Multivariate Analysis
Explore the key concepts of marginal, conditional, and joint probability in multivariate analysis, as well as the notion of independence and Bayes' Theorem. Learn how these probabilities relate to each other and the importance of handling differences in joint and marginal probabilities.
5 views • 43 slides
How to get Small Marginal Farmer Certificate in Tamil Nadu
The Marginal Farmer Certificate is issued by the Tahsildar\/Deputy Tahsildar in the Taluk to farmers who own up to 2.5 acres. This certificate allows them to avail of subsidy programs for micro-irrigation and water management. Farmers with more than five acres do not need certificates to access thes
2 views • 5 slides
Outcomes of Ventral Incisional Hernias <2cm: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis
This study presents outcomes of ventral incisional hernia repair <2cm using a propensity score-matched analysis. The research evaluates mesh versus primary repair methods and explores complications and recurrence rates. Insights from adult patients undergoing hernia repair from 2012-2021 are include
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Consumption, Saving, and Investment in Economics
Consumption in macroeconomics refers to total spending on consumer goods and services, while saving is the act of abstaining from consumption. Investment involves creating capital goods and acquiring financial assets. Engle's Law states that the proportion spent on necessities decreases with income.
0 views • 13 slides
Investigation of Marginal ELCC Generation Methodology for Renewable Technologies with Storage Combinations
This project aims to develop a methodology to calculate Marginal ELCCs for non-dispatchable technologies like Solar PV and Wind, along with various storage durations. It proposes leveraging SERVM for LOLE Events, analyzing peak shaving capabilities of storage technologies, and evaluating ELCC via si
0 views • 10 slides
Proposed Changes to Forward Capacity Cost Allocation
The document discusses proposed changes to the allocation of forward capacity costs effective June 1, 2020. It highlights the need for transparency in cost allocation, focusing on zonal demand curves and the Marginal-Reliability Impact. The current opaque method is critiqued for potential non-intuit
0 views • 47 slides
Understanding Adjusted Predictions and Marginal Effects in Stata
This presentation by Richard Williams from the University of Notre Dame discusses the importance of adjusted predictions and marginal effects in interpreting results. It explains factor variables, different approaches to adjusted predictions, and uses NHANES II data to demonstrate concepts. The talk
0 views • 49 slides
Understanding the Law of Equi-Marginal Utility in Economics
Law of Equi-Marginal Utility, propounded by Hermann Heinrich Gossen, explains how consumers distribute their income among different goods to maximize satisfaction. It involves equalizing the marginal utility per unit of money spent across various goods. The law is based on the assumptions of rationa
0 views • 8 slides
Integration Approaches of Propensity Scores in Epidemiologic Research
Propensity scores play a crucial role in epidemiologic research by helping address confounding variables. They can be integrated into analysis in various ways, such as through regression adjustment, stratification, matching, and inverse probability of treatment weights. Each integration approach has
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Keynesian Consumption and Savings Functions in Macroeconomics
Keynesian consumption function details the relationship between total consumption and gross national income. It emphasizes the stability of aggregate consumption and the marginal propensity to consume. Similarly, Keynesian savings function illustrates the link between savings and national income, hi
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Equilibrium in Perfect Competition Markets
Perfect competition in economics refers to a situation where numerous buyers and sellers are involved in trading identical goods freely, with full market knowledge and no government restrictions. Key characteristics include a large number of buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, free entry and e
1 views • 14 slides
Understanding Utility: Marginal vs. Total Utility
Utility in economics is the satisfaction derived from consuming goods or services. Marginal utility measures the change in total utility as consumption increases, whereas total utility is the sum of satisfaction obtained from consuming different units of a commodity. Consumers aim to maximize total
2 views • 11 slides
Understanding Utility: Meaning, Concept, and Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
Utility is the satisfaction or well-being a consumer derives from consuming goods or services. Total utility is the sum of satisfactions, while marginal utility is the additional satisfaction from one more unit consumed. Utility can be measured and ranked but not numerically. The Law of Diminishing
3 views • 9 slides
Understanding Monopoly Power and Regulation in Economics
