motion, distance, speed, and velocity as they relate to Newton's Laws of Motion. Learn about measuring motion, calculating speed, graphing motion on distance-time graphs, and understanding velocity. Discover how motion is constant and how relative motion is used. Practice cal
3 views • 36 slides
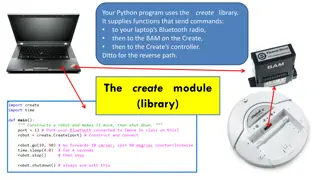
Python Create Library Overview
This Python program uses the Create library to send commands, enabling communication between your laptop's Bluetooth radio, the BAM on the Create robot, and the Create's controller. The library facilitates non-blocking commands for controlling the robot's movements and sensors, with specific instruc
5 views • 9 slides
Futuristic Patient Assistant Robot Enhancing Healthcare
This research project introduces a patient assistant robot supervised by Dr. Ahmed Mostafa and presented by a team comprising Amira Ibrahim Sayed, Asmaa Mohamed Saad, and Amna Ahmed Mohammed. The robot aims to assist individuals with infectious diseases by providing essential care and isolating them
2 views • 22 slides
Universal Collaborative Robot Platform Revolutionizing Robotics Industry
The Universal Collaborative Robot Platform is a game-changer in the robotics world, providing full autonomy, innovation, creativity, and enhanced productivity through robot collaboration. With features like universal robot communication protocols, centralized fleet management, mobile autonomy, and A
0 views • 14 slides
Dependent and Relative Motion in Dynamics
Dependent Motion and Relative Motion are fundamental concepts in Dynamics, providing the foundation for future analysis. Dependent Motion involves constraints like ropes or cables, while Relative Motion considers observers in motion. Dynamics involves applying a limited set of equations in diverse w
2 views • 18 slides
Motion: Types and Physics
Motion refers to a body changing position with respect to its surroundings. Different types of motion include linear, rotatory, and oscillatory motion. The physics relating to motion is called Mechanics, which comprises Dynamics and Kinematics. Scalars and vectors play a crucial role in describing t
5 views • 8 slides
Motion Perception in Computational Vision
In computational vision, the concept of motion opponency plays a crucial role in how the brain processes left and right motion inputs. By examining psychophysical results and the construction of motion opponent energy filters, we explore how the brain handles motion information. Additionally, the Ve
3 views • 23 slides
Motion in Physics: Definitions and Examples
An object is said to be in motion if it changes position with time, while rest implies no change. Learn about types of motion such as linear and circular, as well as vibratory motion and reference points. Explore how objects can be in motion relative to one reference point while at rest relative to
3 views • 4 slides
Evolution of Motion Theories: Aristotle to Einstein
Explore the progression of motion theories from Aristotle's belief in a force for motion to Galileo's discoveries on gravity, Newton's laws of motion, and Einstein's theories of relativity and quantum mechanics. Discover how our understanding of motion has evolved over the centuries, shaping the way
3 views • 20 slides
PROJECTILE MOTION
Fundamental concepts of projectile motion, where objects follow paths influenced by gravity and initial velocity. Dive into the separable X and Y motion components, superposition principle, initial velocity considerations, equations for motion, and trajectories on level ground. Discover the interpla
0 views • 8 slides
Robocup Localization - Keys for Robot Functionality
Localization plays a crucial role in helping robots understand their position and make decisions. It is essential for tasks such as planning moves and solving vision-related problems. Implementation involves using a combination of data from robot vision, internal gyro, and motion to estimate the rob
2 views • 39 slides
Robocup HR-OS5 Humanoid Research Robot Specs and Motion Details
The HR-OS5 Humanoid Research Robot specifications include the use of Dynamixel Servos, sensors like gyroscope and accelerometer, a camera system with microphones, and Intel computing units. The motion focus involves enhancing walking capabilities, ball kicking, stability in movements like standing u
0 views • 4 slides
Robocup Motion: HR-OS5 Humanoid Research Robot Specs & Demo
The RobocupRobocupMotion team focused on enhancing the motion capabilities of the HR-OS5 Humanoid Research Robot for the 2016 Robocup KSL in Germany. They worked on walking, ball kicking, stability, goalkeeper skills, and more. The robot utilized Dynamixel Servos, sensors like a gyroscope and accele
3 views • 4 slides
Robot Motion Planning and Configuration in Computational Geometry
This lecture notes outline the fundamentals of robot motion planning, discussing configuration space, collision-free path planning, and degrees of freedom in computational geometry. The content covers static environments, reference points for robots, configurations with rotation, and degrees of free
1 views • 21 slides
DIY Mobile Controlled Robot without Microcontroller for Long-Distance Wireless Control
Learn how to build a mobile-controlled robot without a microcontroller using DTMF tones for long-distance wireless control. This beginner-friendly project utilizes two mobile phones and basic components to create a versatile robot for various applications such as search and rescue or remote monitori
13 views • 11 slides
Summer 2024 Robotics Course Preparation for XRP Robot
Dive into the summer 2024 robotics course designed for the XRP robot connected via wifi. Get hands-on with assembling the robot, configuring the Raspberry Pi Pico, and setting up the robot's wifi network. Follow the step-by-step instructions to ensure your robot is ready for an exciting learning exp
0 views • 14 slides
Robot Motion Through Differential Kinematics
Delve into the world of robot motion by exploring the Differential Kinematics method, which involves analyzing pose velocities of frames using differential forms of homogeneous transformations. This chapter compares this approach to conventional dynamics vector methods and discusses the crucial role
2 views • 37 slides
Exploring Robotics in Mechatronics: ELC4047 Course Overview
Dive into the world of robotics with the elective course ELC4047, focusing on classification, types, motion, and planning. Understand the relationship between robotics and mechatronics, and explore different types of robots such as vehicles, humanoid, snake, spider, quad-rotor, and serial robot arm.
2 views • 8 slides
Design Project: Biped Robot Balancing and Movement
This design project focuses on creating a biped robot for balancing and movement on various terrains. The robot features autonomous capabilities and wheels for stability, allowing it to move in all directions. Control is achieved through uploaded instructions. The project includes detailed design de
0 views • 25 slides
Task and Motion Planning in Robotics: A Hierarchical Approach
Explore the challenges and strategies of creating a general agent capable of robustly performing diverse tasks in varied environments through a hierarchical task and motion planning approach. Delve into the history of deep reinforcement learning and the fusion of symbolic task planning with low-leve
0 views • 24 slides
Kinematics: Describing Motion and Equations of Motion
Explore the principles of kinematics, including uniformly accelerated motion, interpreting graphs, and solving motion problems using equations. Learn about vectors, sign conventions, and analyze motion through various graph reviews. Understand the concepts of constant motion and acceleration, along
4 views • 13 slides
Motion Maps and Complicated Motion Patterns
Explore the concept of motion maps and complicated motion patterns in science, understanding how to represent objects' positions, directions, and velocities using dots and arrows. Learn how to draw motion maps and analyze examples of accelerating and constant velocity motion scenarios.
0 views • 10 slides
Lecture on Rotational Motion in Classical Mechanics
Explore the concepts of rotational motion including rigid body motion, moment of inertia tensor, torque-free motion, comparison of analysis in inertial vs. non-inertial frames, and properties of frame motion (rotation) in this lecture. Understand the physics of rigid body motion, effects on accelera
3 views • 22 slides
Computational Geometry and Robot Motion Planning
Learn about configuration space, collision-free path planning, degrees of freedom, and manipulators in computational geometry and robot motion planning from the lecture notes of Introduction to Computational Geometry. Understand concepts such as configuration representation, rotation, and degrees of
1 views • 21 slides