Knowledge and Curriculum
Various forms of curriculum, the importance of curriculum, new trends in education, and the relationship between power and ideology in curriculum development. Understand the role of the state in curriculum development and the impact of meritocracy on the curriculum.
2 views • 16 slides
Angela Carter and Her Influential Works: A Contextual Analysis
Angela Carter, an English novelist known for her feminist and magical realism works, was influenced by her personal experiences and feminist ideologies. Her notable works include "The Bloody Chamber" and "The Sadeian Woman and the Ideology of Pornography". Carter's unique perspective on women's role
0 views • 26 slides
The Significance of Media in Language Learning
Media plays a crucial role in language learning by raising awareness of the ideology behind linguistic structures and providing valuable information on society and culture. Linguists are drawn to media language for research purposes and to understand its impact on language use and attitudes. Media s
11 views • 5 slides
Mahatma Gandhi and His Ideology in Indian History
Mahatma Gandhi, a pivotal figure in India's freedom struggle, advocated for non-violence, truth, and self-realization. He reshaped the Indian National Congress and empowered the masses to fight against injustice through civil disobedience. Gandhi's ideologies of swadeshi, local democracy, and truste
0 views • 28 slides
Objectives and Aims of Teaching Pakistan Studies in Education
Understanding the objectives and aims of teaching Pakistan Studies is essential for educators. Objectives serve as guiding points in the teaching-learning process, providing a framework for evaluation and development. On the other hand, aims are broader and philosophical, focusing on the purpose and
0 views • 48 slides
Understanding Religious Conflict: Definition and Types Explored
Religious conflict is a complex and recurring concept throughout history. Scholars have defined it as disagreements between religious groups. This conflict arises from contentious issues touching on ideology, morality, power, and identity, influenced by various socio-political, economic, and cultura
1 views • 13 slides
European Imperialism in the Late 19th Century
European nations in the late 1800s pursued imperialism to expand their empires for economic, political, and social reasons. Motives included economic interests, political and military ambitions, and the ideology of Social Darwinism. The Industrial Revolution fueled the need for resources and markets
1 views • 14 slides
Terrorism: A Global Threat in International Politics
The rise of terrorism as a global menace is a significant factor in contemporary international politics. Fueled by advancements in technology and ideology, terrorism poses a formidable challenge, exemplified by events like the 9/11 attacks. Efforts are needed to combat terrorism on both national and
0 views • 24 slides
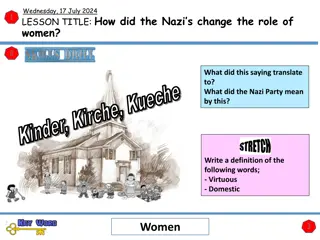
Women's Role in Nazi Germany: Impact and Ideology
Explore how the Nazis shaped the role of women through policies and propaganda, emphasizing domesticity and motherhood. Analyze key figures like Joseph Goebbels and Hitler's perspectives on women's place in society. Understand the contrast between women's lives in Weimar and Nazi Germany.
0 views • 18 slides
Nazi Policies Towards Women: A Critical Analysis
Nazi policies towards women aimed to control and manipulate their roles in society, focusing on reducing women in the workforce, promoting Aryan reproduction, emphasizing purity and health, and encouraging Aryan marriage. These policies restricted women's freedoms and autonomy, enforcing strict guid
0 views • 11 slides
Theories of International Relations Overview
The field of International Relations (IR) encompasses various theories that seek to explain global phenomena, drawing from disciplines like history, philosophy, and economics. Theory, derived from contemplation and speculation, organizes ideas to explain issues such as state emergence, conflict caus
1 views • 47 slides
Discursive Construction of Legitimation: Understanding Authority and Ideology
Systems of authority aim to establish legitimacy through discourses. Legitimation involves self-orientation, justification, and the imposition of ideologies. This practice encompasses various principles and categories such as moral evaluation, rationalization, and multimodal approaches, shaping soci
1 views • 36 slides
Understanding Class Struggle in Animal Farm through Marxist Ideology
Animal Farm, written by George Orwell, explores the concept of class struggle through the lens of Marxist ideology. The novel depicts the conflict between the bourgeoisie, represented by characters like Mr. Jones, and the proletariat, symbolized by the other animals on the farm. Through the story of
0 views • 12 slides
Critiques of Modernity and Liberal Ideology: Marcuse and Habermas
Herbert Marcuse's concept of One-Dimensional Man critiques capitalism's impact on human freedom and alienation in Western society. Marcuse emphasizes awakening individuals to their alienation to ignite their urge for freedom. Jurgen Habermas, in contrast, focuses on rational critique rooted in human
