RNA Interference Therapy Zilebesiran's Impact on Hypertension
Explore Zilebesiran, an investigational RNA interference therapeutic targeting hepatic AGT synthesis for hypertension. Primary findings from Phase 2 trial KARDIA-1 reveal sustained blood pressure reduction. Addressing the unmet need for innovative antihypertensive treatments.
0 views • 12 slides
Insect Abdominal Structures and Appendages: An Overview
The abdomen of insects plays crucial roles in respiration, reproduction, digestion, excretion, and metabolism. The number of abdominal segments varies across species, with reductions and modifications seen in different insect groups. From the propodeum to pregential and postgenital segments, each pa
1 views • 6 slides
Liver Transplant in India for treatment
Liver is the largest gland in our body, and an important metabolic organ which carries out many essential biological functions. The liver is a wedge-shaped, reddish-brown in color with two lobes of different size and shape. The approximate weight of a human liver is 1.5 kilograms. It is in the upper
5 views • 2 slides
Anatomy of Intestine in Domestic Animals
The intestine in domestic animals plays a vital role in digestion and absorption. It consists of the small intestine for chemical digestion and absorption and the large intestine for water absorption and excretion. This article covers the gross anatomy, histology, and embryology of the intestine, de
2 views • 84 slides
Understanding Bilirubin: What You Need to Know
Bilirubin is a yellowish substance formed during the breakdown of red blood cells, traveling through the liver before excretion. High levels indicate hyperbilirubinemia, often signaling underlying health issues. It's a common occurrence in newborns as well. The compound plays a crucial role in the b
0 views • 19 slides
Heart Treatment in India
Treatment for the heart focuses on reducing excess fluid volume and edema and boosting the heart's pumping ability. The immediate goals include preventing progressive failure or in the worst case, sudden death. The aggressiveness in therapy is proportionate to levels of heart failure. As a common po
0 views • 2 slides
Understanding Acetaminophen Poisoning: Mechanism, Toxicity, and Treatment
Acetaminophen poisoning occurs when the body is overwhelmed by high doses of the drug, leading to liver toxicity and potentially fatal consequences. The mechanism of toxicity involves the depletion of glutathione and the formation of a harmful metabolite, N-acetyl-para-benzoquinoneimine (NAPQI). Con
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Hypokalemia and Potassium Regulation
Hypokalemia is a condition characterized by low potassium levels, crucial for intracellular functions. The Na+/K+ ATPase pump maintains the ICF/ECF gradient. Potassium excretion occurs mainly via the kidneys, with minimal variation in proximal tubule reabsorption. The collecting duct plays a vital r
0 views • 50 slides
The Basics of Life: Understanding Biology and Life Functions
Biology is the study of life, which involves understanding the characteristics that define living organisms. These characteristics include nutrition, transport, respiration, excretion, synthesis, regulation, and growth. Each of these life functions is essential for the survival and functioning of al
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Fat Cow Syndrome in Cattle: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Fat Cow Syndrome, also known as Fatty Liver Disease in Cattle, is a condition commonly seen in high-producing cows during the transition period around calving. The disease is characterized by mobilization of excessive body fat to the liver due to negative energy balance, leading to hepatic lipidosis
1 views • 10 slides
Renal Pharmacology: Drug Excretion and Renal Clearance Questions
This comprehensive set of questions and answers covers topics related to drug excretion and renal pharmacology. It includes information on glomerular filtration, drug excretion mechanisms, dosage adjustments in renal impairment, factors influencing drug excretion, and the effects of long-term NSAID
0 views • 55 slides
Understanding Bilirubin: Estimation, Implications, and Causes of Jaundice
Bilirubin, a yellow compound in the catabolic pathway, plays a crucial role in health. Estimating serum bilirubin levels is key in diagnosing conditions like jaundice. Elevated levels, above 2 mg/dl, can indicate disease. Jaundice, characterized by skin and eye discoloration, has pre-hepatic, hepati
0 views • 16 slides
Nutritional Considerations for Chronic Liver Disease in Critical Care