Degree of Monopoly Power is measured by the difference between marginal cost and price, with a greater difference signifying larger monopoly power. Prof. Abba P. Lerner's formula for monopoly power emphasizes the gap between price and marginal cost. Monopoly power can also be assessed using price el
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Marginal Propensity to Consume and Save
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) and Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS) measure the ratios of change in consumption and saving to change in disposable income respectively. The relationship between MPC and MPS shows that they equal 1 when combined, with the remainder being saved. The multiplier ef
7 views • 5 slides
Economics of Labor Markets: Factors of Production and Labor Demand
The Economics of Labor Markets explores the markets for factors of production such as labor, land, and capital. Demand for these factors is derived from firms' decisions to produce goods. The labor market, governed by supply and demand forces, exhibits diminishing marginal product of labor due to fi
0 views • 41 slides
Understanding Absorption and Marginal Costing in Accounting
Absorption costing, also known as full costing, encompasses all costs including fixed and variable related to production. It aids in determining income by considering direct costs and fixed factory overheads. Meanwhile, marginal costing focuses on only variable manufacturing costs and treats fixed f
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Propensity Score Methods for Reducing Confounding in Studies
This content discusses the use of propensity score methods to address confounding in observational studies, comparing randomized control trials (RCTs) with observational studies, explaining the potential outcome framework, average treatment effects, and common assumptions made in these methods to re
0 views • 12 slides
Sensitivity Analysis and LP Duality in Optimization Methods
Sensitivity analysis and LP duality play crucial roles in optimization methods for energy and power systems. Marginal values, shadow prices, and reduced costs provide valuable insights into the variability of the optimal solution and the impact of changes in input data. Understanding shadow prices h
0 views • 40 slides
Understanding Marginal Costing in Cost Accounting
Marginal Costing is a cost analysis technique that helps management control costs and make informed decisions. It involves dividing total costs into fixed and variable components, with fixed costs remaining constant and variable costs changing per unit of output. In Marginal Costing, only variable c
1 views • 7 slides
Understanding Keynesian Consumption and Savings Functions in Macroeconomics
Keynesian Consumption Function relates total consumption to national income, with stable characteristics like MPC and APC. Savings Function shows the relationship between savings and income, highlighting the Marginal Propensity to Save and Average Propensity to Save. Both functions are essential con
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Production Function and Laws of Returns in Economics
Production function in economics involves transforming inputs into outputs and understanding the relationship between input quantities and output under a given technology state. Concepts like Total Product, Average Product, and Marginal Product are essential in analyzing production efficiency. The L
1 views • 38 slides
Understanding Consumer Choices and Utility Maximization
Exploring how consumers make consumption decisions based on utility theory, marginal utility, and preferences. Analyzing Lisa's consumption possibilities, total utility, and marginal utility to illustrate economic concepts. Discussing the utility-maximizing rule for optimal decision-making in spendi
0 views • 22 slides
Analysis of 2021 Marginal Generation Costs for San Diego Gas & Electric
The analysis presents the 2021 Marginal Generation Costs methodology filed by San Diego Gas & Electric in April 2016 for the Time-of-Use (TOU) OIR Workshop. It includes forecasts for Marginal Energy Costs (MEC) and Marginal Generation Capacity Costs (MGCC) for the calendar year 2021, based on market
0 views • 6 slides
Estimation of Causal Effects using Propensity Score Weighting
Understanding causal effects through methods like propensity score weighting is crucial in institutional research. This approach helps in estimating the impact of various interventions, such as a writing program, by distinguishing causation from correlation. The use of propensity score matching aids
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Marginal Analysis in Economic Decision-Making
Marginal analysis involves comparing Marginal Benefit with Marginal Cost to determine the optimal quantity for an activity. If Marginal Benefit is greater than Marginal Cost, there is a Net Marginal Benefit; if it's less, there's a Net Marginal Cost. The principle helps weigh costs and benefits befo
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Consumer Equilibrium in Economics
Consumer equilibrium refers to the point where a consumer maximizes satisfaction by spending income on commodities. In single commodity case, equilibrium is achieved when marginal utility equals price. For two commodities, equilibrium is reached when the ratio of marginal utility to price is equal.
