ECMC: Open Source Motion Control with EtherCAT Overview
ECMC is an open-source motion control module designed for EPICS environments, integrating EtherLab's EtherCAT master. It offers advanced features like synchronized motion, distributed clocks, and PLC functionalities, making it ideal for various automation applications. The system architecture and ha
1 views • 42 slides
How To Use Wired Motion Sensor Closet Light
Motion sensor lights provide the convenience of constant, powerful illumination without the need to manually turn them on or off. Additionally, it saves time while looking for switches in places with low lighting that you could miss at first. Compared to traditional lighting solutions, motion sensor
1 views • 1 slides
Projectile Motion: Characteristics, Examples, and Formulas
Projectile motion involves the motion of objects under the influence of gravity, with both vertical and horizontal components. This type of motion is seen in activities such as throwing a ball, kicking a football, or dropping objects. The motion is described by specific formulas, including calculati
2 views • 19 slides
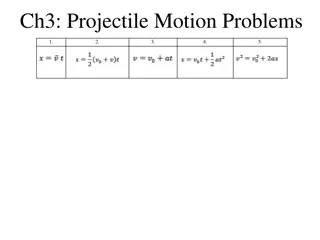
Projectile Motion: Components and Trajectories
Projectile motion involves the horizontal and vertical components of motion, where objects follow parabolic trajectories under the influence of gravity. The horizontal and vertical motions are independent of each other, leading to a variety of curved paths. This phenomenon is illustrated through exa
1 views • 13 slides
Projectile Weaving Machines in Fabric Manufacture
Projectile weaving machines revolutionized fabric manufacturing with their unique weft insertion system. Introduced by Sulzer Brothers in 1953, these machines feature separate units for picking and projectile receiving, utilizing a gripper projectile to carry the weft thread without the need for win
0 views • 13 slides
Projectile Motion: An In-depth Analysis
Explore the principles of projectile motion through images illustrating the effects of gravity on launched objects. Learn about the vertical and horizontal components, velocity changes, range, and how different launch angles impact the trajectory and distance traveled by projectiles.
0 views • 19 slides
Newton's First Law of Inertia
Newton's first law of inertia states that objects remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. This law, also known as the law of inertia, explains how objects tend to maintain their current state of motion unless influenced by an external force. Objects at rest stay a
0 views • 14 slides
Motion: Frames of Reference and Relative Motion
Motion is defined as a change in position over time. To describe motion accurately, one needs to understand frames of reference and relative motion. Frames of reference are systems of objects used to determine if something is in motion, while relative motion involves movement in relation to a refere
3 views • 14 slides
Motion: Concepts and Definitions in Physics
Motion in physics is defined as the change in position of an object over time. It involves concepts like rest, motion, distance, displacement, rate of motion, and types of motion. Rest and motion are relative to a reference point, while distance and displacement differ in their scalar and vector nat
2 views • 25 slides
Engineering Dynamics Principles and Problem Solving
Understanding the laws of motion and their application in dynamics is crucial in engineering. This content explains the concepts of force, acceleration, and inertia through practical examples such as projectile motion and frictional forces on a baggage truck. It also demonstrates how to calculate ma
0 views • 10 slides
Introduction to Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines in Mechanical Engineering
Theory of Mechanics delves into motion, time, and forces, with Kinematics focusing on motion analysis without considering external forces. Kinetics, a branch of Theory of Machines, deals with inertia forces resulting from mass and motion. Dynamics combines Kinematics and Kinetics to study motion and
0 views • 14 slides
Linear and Rotational Motion in Physics
Explore the concepts of linear momentum, center of mass, rotational motion, and angular displacement in physics. Learn how to determine the center of mass of objects, analyze motion of particle groups, and understand the conservation of momentum in systems under external forces. Delve into the funda
0 views • 18 slides
Circular Motion in Physics
Circular motion involves objects moving in a circular path at a constant speed, experiencing acceleration and centripetal force. This motion is characterized by angular speed, centripetal acceleration, and the necessary centripetal force. The concept of uniform circular motion and angular displaceme
3 views • 38 slides
Newton's First Law of Motion
