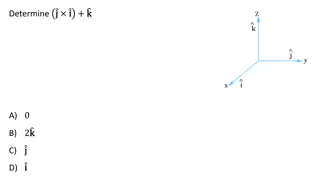
Understanding Momentum and Impulse in Physical Science
Momentum and impulse play crucial roles in physical science, with momentum defined as mass multiplied by velocity and impulse as the change in momentum. This concept is explored through examples and discussions on Newton's Second Law and practical applications in everyday life, such as airbags in ca
3 views • 8 slides
Understanding Angular Momentum in Mechanics
Explore the key concepts of angular momentum in mechanics, including the difference between linear and angular quantities, angular momentum calculations, conservation principles, and practical examples illustrated on whiteboards. Delve into formulas, equations, and scenarios to grasp the fundamental
4 views • 27 slides
Angular Mechanics - Angular Momentum Concepts and Examples
Understanding angular momentum in mechanics involves reviewing linear and angular quantities, comparing angular to linear formulas, and exploring examples of angular momentum and conservation principles. The content covers key factors like angular quantities, torque, and moment of inertia, along wit
3 views • 23 slides
Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle in Elementary Quantum Mechanics
Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle, proposed by German scientist Werner Heisenberg in 1927, states the impossibility of simultaneously and accurately determining the position and momentum of microscopic particles like electrons. This principle challenges classical concepts of definite position and m
0 views • 49 slides
New ILD Strategy: Consequences on ILD Tracking and Momentum Resolution
The ILD collaboration is adapting its strategy for potential circular colliders like FCC or CEPC, discussing challenges in tracking distortion correction, momentum resolution requirements, and handling various backgrounds. The focus is on optimizing the ILD design to meet the evolving collider lands
0 views • 11 slides
Fluid Mechanics Problem Solving with Bernoulli and Momentum Equations
Explore solved problems related to Bernoulli and momentum equations in fluid mechanics, including calculations of discharge, velocity, flow types, pressure losses, and energy lines. Dive into scenarios involving conduit profiles, pipeline configurations, and Reynolds number calculations for water an
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Momentum and Impulse in Sports
Momentum and impulse play a crucial role in sports performance. In a volleyball scenario where a ball is hit back by a player, understanding the change in speed, velocity, and force exerted can enhance gameplay strategies. Momentum is a key physics concept that affects an object's motion and the for
0 views • 40 slides
Understanding Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals for Efficiency
Explore key concepts in thermodynamics and fluid mechanics such as the equation of continuity, the first law of thermodynamics, the momentum equation, Euler's equation, and more. Learn about efficiency, internal energy, and the laws governing energy transfer in various systems. Delve into topics lik
2 views • 12 slides
Understanding Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics
Exploring the concept of total angular momentum in quantum mechanics, which involves the quantization of orbital and spin angular momenta. The coupling of these vectors leads to the formation of total angular momentum, with implications for the behavior of single-electron systems like the hydrogen a
0 views • 16 slides
Application of the Momentum Equation in Fluid Mechanics
Explore examples of applying the momentum equation in fluid mechanics, including calculating forces in pipe bends, nozzles, impacts on surfaces, and around vanes. The analysis involves determining total force, pressure force, and resultant force through control volume diagrams and coordinate axis sy
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Impulse and Momentum in Particle Motion
Exploring the concept of impulse and momentum in particle dynamics. Learn how these principles are used to solve problems involving force, mass, velocity, and time. Understand the impact of impulsive motion and how it affects the motion of particles in different scenarios.
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Momentum and Newton's Laws in Physics
Momentum is the product of mass and velocity, influencing an object's resistance to changes in motion. Newton's second law relates force to acceleration, while impulse is crucial in altering an object's momentum. Explore examples illustrating these concepts in action.