1 views • 5 slides
Understanding Liberalism: Key Ideas and Historical Context
Liberalism, a prominent political ideology, emerged in the 19th century and is closely linked to capitalism. It stands against absolutism and feudal privileges, advocating for individualism, freedom, reason, equality, toleration, consent, and constitutionalism. The evolution of liberalism emphasized
1 views • 18 slides
Key Terms in Ch. 21: Reaction, Revolution, and Romanticism, 1815-1850
The key terms discussed in Chapter 21 include principle of legitimacy, balance of power, ideology, conservatism, principle of intervention, ultraroyalists, ministerial responsibility, and liberalism. These terms highlight important political philosophies and concepts during the post-Napoleonic era a
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Socialism: A Comprehensive Overview
Socialism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for collective or state ownership of production, distribution, and exchange. It emerged in the early 19th century as a response to industrial capitalism, aiming for a more egalitarian society that prioritizes collective well-being. Social
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Socialist Democracy: A Political Ideology Explained
Socialist democracy is a political idea that combines elements of democracy and socialism, rejecting capitalism and authoritarian socialism. Proponents advocate for democratic decision-making and public ownership of the means of production. They believe in economic equality, government regulation of
1 views • 13 slides
Directive Principles of State Policy in the Indian Constitution
The Directive Principles of State Policy in the Indian Constitution provide guidelines for governance, focusing on social justice, economic welfare, and a just society. These principles are inspired by socialist ideology and aim at ensuring social and economic justice by minimizing inequalities, pro
2 views • 16 slides
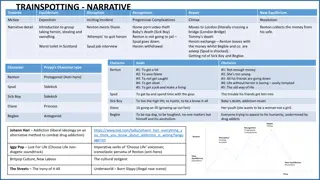
Exploring Ideology and Narrative in Trainspotting
A deep dive into the narrative structure and ideological themes of the film Trainspotting, examining character goals, obstacles, and the protagonist's journey through addiction and self-discovery. The film's portrayal of addiction, socialism, liberalism, and post-Thatcherite counter-culture is explo
1 views • 7 slides
Social Work Ideology for the 21st Century: Educational Imperative
Social work education must adapt to current global challenges by reexamining ethical principles in light of perpetual warfare, fake news, and economic globalization. This paper discusses the relevance of social values in a changing world and proposes pedagogies for promoting a modern social work ide
0 views • 14 slides
Manifest Destiny: The Annexation of New Mexico and California
The expansion of the United States into the territories of New Mexico and California, driven by the ideology of Manifest Destiny, involved a complex interplay of historical events including the Santa Fe Trail, Spanish missions in California, conflicts with Mexican settlers, and President Polk's stra
0 views • 11 slides
Nazi Persecution of Minorities: Targets and Rationale
The Nazis targeted various groups for persecution, believing in a racial hierarchy where certain races were deemed inferior. They aimed to eliminate those they considered undesirable, including Gypsies, black people, the mentally disabled, homosexuals, and more. The Nazis' actions were driven by the
7 views • 12 slides
Understanding Ideology and Society: Perspectives and Beliefs
Explore the significance of ideology in shaping societal perspectives, beliefs, and values. Understand the impact of ideologies on laws, societal structures, and individual behavior. Delve into concepts such as liberalism, individualism, and collectivism to gain insights into human societies through
4 views • 26 slides
Understanding Critical Theory in International Relations: A Deep Dive
Critical theory in IR since the mid-1980s challenges traditional views by emphasizing culture, ideology, and societal structures over objective truths. This approach questions the relationship between theory and practice, highlighting issues of inequality beyond just class, including race, ethnicity
0 views • 9 slides
Rahul Gandhi: Hope of Congress and the Nation
Congress leaders and workers see Rahul Gandhi as a promising figure for the party and the country, with slogans praising him raised at a party convention in Hyderabad in 2006. During his speech, Rahul emphasized the need to stay true to the party's ideology and work together to strengthen both the p
0 views • 6 slides
Exploring Postmodernism: Art, Literature, and Philosophy
Postmodernism challenges traditional beliefs about language, identity, and reality. It is characterized by skepticism, subjectivism, and a critical view of ideology in politics and economics. Key thinkers like Thomas Pynchon, Donald Barthelme, and Jean-François Lyotard have contributed to shaping t
