Understanding Extracellular Matrix (ECM) and Its Functions
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) is a complex network of proteins, glycoproteins, and macromolecules that provide structural support, regulate cell activities, and play crucial roles in various tissues. It consists of two main types - interstitial matrix and basement membrane, each serving specific functi
12 views • 25 slides
Evolution and Characteristics of Archegoniates in Plant Kingdom
Archegoniates, believed to have originated from ancestral green algae, exhibit unique characteristics such as heterospory, presence of archegonia for egg production, and multicellular generations with heteromorphic alternation. They adapted to land by developing specialized structures like rhizoids,
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Homeostasis in Living Organisms
Homeostasis, derived from Greek meaning "standing still", is crucial for maintaining balance in living organisms. It involves regulating internal variables to prevent disease or death. Ancient Greeks emphasized the importance of harmony and equilibrium in life. Claude Bernard and Walter B. Cannon fu
1 views • 29 slides
Understanding Levels of Organization in Living Organisms
Explore the levels of organization in living organisms, from atoms to cells, and the differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Learn about prokaryotes, eukaryotes, cell differentiation, chromosomes, and the importance of stem cells in development and repair.
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Living Things: An Overview of Classification
Living things share common characteristics like being made of cells, responding to the environment, and reproducing. Macromolecules in cells help them function, and unicellular and multicellular organisms differ in structure. The levels of organization in multicellular organisms are explained, along
0 views • 18 slides
The Fascinating Venus Fly Trap - A Carnivorous Plant
The Venus Fly Trap, scientifically known as Dionaea muscipula, is a unique carnivorous plant found in the southern swamps of the US. It is a eukaryotic, multicellular autotroph that thrives in poor, nutrient-deficient soils by capturing insects for essential nutrients like nitrogen. Its trapping mec
0 views • 12 slides
Amazing Facts About Goliath Bird-Eating Spiders
The Goliath bird-eating spiders, belonging to the Animalia kingdom, are fascinating creatures found in South America. They are eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic, and exhibit sexual reproduction. These spiders have unique features like venomous glands, sensory hairs, and the ability to produce
0 views • 8 slides
The Fascinating World of Ligers: A Unique Hybrid Species
Ligers are captivating hybrid creatures born from the union of lions and tigers. Being eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic, and motile organisms with no cell wall, ligers exhibit intriguing reproductive behaviors and are considered part of the Animalia kingdom. Despite their infertility, the su
4 views • 8 slides
Exploring Multicellular Organisms: Structures and Functions
Learn about multicellular organisms, including examples like humans, animals, and plants, and how their cells, tissues, organs, and systems work together to perform various functions. Understand the difference between single-celled and multicellular organisms and why some require specialized cells t
0 views • 15 slides
Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms: A Comparative Analysis
Unicellular and multicellular organisms differ in structure, division of labor, specialization, exposure to environment, response to injury, size limitations, lifespan, and ability to divide. Unicellular organisms have a single-cell body, limited operational efficiency, and face challenges in size a
0 views • 12 slides
Immune Responses to Parasitic Infections and Evasive Strategies by Protozoan and Helminth Parasites
Parasitic infections pose complex challenges to the immune system due to the diverse nature of parasites, including protozoans and helminths. Protozoan parasites move between arthropod vectors and mammalian hosts, requiring both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses. Meanwhile, helminths, as mu
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Cellular Division and Cell Cycle Regulation
Explore the concept of cellular division and the cell cycle through a comprehensive unit designed to address common misconceptions. Students will learn about oncogenes, tumor suppressors, and the regulation of cell division in multicellular organisms. Emphasis is placed on differentiating between th
0 views • 22 slides
Introduction to Porifera: The Simple Multicellular Animals Known as Sponges
Porifera, a phylum of simple multicellular animals known as sponges, lack proper tissues and organs. They are filter feeders found in aquatic environments, with varied shapes and structures. Nutrition, digestion, respiration, excretion, and reproduction in sponges occur uniquely, making them intrigu
0 views • 18 slides
Exploring the World of Protists: A Kingdom of Diversity
Protists are eukaryotes that cannot be classified as plants, animals, or fungi. They thrive in moist environments and showcase a remarkable diversity within the Kingdom Protista. From animal-like protozoa to plant-like autotrophs and fungus-like heterotrophs, this kingdom contains a wide array of un
0 views • 18 slides
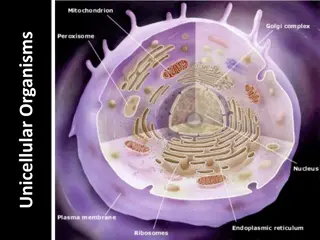
Unveiling the World of Unicellular Organisms