1 views • 9 slides
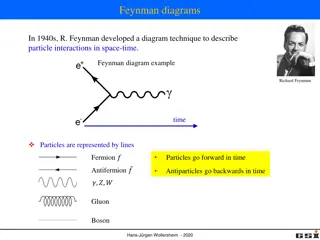
Understanding Feynman Diagrams in Particle Physics
Feynman diagrams, developed by Richard Feynman in the 1940s, are a graphical technique to represent particle interactions in space-time. These diagrams use lines to depict particles, with fermions moving forward in time and antifermions moving backward. Vertices in the diagrams represent points wher
1 views • 19 slides
Understanding Momentum in Physics
Explore the concept of momentum in physics through scenarios involving collisions and rotational displacement. Learn how momentum is conserved in different situations and its impact on the final direction of motion. Discover the relationship between velocities, masses, and changes in momentum in var
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Impulse and Momentum in Physics
Impulse, defined as the force times the time over which it acts, is crucial in changing an object's momentum. Various scenarios such as golf impact, billiard ball collisions, and skateboard acceleration are explored to demonstrate the importance of force, time, and impulse in physics concepts. Learn
14 views • 9 slides
Physics Applications: Momentum, Impulse, and Recoil Calculations
Explore various physics scenarios involving momentum, impulse, and recoil in this collection. Calculate the impulse of net force, average net force, recoil velocity of a rifle, and initial speed of a bullet using principles of conservation of momentum. Solve problems related to multi-dimensional imp
0 views • 5 slides
Understanding Linear Momentum and Collisions in Physics
Exploring the concepts of linear momentum, collisions, and conservation of energy in physics, this content covers topics such as momentum definition, conservation laws, impulse, types of collisions, and examples of perfectly inelastic and elastic collisions. It also includes a practical blackboard e
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Momentum in Physics
Explore the concept of momentum and how it relates to the motion of objects. Learn how to calculate momentum, find velocity, and understand impulse in this comprehensive guide. Engage with examples and interactive questions to deepen your understanding of this fundamental concept in physics.
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding the Energy-Momentum Tensor of the Electromagnetic Field
Exploring the intricacies of the energy-momentum tensor of the electromagnetic field, including its components, symmetries, and implications on field interactions and invariants. Delve into the mathematical derivations and transformations involved in studying this fundamental concept in electromagne
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Momentum and Collisions in Physics
Momentum plays a crucial role in analyzing collisions, where objects exert forces on each other over short time intervals. Conservation of momentum, following Newton's laws, allows predicting outcomes in collisions by redistributing momentum among objects. The concept is illustrated through examples
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Conservation of Momentum in Physics
Conservation of momentum in physics addresses how the total momentum of a system remains constant in a collision or interaction between objects. Newton's Third Law and the law of conservation of momentum play key roles in explaining the transfer of momentum between objects during collisions. Momentu
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Linear Impulse and Momentum in Mechanics
Explore the principles of linear impulse and momentum, conservation of linear momentum, mechanics of impact, and more in this study module. Learn to analyze forces, solve problems involving fluid streams and propulsion, and apply these concepts to real-world scenarios. Engage in practical problem-so
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Momentum and Impulse in Physics
Explore the concepts of momentum and impulse in physics, including the definition of momentum, the impulse-momentum theorem, and how factors affect object motion post-collision. Discover how momentum plays a vital role in describing an object's motion and learn about the relationship between force,
0 views • 30 slides
Understanding Relativistic Energy and Momentum in Particle Physics
Discuss the new definition of momentum and the concept of total relativistic energy. Explore the use of momentum-energy conservation in scenarios involving zero rest mass particles. An example of an inelastic collision is provided to demonstrate the application of these principles.
0 views • 51 slides
Understanding Momentum, Impulse, and Collisions in Physics
Learn about momentum, impulse, and collisions in Chapter 8 of physics. Understand how linear momentum, impulse, and the Impulse-Momentum theorem are crucial in analyzing collisions and conservation of momentum. Explore real-world applications in sports and scenarios like a child driving a bumper car
0 views • 19 slides
Exploring Transverse Momentum Distributions (TMDs) at the GDR PH-QCD Annual Meeting
The Annual Meeting of the GDR PH-QCD focused on discussing Transverse Momentum Distributions (TMDs) and their significance at small kT and small x values. Topics covered include gauge-invariant correlators, PDFs, and PFFs, as well as the utilization of color gauge links in describing partonic transv
0 views • 33 slides
Momentum and Collisions Explained Through Illustrations
Explore various scenarios involving momentum, collisions, and elastic interactions through illustrated examples. Understand concepts such as total momentum in different situations, speeds of masses after collisions, momentum conservation in 1-D and 2-D collisions, and changes in momentum direction.
