Understanding Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
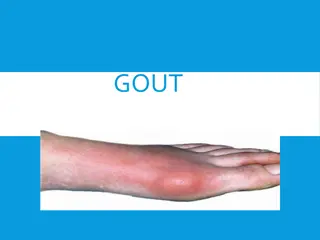
Gout is a metabolic disorder characterized by high levels of uric acid in the blood, leading to recurrent episodes of acute arthritis. The condition is often preceded by hyperuricemia and can result in complications such as renal calculi and tophi. Treatment involves managing uric acid levels throug
1 views • 35 slides
Understanding Drug Action Mechanisms and Receptor Targets
Pharmacodynamics involves studying the effects of drugs on biochemical and physiological levels, focusing on drug actions through receptor-mediated and non-receptor mechanisms. The interaction between drugs and targets like proteins and enzymes impacts cellular functions. Different binding forces, s
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Gout: Pathophysiology, Stages, and Treatment Options
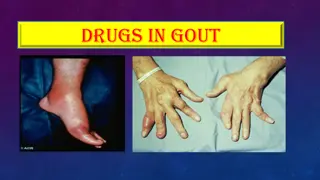
Gout is characterized by acute inflammatory arthritis due to sodium urate crystal deposits. Untreated gout can lead to complications like tophi, nephrolithiasis, and joint inflammation. The disease progresses through stages: acute, asymptomatic hyperuricemia, intercritical, and chronic gout. Treatme
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Gout: Pathophysiology and Pharmacotherapy Overview
Gout is a condition caused by the accumulation of urate crystals, leading to inflammation and various symptoms like acute arthritis and joint destruction. This article delves into the pathophysiology of gout, highlighting factors like hyperuricemia and crystal formation. It also discusses pharmacoth
2 views • 30 slides
Understanding Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism in Genetic Disorders
Explore the intricate pathways of purine and pyrimidine catabolism, salvage, and degradation. Uncover the causes and symptoms of genetic disorders like Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome and Gout. Discover the importance of ribonucleotides conversion to deoxyribonucleotides in DNA synthesis. Dive into the mechani
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Gout in Birds: Clinical Findings and Management Approaches
Gout in birds is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by abnormal uric acid accumulation. It can affect both visceral and articular tissues, leading to various clinical findings such as nodules, polyuria, and anemia. Diagnosis involves physical exams, blood tests, and imaging. Treatment focuses o
3 views • 8 slides
Understanding Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Gout is a condition caused by excessive uric acid levels in the blood, leading to crystal deposits in joints and tissues, resulting in intense pain, inflammation, and redness. Commonly seen in the first metatarsophalangeal joint, gout can present with joint changes and decreased mobility. Recognizin
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Arthritis: Types, Causes, and Symptoms
Arthritis is inflammation of joints causing pain and limited function. It can be due to injury, metabolic abnormalities, hereditary factors, infections, or autoimmune conditions. Types include Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Gout, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Reactive Arthr
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Crystalarthropathies and Gout: A Comprehensive Overview
Crystalarthropathies encompass a group of diseases characterized by hyperuricemia and uric acid crystal formation, leading to conditions like gouty arthritis and nephrolithiasis. Primary gout, characterized by hyperuricemia without an identifiable underlying cause, primarily affects older men. Mecha
0 views • 34 slides
Understanding Purine Degradation and Gout
Purine degradation pathway involves the breakdown of dietary nucleic acids, mainly from meat, into uric acid through specific enzymatic steps. Excessive uric acid production can lead to conditions like gout and hyperuricemia. Humans excrete uric acid in the urine as the final product, while other an
1 views • 12 slides
Overview of Alkaloids in Pharmacognosy
Alkaloids are a diverse group of compounds containing nitrogen that are derived from amino acids like phenylalanine or tyrosine. Protoalkaloids, such as ephedrine, are derived from common amino acids and do not contain a heterocyclic ring. Ephedrine, obtained from Ephedra sinica, has CNS stimulatory
0 views • 11 slides
Comprehensive Guide to Gout: Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Prevention
Gout is a form of arthritis characterized by painful joint inflammation due to urate crystal deposits. This guide covers the stages of gout, treatment options (both drug and non-drug), and the importance of managing the condition to prevent complications. Learn about the epidemiology, stages, and th
0 views • 35 slides
Musculoskeletal Conditions Management Guidelines 2018
This document highlights the management guidelines for musculoskeletal conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and gout, emphasizing the use of medications like prednisone and proton pump inhibitors in certain situations to minimize pain and reduce risks of complications. It also provides resources
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Serum Uric Acid Levels and Hyperuricemia
Serum uric acid is a crucial marker of purine metabolism, with elevated levels indicating hyperuricemia which can lead to conditions like Gout. The measurement of serum uric acid helps in diagnosing hyperuricemia, with serum being the preferred specimen for testing. Various factors such as diet, gen
0 views • 12 slides