Exploring the foundational concepts of motion and forces, this content delves into Isaac Newton's First Law of Motion. Describing how objects behave when the net force acting on them is zero, the law highlights the significance of inertia and balanced forces in determining an object's state of rest
0 views • 9 slides
Projectile Motion in Physics
A projectile, acted upon by gravity, follows a parabolic path in projectile motion. By choosing appropriate coordinates and strategies, analyzing motion along vertical and horizontal axes becomes manageable. Key formulas and strategies help in determining components of velocity, maximum height, time
6 views • 25 slides
Advanced Projectile System in Unreal Engine 4
Learn about creating advanced projectiles in Unreal Engine 4 using key elements such as Actor Class, Collision Volume, Particle System, and Projectile Movement Component. Explore the use of Line Tracing and Hit Result Structure for more complex projectile interactions and effects. Understand the imp
2 views • 17 slides
Physics Problems on Projectile Motion
Projectile motion problems involving various objects such as turkeys, pot pies, lemons, rockets, nuggets, gourds, and watermelons being launched or thrown vertically up or down, each with unique initial velocities and times in the air. The problems require calculating maximum heights, initial veloci
1 views • 10 slides
Vertical Motion and Gravity in Kinematics
Explore the principles of vertical motion and gravity in kinematics through scenarios involving throwing objects, free-fall motion, and calculating heights. Learn how to model vertical motion with acceleration due to gravity, find maximum heights of thrown objects, solve extended problems, and under
3 views • 12 slides
Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore the fundamental concepts of Newton's Laws of Motion, including net forces, combining forces, balanced versus unbalanced forces, and the concept of inertia. Learn how these principles explain the behavior of objects in motion and at rest, and discover the impact of mass on an object's resista
0 views • 17 slides
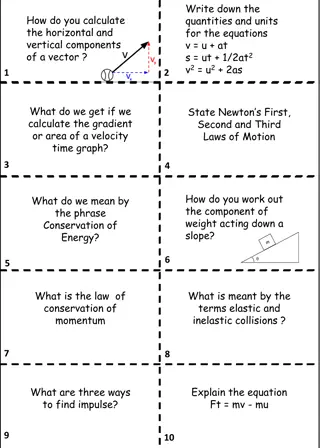
Physics Concepts and Laws Explained
Quantities and units in physics equations, calculation of vector components, laws of motion, conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, impulse, elastic and inelastic collisions, gravitational potential energy, projectile motion, satellite motion, special relativity postulates, time dilation
0 views • 10 slides
Joint Motion: Osteokinematic and Arthrokinematic Movements
Joint motion involves osteokinematic movements, which are under voluntary control and include flexion, extension, and more. End-feel sensations like bony, capsular, and springy block indicate different joint conditions. Arthrokinematic motion refers to how joint surfaces move during osteokinematic m
1 views • 17 slides
Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion explain the relationship between forces and motion. The first law states that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a net force, while the second law describes how force is related to an object's mass and acceleration. The third law states that for every ac
0 views • 21 slides
Kinematics in Physics: The How and Why of Motion
Explore the fascinating world of kinematics in physics through the concept of motion, acceleration, and free-fall. From constant acceleration to projectile motion, unravel the principles behind bodies in motion. Delve into the discoveries of scientists like Galileo and experience free-fall demonstra
0 views • 21 slides
Maximizing Projectile Distance with Trebuchet Release Points
Experiment conducted to determine the optimum release point on a trebuchet arm for maximum projectile distance. Hypothesis stated that the projectile would travel farthest when released at the longest point. Limited prior research on trebuchet arm length and its impact on distance. Materials used in
0 views • 15 slides
2D Kinematics and Projectile Motion in Physics
Explore the principles of 2D motion in physics, including vector quantities, kinematic equations, and problem-solving techniques. Dive into projectile motion, understanding its components and variables, and how to analyze trajectories. Enhance your knowledge through practical examples and challenges
0 views • 11 slides
Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion describe how objects behave in response to external forces. The first law states that objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by a force, while objects at rest stay at rest. The second law relates force, mass, and acceleration, showing how they are interconnected
0 views • 11 slides
Kinematics-Based Cannon Projectile Simulation Project