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Utility and Marginal Utility in Economics
Utility refers to the satisfaction a consumer receives from consuming commodities. It is a subjective concept that can be measured through cardinal or ordinal approaches. Cardinal approach involves measuring utility numerically, while ordinal approach orders levels of satisfaction based on utility.
0 views • 16 slides
Maximizing Profit in a Corn Production Scenario
In a perfectly competitive labor market producing corn, we aim to determine the optimal number of farmworkers to hire for profit maximization. By comparing the Marginal Revenue Product and Marginal Factor Cost, we analyze the additional corn production with each added worker. Through step-by-step ca
0 views • 12 slides
Optimizing Labor for Profit in a Competitive Market
Understanding the profit-maximizing quantity of labor in a competitive market for corn production. Analyzing the relationship between marginal revenue product and marginal factor cost to determine the ideal number of farmworkers to hire for maximum profits. A step-by-step mathematical calculation pr
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Competitive Factor Market in Labor Economics
A competitive factor market involves a large number of sellers and buyers of a factor of production, like labor. With no single entity influencing prices, each acts as a price taker. The demand for factors depends on firms' output levels and input costs, leading to derived demands. Profitability of
0 views • 43 slides
Probabilistic Graphical Models Part 2: Inference and Learning
This segment delves into various types of inferences in probabilistic graphical models, including marginal inference, posterior inference, and maximum a posteriori inference. It also covers methods like variable elimination, belief propagation, and junction tree for exact inference, along with appro
0 views • 33 slides
Understanding Integration: From Marginal Utility to Definite Numeric Solutions
Integration plays a crucial role in mathematics, connecting concepts such as marginal utility and total utility functions, differential coefficients, rules for indefinite integration, and the process of definite integration. Learn about notation, rules, and examples to grasp the fundamentals and app
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Monopolies in Economics
Monopolies are considered inefficient because they can earn long-term profits. In a monopoly equilibrium, the relationship between price, marginal revenue, and marginal cost differs. Natural monopolies can supply goods at lower costs. Compared to perfectly competitive firms, monopolies charge higher
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Profit Maximization and Revenue Concepts in Economics
Explore the concepts of profit maximization, revenue generation, and marginal analysis in economics. Learn how to define profit, calculate total revenue and cost, and understand marginal revenue. Discover the significance of marginal value of product and its impact on business decision-making.
0 views • 60 slides
Understanding Two-Way Tables and Probability
Two-way tables are used to display data collected from two different categories. By organizing data in a two-way table, you can find joint frequencies, marginal frequencies, and interpret the results. In this context, learn how to create two-way tables, calculate marginal frequencies, find joint fre
0 views • 15 slides
The SMDHU Experience with Program Budgeting and Marginal Analysis
The SMDHU faced challenges due to a grant freeze in 2015, resulting in staff reductions, departmental changes, and operational savings. This led to the adoption of Program Budgeting and Marginal Analysis (PBMA) as a resource management tool. PBMA was chosen after groundwork and evaluation, aiming to
0 views • 17 slides
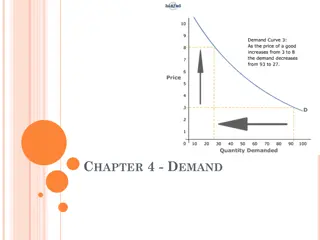
Understanding Demand in Chapter 4
In Chapter 4, the concept of demand is explored, encompassing the desire, ability, and willingness to purchase a product. It delves into the demand schedule, demand curve, law of demand, and factors influencing demand such as consumer income. The chapter also covers marginal utility and the diminish
0 views • 18 slides
Demand, Supply and Price Theory
Delve into the fundamental concepts of economics such as opportunity cost, incentives, trade among countries, productivity, and the relationship between marginal benefit and marginal cost. Explore the application of the scientific method in economics, three economic models, and the workings of marke
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Marginal Productivity in Health Economics
Learn about the concept of marginal productivity in health economics, the difference between average and marginal productivity, and how it applies to the productivity of medical care. Discover examples of how productivity changes along the extensive margin in specific medical interventions like scre
0 views • 30 slides