Malnutrition is common in chronic liver disease, leading to complications such as ascites and infections. Sarcopenia and weight loss are prevalent regardless of BMI. Critical care patients with liver disease face challenges due to limited physiological reserve, with main causes for ICU admission bei
1 views • 17 slides
Understanding Nasopulmonary Drug Delivery System
Nasopulmonary drug delivery system, utilizing the nasal route for drug administration, offers advantages such as hepatic first-pass metabolism avoidance and rapid drug absorption. This system is beneficial for pharmacologically active compounds with poor stability in gastrointestinal fluids. While i
0 views • 35 slides
Understanding Phenytoin Therapy - Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Serum Concentrations
Phenytoin, a medication with high protein binding and hepatic metabolism, exhibits saturated pharmacokinetics with a narrow therapeutic range of 10-20 µg/mL for total serum concentrations. Adverse effects vary with serum levels: minor CNS depression at >15 µg/mL, nystagmus at >20 µg/mL, and ataxi
0 views • 55 slides
Safety and Feasibility of TIPS in Elderly Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
Challenging liver cirrhosis management in elderly patients with refractory ascites has high mortality rates, and transplantation is not always viable. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) serves as a non-curative treatment option, aiming to reduce portal hypertension. The procedure i
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Renal Block: Drugs, Excretion, and Treatment Essentials
Renal block plays a crucial role in drug excretion, with processes like glomerular filtration and tubular secretion affecting drug elimination. Factors like blood flow, physiochemical properties, and urine pH influence renal excretion of drugs. Competition between drugs for transporters can have ben
0 views • 10 slides
Overview of Veins and Venous Circulation in the Body
Veins play a crucial role in the circulatory system by carrying deoxygenated blood back to the heart. This lecture covers the general principles of veins, the anatomy of major veins like the superior and inferior vena cavae, tributaries, and their roles in different parts of the body. It also discus
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Drug Absorption, Excretion, and Bioavailability in Humans
Delve into the complex processes of drug absorption, excretion, and bioavailability in the human body. Learn about the various factors affecting drug absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, including biological, physiochemical, and pharmaceutical factors. Explore the mechanisms of drug transport
0 views • 24 slides
Evaluation and Management of Incidental Liver Lesions
Understanding the natural history, evaluation, and management of benign liver lesions is crucial for diagnosing incidental liver findings. Common benign liver lesions include hepatic hemangioma, focal nodular hyperplasia, hepatic adenoma, and hepatic cyst. Differential diagnosis plays a key role in
0 views • 37 slides
Portal Vein Imaging Techniques and Anomalies Overview
Portal vein imaging is crucial for evaluating conditions affecting the abdominal part of the gastrointestinal tract. Techniques such as spleno-portography and CT triphasic contrast imaging are used to visualize the portal vein and diagnose anomalies like portal-systemic collaterals and porto-systemi
4 views • 7 slides
Understanding the Anatomy of the Large Intestine
The large intestine plays a crucial role in digestion. This comprehensive overview covers the different parts of the large intestine, characteristic features of the colon, anatomy details, peritoneal covering, relations with surrounding structures, arterial and nerve supply, and important flexures l
0 views • 13 slides
Structure and Function of a Serous Compound Tubulo-acinar Gland
A detailed description of a compound tubulo-acinar gland with serous-secreting nature is provided, highlighting its cellular composition, arrangement of ducts, and connective tissue organization. The glandular structure, including adenomeres, centroacinar cells, and myoepithelial cells, is discussed
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Complications of Liver Cirrhosis
Recognize major complications of liver cirrhosis including hepatic failure, portal hypertension, ascites, hepatorenal syndrome, and esophageal varices. Learn about the pathogenetic mechanisms, clinical features, and pathological findings associated with these complications.