Practice coding kinematics-based behavior using vectors in UE4 to create a simulation where a cannon automatically adjusts its angle to hit a moveable target with a projectile, showcasing parabolic movement. Submission requirements include creating a Windows .exe build, providing a README.txt with d
0 views • 6 slides
How Variables Affect Projectile Motion
Discover how factors like height, mass, speed, and more influence the trajectory and distance a projectile can travel in the PHET Projectile Motion Lab. Complete tests, analyze data, and work on challenges to deepen your understanding of projectile motion. Engage with various parameters to uncover t
0 views • 12 slides
Motion and Newton's Laws
Explore the concepts of motion, distance, speed, and velocity as they relate to Newton's Laws of Motion. Learn about measuring motion, calculating speed, graphing motion on distance-time graphs, and understanding velocity. Discover how motion is constant and how relative motion is used. Practice cal
0 views • 36 slides
Projectile Target Simulation with MATLAB
Explore three challenging problems involving projectile simulations with MATLAB. Step-by-step solutions are provided to create simulations, determine optimal parameters, utilize animated lines for trajectory visualization, and incorporate drag force equations. Enhance your MATLAB skills in projectil
0 views • 4 slides
Mastering Type III Projectile Motion: Problems and Solutions
Explore the world of Type III projectile motion involving angles different from zero degrees. Learn how to solve problems step by step, understand maximum range calculations, and assess performance through various assignments. Engage in simulations, experiments, and assessments to enhance your under
0 views • 7 slides
Motion and Newton's Laws
Motion is the constant change in position of objects, measured by distance and displacement. Speed is the rate of motion, while velocity includes direction. Graphing motion helps visualize speed changes over time. Newton's Laws explain the behavior of objects in motion.
0 views • 38 slides
Dependent and Relative Motion in Dynamics
Dependent Motion and Relative Motion are fundamental concepts in Dynamics, providing the foundation for future analysis. Dependent Motion involves constraints like ropes or cables, while Relative Motion considers observers in motion. Dynamics involves applying a limited set of equations in diverse w
1 views • 18 slides
Motion: Types and Physics
Motion refers to a body changing position with respect to its surroundings. Different types of motion include linear, rotatory, and oscillatory motion. The physics relating to motion is called Mechanics, which comprises Dynamics and Kinematics. Scalars and vectors play a crucial role in describing t
0 views • 8 slides
Projectile Motion in Physics
Projectile motion is the motion of an object near the Earth's surface influenced by gravity. This concept has a historical background from Aristotle to Galileo and Newton, with forces like gravity and air resistance playing crucial roles. Models with and without air resistance are discussed, leading
0 views • 19 slides
Projectile Motion Practice Problems and Solutions
Explore a series of projectile motion problems and solutions involving scenarios such as a ball being kicked, a football being kicked by a place-kicker, an airplane dropping a care package, and a player throwing a ball horizontally. Learn to calculate speed, time in the air, maximum height, hang tim
0 views • 6 slides
Motion Perception in Computational Vision
In computational vision, the concept of motion opponency plays a crucial role in how the brain processes left and right motion inputs. By examining psychophysical results and the construction of motion opponent energy filters, we explore how the brain handles motion information. Additionally, the Ve
0 views • 23 slides
Projectile Motion: Concepts and Applications
Explore the principles of projectile motion, focusing on the independent horizontal and vertical components of motion. Learn how to analyze and compare scenarios such as dropping objects vertically and leaping horizontally. Dive into examples and calculations related to the range of projectiles, inc
0 views • 21 slides
Motion in Physics: Definitions and Examples
An object is said to be in motion if it changes position with time, while rest implies no change. Learn about types of motion such as linear and circular, as well as vibratory motion and reference points. Explore how objects can be in motion relative to one reference point while at rest relative to
0 views • 4 slides
Evolution of Motion Theories: Aristotle to Einstein
Explore the progression of motion theories from Aristotle's belief in a force for motion to Galileo's discoveries on gravity, Newton's laws of motion, and Einstein's theories of relativity and quantum mechanics. Discover how our understanding of motion has evolved over the centuries, shaping the way
0 views • 20 slides