Understanding Logical Form and Equivalence in Conditional Statements
Delve into the intricacies of logical form, equivalence, and compound statements in the realm of propositional logic. Explore valid and invalid arguments, conditional statements, and the logic of compound statements with puzzles to sharpen your logical reasoning skills. Unravel scenarios like determ
2 views • 81 slides
Coherence and Cohesion
Cohesion and coherence play crucial roles in academic writing by ensuring logical flow and connection between ideas. Cohesion involves linking sentences using devices like conjunctions, pronouns, and repetition, while coherence focuses on organizing ideas into paragraphs that logically develop the a
0 views • 13 slides
Introduction to 1st Order Predicate Logic in Logical Thinking
Explore the limitations of propositional logic and the enhanced expressive power of 1st order predicate logic (PL1). Understand how PL1 allows for analyzing the structure of atomic propositions and proving arguments that depend on these structures. Through examples and valid argument schemata, delve
1 views • 26 slides
Understanding the Five Parts of a Classical Argument
The classical argument is composed of five main parts: Introduction, Narration, Confirmation, Refutation and Concession, and Summation. Each part plays a crucial role in presenting a well-structured and persuasive argument, with devices and strategies such as diction, syntax, and figurative language
0 views • 6 slides
Logical Expressions and Symbolism in Sentential Logic
Understanding sentential logic, logical expressions, and symbols through examples of logical reasoning and inference. Explore the concepts of logical OR, AND, negation, and the complexities of inclusive and exclusive logic in various scenarios.
1 views • 33 slides
Understanding Boolean Algebra and Logical Statements
Introduction to Boolean algebra, logical statements, and compound statements. Explore the concepts of Boolean variables, logical operators, writing conventions, equivalence in Boolean algebra, and truth tables. Learn how to analyze and evaluate logical expressions using truth tables.
1 views • 25 slides
Exploring Contradictions and Logical Impossibilities
Explore a series of paradoxes and logical puzzles, ranging from being in two places at once to time travel conundrums. Discover the concept of contradictions and logical impossibilities through thought-provoking scenarios and riddles. Dive into the realm of impossibilities and challenge your underst
1 views • 6 slides
Understanding the Key Elements of an Argument
An argument is an intellectual process that involves a series of connected statements to establish the validity of a proposition. This process typically includes elements such as a hook, claim, support with reasons and evidence, and counterclaims with concessions and refutations. Each element plays
0 views • 13 slides
Enhancing Logical Reasoning in Decision Making Process
Federal Criterion #28 emphasizes the importance of stating logical reasons for decisions that align with findings of fact and conclusions of law. This criterion is key to ensuring fairness and accuracy in legal analysis. The scoring criteria, national appeals review results, and ways to improve scor
1 views • 8 slides
Preparing for Oral Argument in the Eleventh Circuit: Essential Tips
Understand the process of oral arguments in the Eleventh Circuit, including when to request oral argument, FRAP 34 guidelines, and how to handle the notice of oral argument. Get insights on making the most of oral argument opportunities and potentially shaping circuit law.
0 views • 32 slides
Understanding Indirect Proofs: Contradiction and Contraposition Examples
Indirect proofs offer a roundabout approach to proving statements, with argument by contradiction and argument by contraposition being the main techniques. Argument by contradiction involves supposing the statement is false and deriving a contradiction, while argument by contraposition relies on the
1 views • 18 slides
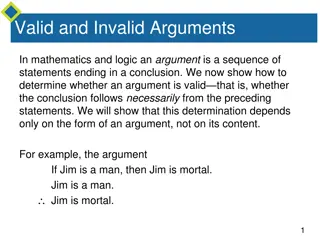
Understanding Valid and Invalid Arguments in Mathematics and Logic
In mathematics and logic, determining the validity of an argument depends on its form rather than its content. An argument is considered valid if the conclusion necessarily follows from the premises. This determination involves analyzing the abstract form of the argument, constructing truth tables t
0 views • 32 slides
Emotional and Logical Appeal in 'Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God'
Exploring Jonathan Edwards' persuasive techniques through appeals to fear, hope, and logic in 'Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God'. This analysis delves into the emotional impact of imminent damnation, the comforting notion of salvation, and the rational arguments presented to sway the congregatio
0 views • 7 slides
Logical Argument Examples with Premises and Conclusion
Examples of logical arguments presented in premise-conclusion format, showcasing how premises lead to conclusions in various scenarios such as academic requirements, police adages, political succession, and military roles.
