Computability: Exploring Theoretical Limits of Computation
Delve into computability theory, focusing on what is computable and the limits of computation. Explore concepts like Rice's Theorem, the Halting Problem, and classes of expressiveness in computability theory, such as combinational logic, finite-state machines, pushdown automata, and Turing machines.
5 views • 43 slides
Introduction to Regular Expressions and Equivalence to Finite Automata
Regular expressions (REs) are used to describe languages by algebra and are equivalent to finite automata. They define regular languages precisely using operations like union, concatenation, and Kleene star. The concatenation of languages combines strings from two languages, while the Kleene star re
9 views • 106 slides
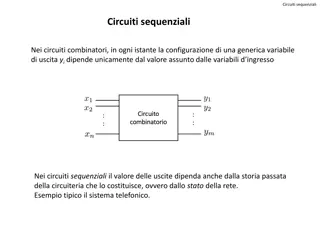
Understanding Sequential Circuits: A Brief Overview
Sequential circuits differ from combinational circuits in that the output depends not just on the current input but also on the circuit's past history. This overview covers the basics of sequential circuits, including finite-state automata, states, transitions, and memory elements like flip-flops.
2 views • 50 slides
Understanding Formal Languages and Automata Theory
This course delves into abstract models of computers and computation, offering essential concepts and principles for understanding the fundamental nature of the computer field. Exploring topics such as regular expressions, context-free grammars, and automata theory, students gain insights into the p
3 views • 11 slides
Understanding Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) in Regular Language Theory
An exploration of Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) in the context of Regular Languages, covering their definition, functioning, application in recognizing input strings, and building a DFA for a specific language. The Chomsky Hierarchy and the significance of Regular Languages are also briefly di
0 views • 41 slides
Understanding Pushdown Automata and Language Acceptance
Pushdown Automata (PDA) provide a theoretical framework for recognizing context-free languages. In PDA, the acceptance of a language depends on reaching a final state or having an empty stack. This concept is illustrated through examples and the distinction between deterministic and non-deterministi
0 views • 10 slides
Exploring E.T.A. Hoffmann's "The Sandman": A Study in Romanticism, Irony, and the Uncanny
Delve into the world of E.T.A. Hoffmann's literary masterpiece "The Sandman," where themes of Romanticism versus rationality, irony, and the uncanny intertwine. Through the characters of Nathaniel and Clara, the story explores the tensions between passion and reason, imagination and reality. Dive de
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Computer Theory: From Automata to Turing Machines
Dive into the world of computer theory, exploring concepts like automata, formal languages, and Turing machines. Learn about pioneers like Alan Turing and the fundamental questions in computer science, from computability to complexity.
0 views • 44 slides
Understanding Myhill-Nerode Theorem in Automata Theory
Myhill-Nerode theorem states that three statements are equivalent regarding the properties of a regular language: 1) L is the union of some equivalence classes of a right-invariant equivalence relation of finite index, 2) Equivalence relation RL is defined in a specific way, and 3) RL has finite ind
1 views • 20 slides
Understanding Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) and Pushdown Automata
Exploring Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) and Pushdown Automata, covering definitions, examples, ambiguity, and conversions. Learn about generating strings, CFG formal definitions, ambiguity in grammars, and more. Connect with the basics of context-free languages and their relations to PDAs. Dive into
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Chomsky Hierarchy in Language Theory
Explore Chomsky Hierarchy in language theory, including different types of languages, grammars, and automata. Learn how to prove if a language is regular, context-free, recursive, or recursively enumerable. Understand the closure properties of regular, context-free, recursive, and recursively enumer
2 views • 10 slides
Equivalence of Regular Expressions and Finite Automata
Regular expressions are an algebraic method to describe languages, specifically the regular languages. They are defined recursively based on symbols and operations such as concatenation and closure. Precedence rules and examples are also provided. The equivalence between regular expressions and fini
0 views • 25 slides
Exploring Engineering Mathematics and Automata Theory Concepts
Delve into topics such as automata theory, Turing machines, and mathematical approaches for addition using unary numbers. Discover state transition diagrams and gain insights into the workings of Turing machines in computer science.