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Popular Culture and Ideology
Popular culture encompasses the lived practices and artistic products of society, contrasting with high culture. Various definitions highlight its appeal to a wide audience and its distinction from high culture. The relationship between popular culture and ideology is explored through practices that
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Evaluation and Ideology in Translation
Evaluation plays a crucial role in the study of translation, influencing both meaning and value in communication. This evaluation is reflected through language elements like accentuation, deletion, and substitution. Appraisal, stance, and evaluation are key terms in linguistic analysis that focus on
2 views • 22 slides
Analysis of Ideology in Thomas Pynchon's "The Crying of Lot 49
This analysis delves into the story and ideology in Thomas Pynchon's novel "The Crying of Lot 49". The plot follows Oedipa Maas as she investigates the mystery of Tristero, a secret postal service. Set in California during the 1960s, the novel reflects the societal context of America during the Cold
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Popular Culture: Definitions and Perspectives
Popular culture encompasses artistic and intellectual products, lived practices, and ideologies within society. It can be defined in various ways, reflecting what is widely liked and created by the people. This cultural phenomenon is shaped by power dynamics, social realities, and distinctions from
0 views • 18 slides
Challenges and Opportunities in EU-China Strategic Partnership
The EU-China strategic partnership faces challenges concerning ideology, human rights, and political systems, while also presenting opportunities for cooperation based on mutual interests. The EU aims to engage China politically, support its transition towards an open society, and integrate it into
0 views • 9 slides
Challenges Facing the Lord's Church: Navigating Postmodernism and Uncertainty
Amidst the challenges faced by the Lord's Church, including postmodernism and uncertainties regarding baptism, music, women's involvement, and more, there is a struggle to hold onto traditional beliefs while adapting to modern shifts in ideology and practice. Some have embraced change, while others
0 views • 40 slides
Exploring the Moral Foundations of Capitalism
Delve into the historical origins and ethical principles underpinning capitalism as seen through iconic quotes, foundational texts, and philosophical analysis. Understand the intertwined concepts of liberty, economics, philosophy, and ethics that shape capitalist ideology and practices, emphasizing
0 views • 42 slides
Changing Trends in Cuban-American Voter Ideology
Explore the evolving political ideology of Cuban-American voters from 1991 to 2011 through data on migration, residency, naturalization, and political exceptionalism. Uncover how these trends have influenced Miami's Latino demographics and the Cuban perspective on US/Cuba relations.
0 views • 24 slides
Evaluating the Impact of Communism on Climate Change in China
This study analyzes the effects of political ideology on climate change in China, specifically focusing on the difference in extreme temperatures from 1954 to 2010. Results show a significant decrease in extreme temperatures in earlier years followed by an increase from 2000 onwards, particularly du
0 views • 73 slides
The Rise of Communism in Russia: Key Figures and Events
Russia's transition to communism was marked by social and political upheaval, with figures like Karl Marx, Lenin, Trotsky, and Stalin playing pivotal roles. The Russian Revolution, civil war, and the rise of the Soviet Union reflected a shift towards communist ideology, leading to significant change
0 views • 37 slides
Allegorical Representation of GDR Oppression in "Stasiland
The imagery in "Stasiland" delves into the symbolism of GDR oppression through cultural artifacts like The Lipsi dance, revealing the manipulative propaganda tactics of the regime. Funder's portrayal of the dance reflects the mechanical nature of the Stasi, shedding light on the absurdity of GDR ide
0 views • 11 slides
The Rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party: A Historical Overview
Adolf Hitler, born in Austria in 1889, faced rejection as a painter before turning to politics. He led the National Socialist German Workers Party (Nazi) and orchestrated the failed Beer Hall Putsch in 1923. Imprisoned briefly, he penned Mein Kampf that propagated Nazi ideology. By 1932, the Nazi Pa
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Marxist Theory: Key Concepts and Implications
The Marxist theory, rooted in Karl Marx's philosophy, emphasizes the control of means of production as a determinant of societal power dynamics. This ideology examines economic power, materialism versus spirituality, class conflict, and the role of art, literature, and ideologies in shaping culture
0 views • 17 slides