0 views • 30 slides
Understanding Complications of Liver Cirrhosis
Learn about the major complications of liver cirrhosis, including portal hypertension, hepatic failure, ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and more. Explore the pathogenetic mechanisms, clinical features, and pathological findings associated with these complications, and understand the impa
0 views • 31 slides
Benefits of Exercise Therapy in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Exercise therapy plays a crucial role in managing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) by improving hepatic aminotransferases and reducing steatosis. Lifestyle modifications, including increased physical activity, are essential in the treatment of NAFLD. This includes aerobic exercise, resistanc
0 views • 32 slides
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) and Sarcoidosis: A Complex Case Study
This case study delves into a challenging scenario where a hepatologist grapples with a patient presenting HLH associated with liver injury in the context of sarcoidosis. Despite inconclusive initial investigations, further work-up reveals indications of secondary HLH/MAS. The management involves a
0 views • 8 slides
Anatomy and Blood Supply of the Equine Stomach
The equine stomach is relatively small compared to the horse's body size, with distinct regions such as the cardia, fundus, body, and pyloric region. It is located on the left side of the abdomen, under the ribs. The stomach's blood supply includes branches from the aorta, splenic artery, and hepati
0 views • 23 slides
Radiology Imaging of Esophagus and Stomach by Dr. A. Alhawas
View detailed radiology imaging of the esophagus and stomach conducted by Dr. A. Alhawas, showcasing various anatomical structures such as the splenic artery, abdominal aorta, common hepatic artery, and more. Explore pathologically changed layers in pyloric stenosis, arterial blood supply to the pyl
0 views • 8 slides
Functional Anatomy and Blood Supply of the Liver
The liver is a crucial organ with dual functions and a complex anatomical structure. It consists of hepatic lobes and lobules, where hepatocytes play a vital role in various functions. The liver receives blood supply from both the hepatic artery and portal vein, allowing for essential processes such
0 views • 20 slides
Overview of Acute Liver Failure: Causes, Classification, and Diagnosis
Acute liver failure is a severe condition characterized by rapid liver dysfunction within 6 months of symptom onset, leading to encephalopathy, coagulopathy, and jaundice. This condition can be classified as hyperacute, acute, subacute, fulminant, or sub-fulminant based on the duration from jaundice
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI)
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) can present as cholestasis, hepatocyte necrosis, steatosis, vascular damage, and hepatic fibrosis. Various drugs like antibiotics, NSAIDs, recreational drugs, and herbal remedies can cause liver damage. Recognizing DILI is crucial in patients with liver dysfunction o
0 views • 9 slides
Hydropericardium Hepatitis Syndrome (HHS) in Poultry: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
HHS is an acute infectious disease in chickens characterized by high morbidity and mortality, excess pericardial fluid, and multifocal hepatic necrosis. It mainly affects broilers and broiler parents, with clinical signs such as sudden mortality, lethargy, and ruffled feathers. Post-mortem lesions i
0 views • 6 slides
Nutrition and Cystic Fibrosis: Management of CF-Related Complications
Explore the nutrition implications and management strategies for CF-related liver disease, gastrointestinal complications, and CF-related diabetes in patients. Learn about the proposed mechanisms, prevalence rates, and consequences of hepatic complications in cystic fibrosis. Gain insights into neon
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Bile Acid Sequestrants and Fibrates in Clinical Pharmacy
Bile acid sequestrants such as colestipol and cholestyramine act by binding bile acids, promoting hepatic conversion of cholesterol, and increasing LDL-receptor activity to clear LDL-cholesterol. They may interfere with fat-soluble vitamin absorption and have common side effects like constipation an
0 views • 27 slides
Challenges in the Management and Treatment of HIV/Hepatitis C Virus Coinfection
This presentation by Dr. Ricardo A. Franco focuses on the challenges faced in managing and treating patients with HIV/Hepatitis C virus coinfection. It discusses the burden of HCV mono-infection and HIV/HCV co-infection, the impact of HIV co-infection on survival in HCV-related cirrhosis, and the ro
0 views • 26 slides
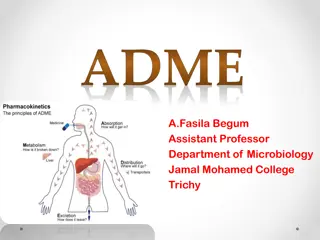
Understanding ADME in Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacology, focused on ADME processes, play a crucial role in drug development and delivery. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion determine how drugs interact within the body. Absorption involves transfer into the bloodstream, while distribution entails the spre
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Drug Metabolism and Excretion in Pharmacology
Drug metabolism involves the biotransformation of pharmaceutical substances in the body, primarily in the liver, to facilitate their elimination. This process helps convert drugs into less active forms for enhanced elimination through various reactions in Phase I and Phase II metabolism. Factors suc
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Drug Metabolism and Excretion in the Human Body
In the realm of pharmacology, the process of eliminating drugs from the body involves hepatic metabolism, biliary elimination, and urinary excretion. Once a drug is introduced into the system, these routes of elimination come into play, highlighting the crucial role they play in drug clearance and e
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Serum Bilirubin: Types, Estimation, and Causes of Jaundice
Serum bilirubin levels are crucial in diagnosing conditions like jaundice, with total, direct, and indirect bilirubin playing key roles. Excess bilirubin in the blood can lead to jaundice, characterized by yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes. Different types of jaundice, including pre-hepatic,
0 views • 14 slides