Discover the fascinating world of unicellular organisms through examples like Amoeba and Paramecium. Compare the characteristics and functions of unicellular and multicellular organisms, explore their feeding, movement, waste removal, and reproduction processes, and delve into the diversity of cell
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms in Biology
Explore the basic differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms, including the distinctions between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Unicellular organisms, such as bacteria and amoeba, consist of a single cell and are often microscopic. Examples of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic unicellula
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Protists: Unicellular Organisms and Their Classification
Protists are diverse unicellular organisms that can be classified based on their nutrition and movement methods. They include protozoans, algae, and heterotrophs like molds, each playing unique roles in ecosystems. From Didinium to multicellular algae, explore the fascinating world of these microsco
0 views • 8 slides
Exploring Kingdoms Protista and Fungi: Characteristics and Structures
Dive into the world of Protista and Fungi through this interactive review. Discover the unique characteristics of protists, identify different types of protists, and learn about essential structures in protists such as contractile vacuoles. Explore the significance of compounds like fucoxanthin in b
0 views • 27 slides
General Characteristics and Reproduction in Pteridophytes
Majority of living Pteridophytes, including terrestrial, aquatic, xerophytic, and epiphytic species, exhibit unique characteristics in their plant body structure. They possess sporophytic plant bodies with differentiated root, stem, and leaves, showcasing a variety of forms and adaptations. Reproduc
0 views • 21 slides
The Fascinating World of Algae and Protists
Algae, diatoms, dinoflagellates, euglenoids, and red algae are diverse plant-like protists crucial for Earth's ecosystems. They range from unicellular to multicellular forms, contributing significantly to oxygen production and food chains. While some like red algae thrive in deep ocean waters, other
0 views • 20 slides
The Cellular Basis of Inheritance in Biology
Understanding the significance of meiosis and sexual reproduction, this chapter delves into how multicellular organisms develop from a single fertilized egg through trillions of cell divisions. Exploring the necessity for genetic variation and the difference in reproductive strategies among organism
0 views • 29 slides
Embryology Notes: Development from Fertilization to Gastrulation
Embryology is the study of the development of multicellular animals starting from fertilization when the sperm fertilizes the egg and forms the zygote. This initiates a series of events such as cleavage, morula formation, blastula development, and gastrulation, where three embryonic tissue layers ar
0 views • 24 slides
Intestinal Helminths: Classification, Nematodes, and Common Infections
Intestinal helminths, including nematodes, are classified into unicellular and multicellular parasites. Nematodes are elongated worms found in the human body, causing common infections such as Enterobius vermicularis. The pathology of Enterobius infections often presents with pruritus ani. Learn abo
0 views • 53 slides
Understanding the Significance of the Cell Cycle in Growth and Development
This resource focuses on the cell cycle in the context of growth, development, and proliferation. It covers the significance of cell division, similarities in unicellular and multicellular organisms, the importance of CDK-mediated phosphorylation, and more. Students will learn to create schematic de
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Apoptosis: Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathways
Apoptosis, a programmed cell death process occurring in multicellular organisms, involves characteristic cellular changes leading to cell death. Approximately 50-70 billion cells die daily through apoptosis in humans, serving vital roles like embryo development. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis is a regul
0 views • 18 slides
Overview of Platyhelminthes: Tapeworms and Flukes
Platyhelminthes, such as tapeworms and flukes, are multicellular organisms with a flat body and hermaphroditic reproductive systems. Tapeworms, a type of Cestode, have a unique structure with a scolex and proglottids for reproduction. They are dioecious and develop through the production of proglott
0 views • 24 slides
Evolution and Adaptations of Plants: A Comprehensive Overview
Plants evolved from multicellular aquatic green algae to establish on land, developing strategies like nutrient absorption from soil, water loss prevention with cuticles, and reproduction without water. Vascular tissue, seeds, and flowers brought further advantages for plant growth and complexity.
0 views • 59 slides
Exploring Microbial Diversity: Fungi in Microbiology
Microbes are vital single-celled organisms that exist everywhere, some beneficial while others harmful. Fungi, a crucial group of microbes, can be unicellular or multicellular, with diverse roles in nature and human activities. This article delves into the characteristics and classification of fungi
0 views • 15 slides
Innovative Multicellular Computing Circuits for Genetic Manipulation
Cells are utilized as computational devices in a innovative approach for genetic manipulation. Various logic gates and promoters are combined to achieve complex circuit behavior without the need for genetic manipulation. Advantages include a wide dynamic range and low variability, but with the drawb
0 views • 10 slides