0 views • 23 slides
Formal Verification and Automata Abstraction in Esterel
This content delves into the applications of formal verification and automata abstraction in Esterel, focusing on techniques such as verification by abstraction of automata, boolean verification using BDDs, bounded model checking in SAT/SMT, and more. The work of Gérard Berry at the Collège de Fra
0 views • 38 slides
Abstract Domains for Lists and Heap Structures: A Comprehensive Overview
Explore the concepts of quantified data automata on skinny trees, automatic shapes in static analysis, universally quantified properties on lists, heap configurations with skinny trees, and the extension of quantified data automata over lists. Dive into the abstract domain of automata to capture inf
1 views • 20 slides
Explore the World of Computational Linguistics: An Interactive Journey
Embark on a captivating interactive journey into the realm of computational linguistics through a series of engaging activities and challenges. Discover how machines process texts, decode mysterious languages, understand Japanese with data structures, and more. Test your skills in deciphering langua
0 views • 44 slides
Understanding Finite Automata and Regular Functions in Computer Science
Exploring the concepts of regular functions, languages vs functions, finite-state computation, finite automata with cost labels, finite automata with cost registers, and examples of Cost Register Automata. These topics delve into the theoretical and practical aspects of defining functions and comput
1 views • 46 slides
Regular Expressions Examples in Theory of Automata
Explore various examples of regular expressions in the context of the Theory of Automata, including defining languages based on patterns such as words ending with 'b', containing double letters, starting and ending with double letters, and more.
0 views • 45 slides
Exploring the Legacy of Automata: Insights from Rajeev Alur at VardiFest 2022
Delve into the fascinating journey of Rajeev Alur's contributions to automata theory, from his early mentorship under Moshe Vardi to groundbreaking collaborations and key insights on automata over infinite words. Discover the essence of automata, its significance in decision problems, and the techni
0 views • 32 slides
Compiler Data Structures and NFA to DFA Conversion
Compiler data structures play a crucial role in the compilation process, handling lexical analysis to code generation. Understanding the conversion from non-deterministic finite automata (NFA) to deterministic finite automata (DFA) is essential for efficient language processing and optimization.
0 views • 10 slides
Automata Theory and Theory of Computation Overview
This course overview covers concepts in automata theory and theory of computation, including formal language classes, grammars, recognizers, theorems in automata theory, decidability, and intractability of computational problems. The Chomsky hierarchy, interplay between computing components, modern-
0 views • 42 slides
Undecidability in Rectangular Hybrid Automata Analysis
The undecidability of the reachability analysis in rectangular hybrid automata (RHA) poses challenges for verifying cyber-physical systems. This complexity was demonstrated through a reduction from the Halting problem of two counter machines by Henzinger et al. Additionally, the review of computabil
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding GPU Performance for NFA Processing
Hongyuan Liu, Sreepathi Pai, and Adwait Jog delve into the challenges of GPU performance when executing NFAs. They address data movement and utilization issues, proposing solutions and discussing the efficiency of processing large-scale NFAs on GPUs. The research explores architectures and paralleli
0 views • 25 slides
Planning and Scheduling for On-Board Aerospace Applications: From Safety to Resilience
This document discusses planning and scheduling for on-board aerospace applications, focusing on safety and resilience aspects. It covers topics such as autonomous control, classic engineering with finite state automata, and autonomous system context. The content explores scenarios related to propul
1 views • 7 slides
Understanding Pushdown Automata (PDA) in Computer Science
Pushdown Automata (PDA) are essential in theoretical computer science, serving as an extension of non-deterministic finite automata (NFA). PDAs incorporate a stack, enabling them to recognize non-regular languages. They are described by transitions involving input symbols, state changes, and stack m
0 views • 46 slides
Understanding Pushdown Automata (PDA) in Computer Engineering
Pushdown Automata (PDA) is a powerful computational model that extends the capabilities of Finite Automata (FA) by incorporating a stack memory. PDAs can accept languages that FA cannot, making them essential in theoretical computer science. They consist of components like input tape, finite control
0 views • 59 slides
Theory of Automata: Introduction and Regular Languages Overview
This course delves into the fundamentals of Theory of Automata, exploring topics such as regular languages, finite state models, grammars, Turing machines, and more. Instructor Mr. Muhammad Arif guides students through essential concepts like finite automata, pumping lemma, decidability, and Chomsky
0 views • 95 slides
Exploring Cellular Automata: A Fascinating World of Rules and Patterns
Delve into the intricate realm of cellular automata, from elementary one-dimensional systems to the renowned Game of Life. Discover the versatility and complexity of these systems, including their capacity for simulating universes and implementing logic gates. Uncover the emergence of life-like beha
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Pushdown Automata (PDA) for Context-Free Languages
Pushdown Automata (PDA) is a crucial concept in the theory of computation, specifically for the recognition of context-free languages. PDAs are an extension of nondeterministic finite automata (NFA) with an added stack memory. This summary provides insights into the definition, transition functions,
0 views • 34 slides