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Boolean Algebra and Logical Statements
Boolean Algebra allows for formalizing logical reasoning using variables that can be either true or false. It involves logical statements, compound expressions, logical operators like AND, OR, NOT, writing conventions, equivalence, and truth tables to determine the truth values of statements. By und
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Logical Connectives in Discrete Mathematics
Explore the world of propositional logic and truth tables in discrete mathematics through a peer-instruction approach. Learn about basic logical connectives, new connectives, complex formulas, operator precedence, and the nuances of implication (implies) with engaging examples. Delve into scenarios
0 views • 14 slides
Subject-Object Asymmetries in Zazaki Argument Ellipsis
Many languages allow argument ellipsis (AE), where an argument can be omitted for sloppy or quantificational interpretations. Subject-object asymmetries arise in languages due to subject-verb agreement. This study presents evidence from Zazaki, a Northwestern Iranian language, challenging the anti-a
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Propositional Logic and Logical Operators
Learn about propositional logic, statements, logic operators, compound statements, exclusive-or, logical equivalence, and writing logical formulas for truth tables. Explore how to create compound statements for exclusive-or using different approaches and ensure logical equivalence. Enhance your know
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding the Kalam Argument in the Cosmological Debate
The Kalam Argument, a form of the Cosmological Argument, asserts that everything with existence has a cause, including the universe. Developed by thinkers like al-Kindi, al-Ghazali, and William Lane Craig, it aims to prove that God was the initial cause of the universe. This argument suggests that t
0 views • 17 slides
Exploring Argument Structure and Diagramming in Critical Reasoning
Understanding the two types of argument structures - atomic and complex, with examples and diagrams. Learn how argument diagrams visually represent the structure of an argument, identify significant units like premises and conclusions, and distinguish main conclusions from sub-conclusions. Dive into
1 views • 10 slides
Understanding Logical Relations in Programming Languages
Explore the concept of logical relations in programming languages, focusing on the relation between high-level and low-level programs. Learn about contextual equivalence, its benefits and limitations, and how logical relations offer a robust framework for defining program equivalence. Discover why l
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Laws of Logic and Logical Reasoning
Laws of logic play a crucial role in reasoning and making deductions. This comprehensive guide explains the use of contrapositives, examples of conditional statements, and the significance of laws like the Law of Syllogism. Understanding these principles helps in effectively analyzing statements and
0 views • 8 slides
Introduction to Symbolic Logic: Understanding Logical Inferences
Logic is the study of reasoning methods to distinguish between correct and incorrect arguments. Symbolic Logic involves representing logic symbolically for easier understanding and manipulation. Logical inferences help in making decisions based on reasoning chains. The content discusses the use of l
1 views • 28 slides
Understanding Anselm's Ontological Argument for the Existence of God
Anselm's Ontological Argument posits that the greatest possible being, referred to as God, must exist in reality because existing in reality is greater than existing only in thought. This argument centers on the concept of necessary vs. contingent beings and the idea that the greatest being cannot e
0 views • 32 slides
Identifying Logical Fallacies in Sources: Presentation Assignment
Learn to identify logical fallacies in various sources by analyzing passages and applying the Logical Fallacy Referee tool. Work in pairs to select sources, identify fallacies, and present annotated examples to the class.