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Angular Momentum and Rotational Dynamics in Physics
Explore concepts related to angular momentum, torque, and rotational dynamics in physics. Learn about the behavior of spinning objects, the effects of changing moments of inertia, and how angular momentum is conserved in different scenarios.
0 views • 35 slides
Understanding Momentum and Impulse in Physics
Explore the concepts of momentum and impulse in physics, illustrated through practical examples like a race car crash and a hockey puck's motion. Learn how Newton's laws of motion govern these principles and how they relate to force and velocity. Dive into the interplay between momentum and impulse,
0 views • 22 slides
Angular Momentum Conservation in Physics: Understanding Principles and Applications
Explore the concept of angular momentum conservation in physics, covering conditions for equilibrium, elastic properties of solids, density, specific gravity, fluid dynamics, pressure variations, and Pascal's Principle. Delve into examples like neutron star rotation and planetary motion to understan
0 views • 15 slides
Conservation of Momentum in Collisions: University of Ottawa Physics Lab
Study the conservation of linear momentum and energy in elastic and inelastic collisions in one dimension at the University of Ottawa's physics lab. Analyze the motion of gliders on an air track, observe changes in velocity, momentum, and energy, and compare position-time and velocity vs. time graph
0 views • 15 slides
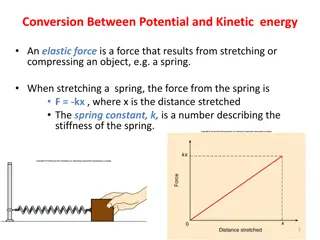
Understanding Energy Conversion, Power, and Momentum in Physics
Exploring the concepts of energy conversion between potential and kinetic energy, the importance of power in work efficiency, and the role of momentum and impulse in describing motion in physics. The discussion covers elastic forces, work done, power calculations, examples of watt and joules, as wel
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Conservation of Linear Momentum
Explore the concept of conservation of linear momentum, principles, and applications like isolated systems, internal forces, and recoil of a rifle. Learn how total momentum remains constant in a closed system where external forces sum up to zero.
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Momentum and Impulse in Physics
Momentum is the product of an object's mass and velocity, while impulse is the change in momentum resulting from a force acting over time. By applying force for a longer duration, momentum can be increased or decreased effectively. The relationship between impulse and momentum is crucial in understa
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Momentum and Impulse in Physics
Momentum, defined as mass x velocity, and impulse, the change in momentum resulting from a force over time, are essential concepts in physics. This chapter explores how momentum can be altered through changes in mass or velocity and how impulse affects momentum. The relationship between force, time,
0 views • 27 slides
Understanding Conservation of Momentum in Physics
Conservation of momentum is a fundamental law stating that momentum is conserved in a closed system where it is neither created nor destroyed, but rather transferred between objects. This principle is applied in various scenarios, such as bullet-gun recoil, collision of objects, and more, to determi
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Angular Momentum in Physics
Learn about the concept of angular momentum in physics through practical examples and explanations. Explore how angular momentum is conserved in rotating bodies and how it impacts various sports activities. Discover the relationships between moment of inertia, angular velocity, and conservation of a
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Momentum in Physics
Momentum, first introduced by Isaac Newton, is symbolized by the letter p and signifies inertia in motion. It is calculated as mass multiplied by velocity (p = m * v) and has the unit of kg * m/s. The amount of momentum depends on the object's mass and speed. A moving object has more momentum if eit
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Zonal Momentum Balance in the Antarctic Circumpolar Current
This study investigates the zonal momentum balance of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) by analyzing the interplay between wind stress, topographic form stress, and eddy dynamics. The research explores the maintenance and adjustment of momentum balance in the ACC, emphasizing the roles of baro
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Gyroscopes and Angular Momentum
Explore the concept of gyroscopes, angular momentum, and gyroscopic effects in vehicles like ships and airplanes. Learn about mass moment of inertia, angular velocity, and the precession of gyroscopes in detail. Dive into the physics behind the change of angular momentum and solve a problem involvin
0 views • 12 slides