0 views • 7 slides
Mastering the Art of Argument in Essay Writing
Embrace the challenges of essay writing by understanding the essence of crafting a strong argument. Learn how to structure your thoughts logically, present evidence convincingly, and engage your readers effectively. Discover the importance of argument in various fields of life and the vital role it
0 views • 20 slides
Analyzing Hume's Critique of the Design Argument by Michael Lacewing
The design argument contends that the intricate order in the universe suggests a designer. Michael Lacewing delves into Hume's objections to this argument, highlighting how the analogy between human-made objects and the universe falls short in establishing a similar cause. Hume questions the logic o
0 views • 10 slides
Peer Instruction in Discrete Mathematics
Explore the world of discrete mathematics with Dr. Cynthia Bailey Lee and Dr. Shachar Lovett through peer instruction. Dive into topics like step-by-step equivalence proofs and the equivalence of logical operators. Discover the different methods to show propositions are equivalent and delve into log
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding the Three Types of Logical Appeals: Logos, Ethos, and Pathos
Explore the different types of logical appeals used in writing - Logos (appeals to reason), Ethos (appeals to values), and Pathos (appeals to emotions). Learn how to balance these appeals to create a persuasive argument and avoid overreliance on emotional manipulation.
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Informal Fallacies: Common Logical Errors in Reasoning
Informal fallacies are mistakes in reasoning or argumentation that can lead to false judgments. They can be subtle and appeal to emotions, making them challenging to avoid. Fallacies of relevance and ambiguity are common types. Examples include argument from ignorance, appeal to authority, and appea
0 views • 5 slides
Unveiling Persuasive Strategies in Atticus' Closing Argument
Explore the comprehensive analysis of persuasive strategies employed by Atticus in his closing argument, including ethos, pathos, logos, and linguistic devices. Delve into the intricacies of sender-receiver relationship, message content, emotional appeals, logical reasoning, and language choices.
0 views • 6 slides
Identify the Error in Logical Inference: Discrete Math Exercise 14
The exercise presents an argument based on logic where it is incorrectly concluded that Lola is happy based on the given premise. The solution points out that while there exists an x that satisfies the premise, it does not necessarily mean Lola is one such x. This highlights the importance of carefu
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Distributed System Synchronization and Logical Clocks
Continuing from the previous lecture on time synchronization, this session delved into logical clock synchronization, mutual exclusion, and election algorithms in distributed systems. Logical clocks, such as Lamport's Clock and Vector Clock, play a crucial role in defining the order of events withou
0 views • 33 slides
Understanding Compound Statements in Logic
The summary discusses the logic of compound statements, covering logical form, equivalence, tautologies, contradictions, conditional statements, valid and invalid arguments, and more. It explains the definitions of statements, negation, conjunction, disjunction, statement form, logical equivalence,
0 views • 12 slides
Mastering Logic & Critical Reasoning: Fallacy Guide
Evaluating arguments in critical thinking involves assessing logical form and identifying informal fallacies. Understanding argument structure, recognizing same form-different content scenarios, and detecting informal fallacies are key aspects of logical reasoning.
0 views • 48 slides
Understanding SDSU's Writing Placement Assessment (WPA)
SDSU's GWAR, an argument-based Writing Placement Assessment, requires students to write an essay analyzing a given argument. Scores range from 2-10, with different score bands dictating course requirements. Achieving a perfect score is subjective, emphasizing clear and concise argument analysis. Som
0 views • 35 slides
Understanding Logical Agents and Propositional Logic in AI
Designing logical agents involves forming representations of the world, using inference for deriving new insights, and deducing actions based on these representations. Knowledge Base (KB) is a crucial component, comprising known facts and current percepts to infer hidden states. Propositional logic,
0 views • 23 slides
Ontological Argument for God's Existence and Challenges
The ontological argument posits that a being than which nothing greater can be conceived must exist in reality, not just in the mind. Critics challenge this argument, citing issues with defining God and debating whether existence can be a characteristic. Gaunilo and Kant present criticisms focusing
0 views • 30 slides
Exploring Different Versions of the Ontological Argument
This content delves into various versions of the ontological argument, including Descartes' and Kant's perspectives. Descartes sought to prove God's existence through reason alone, emphasizing the innate conception of a supremely perfect being. The challenges posed by Kant and Malcolm to this argume
0 views • 24 slides
Advancements in Logical Natural Language Generation from Open-Domain Tables
Cutting-edge research in logical natural language generation (NLG) is transforming the field by moving beyond traditional surface realization to generate summarized text, conclude trends, and apply logical and mathematical operations. By addressing limitations such as lack of logical inference, summ
0 views • 33 slides