Understanding Motion, Forces, and Machines in Physical Science
Explore the fundamental concepts of motion, forces, and machines in physical science. Learn about distance, displacement, speed, velocity, acceleration, forces, and friction. Understand how these concepts shape our understanding of the physical world and impact the behavior of objects in motion.
9 views • 18 slides
Understanding Forces and Motion in Physics
Exploring the concepts of forces and motion, this content delves into the fundamental aspects of how forces impact objects' movement. Covering topics such as measuring force, representing force as a vector, combining forces through addition and subtraction, and understanding balanced and unbalanced
2 views • 61 slides
Understanding Projectile Motion: Characteristics, Examples, and Formulas
Projectile motion involves the motion of objects under the influence of gravity, with both vertical and horizontal components. This type of motion is seen in activities such as throwing a ball, kicking a football, or dropping objects. The motion is described by specific formulas, including calculati
1 views • 19 slides
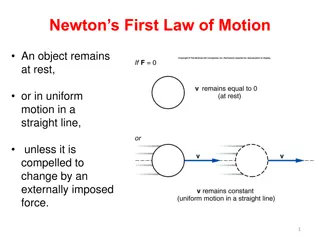
Understanding Newton's First Law of Inertia
Newton's first law of inertia states that objects remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. This law, also known as the law of inertia, explains how objects tend to maintain their current state of motion unless influenced by an external force. Objects at rest stay a
0 views • 14 slides
Exploring Forces: What Makes Things Move?
Delve into the concept of forces and motion, understanding how interactions between objects cause movement. Discover the role of gravity and other forces in initiating, changing, or stopping motion. Engage in investigations and discussions to grasp key science ideas surrounding forces and explore re
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Rotational Motion in Physics
Explore key concepts in rotational motion through common scenarios like a point on a bicycle tire, determining centripetal forces in roller coasters, and understanding the forces at play in loops. Discover the relationship between mass, radius, and centripetal force, as well as the forces involved a
1 views • 23 slides
Exploring How Forces Influence Object Motion
Understanding the concept of forces is essential in predicting the motion of objects. Through practical experiments with cotton balls and a fan, students observe the effects of forces like gravity and air resistance on object motion. By documenting their predictions and observations, students gain v
1 views • 13 slides
Understanding Motion: Frames of Reference and Relative Motion
Motion is defined as a change in position over time. To describe motion accurately, one needs to understand frames of reference and relative motion. Frames of reference are systems of objects used to determine if something is in motion, while relative motion involves movement in relation to a refere
3 views • 14 slides
Understanding Forces in Motion Throughout History
Forces play a crucial role in causing changes in motion, as observed through the perspectives of Aristotle on natural and violent motion, the beliefs about Earth's rest, and Copernicus challenging the geocentric view with a heliocentric model. The concept of forces driving motion has evolved over ce
1 views • 27 slides
Understanding Motion: Concepts and Definitions in Physics
Motion in physics is defined as the change in position of an object over time. It involves concepts like rest, motion, distance, displacement, rate of motion, and types of motion. Rest and motion are relative to a reference point, while distance and displacement differ in their scalar and vector nat
2 views • 25 slides
Understanding Central and Non-Central Forces in Physics
Newton's laws of motion introduced the concept of forces, leading to the classification of fundamental forces like gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear forces. Central forces act toward or away from a fixed center, while non-central forces are affected by additional param
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Van der Waals Forces and Intermolecular Interactions
Van der Waals forces encompass London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding, influencing interactions between atoms and molecules. London dispersion forces are the weakest and present in all molecules, dipole-dipole forces involve permanent dipoles, and hydrogen bonding, the
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Forces in Physics
Explore the concept of forces in physics, including definitions, measurement units, combining forces, and their effects on objects' motion. Learn about balanced and unbalanced forces, net force, force pairs, directions, magnitude, and how to combine forces at right angles. Develop a solid understand
0 views • 24 slides
Introduction to Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines in Mechanical Engineering
Theory of Mechanics delves into motion, time, and forces, with Kinematics focusing on motion analysis without considering external forces. Kinetics, a branch of Theory of Machines, deals with inertia forces resulting from mass and motion. Dynamics combines Kinematics and Kinetics to study motion and
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Gravity and Balanced/Unbalanced Forces in Physics
Explore the fundamental concepts of gravity and balanced/unbalanced forces in physics. Gravity is the force that pulls objects toward each other, acting universally. Balanced forces maintain object stability, while unbalanced forces can cause motion changes based on direction, strength, and mass. Di
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Forces in Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Prof. Madhuri Reddy, an Assistant Professor at Hope Foundation's International Institute of Information Technology, explains the characteristics of forces, systems of forces, and the concept of resultant force and composition of forces in mechanics. Forces are defined as agents that produce or destr
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Linear and Rotational Motion in Physics
Explore the concepts of linear momentum, center of mass, rotational motion, and angular displacement in physics. Learn how to determine the center of mass of objects, analyze motion of particle groups, and understand the conservation of momentum in systems under external forces. Delve into the funda
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore Newton's Laws of Motion including the concepts of force, inertia, acceleration, action and reaction forces, and the role of mass in determining motion. Newton's First Law states that objects at rest remain at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton's Second Law relates accelera
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Motion
Exploring the foundational concepts of motion and forces, this content delves into Isaac Newton's First Law of Motion. Describing how objects behave when the net force acting on them is zero, the law highlights the significance of inertia and balanced forces in determining an object's state of rest
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Forces in Motion
Exploring the concept of forces in motion, this educational material delves into why moving objects slow down and eventually stop. Through various images and questions, students are encouraged to think about the forces acting on objects like soccer balls and understand the impact of surfaces on moti
1 views • 15 slides
Understanding Forces in Motion: A Comprehensive Overview
Forces play a crucial role in our daily activities, influencing motion and direction. This chapter delves into the concept of forces as pushes or pulls, exploring balanced and unbalanced forces and their impact on velocity. By examining real-life scenarios like kicking a soccer ball or opening a doo
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Balanced and Unbalanced Forces in Physics
Forces play a crucial role in determining an object's motion. Balanced forces have a net force of 0 N, resulting in no change in motion, while unbalanced forces lead to a change in motion. Inertia, the resistance to changes in motion, and the concept of combining forces are also important in underst
2 views • 30 slides
Understanding Forces and Mass
Forces, such as contact and non-contact forces, interact with objects to cause motion or deformation. Mass is the amount of matter in an object, measured in kilograms. Learn about applied force, normal force, frictional force, air resistance, spring force, tensile forces, compressive forces, and she
1 views • 29 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore the fundamental concepts of Newton's Laws of Motion, including net forces, combining forces, balanced versus unbalanced forces, and the concept of inertia. Learn how these principles explain the behavior of objects in motion and at rest, and discover the impact of mass on an object's resista
0 views • 17 slides
Newton's First Law of Motion: Inertia and Forces
Understanding the concept of inertia in motion, the role of forces in maintaining or changing motion, and analyzing net forces applied to objects. Also explores scenarios where forces are balanced or unbalanced, affecting the motion of objects.
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Joint Motion: Osteokinematic and Arthrokinematic Movements
Joint motion involves osteokinematic movements, which are under voluntary control and include flexion, extension, and more. End-feel sensations like bony, capsular, and springy block indicate different joint conditions. Arthrokinematic motion refers to how joint surfaces move during osteokinematic m
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Force Diagrams and Balanced/Unbalanced Forces
Explore the concepts of force diagrams, balanced forces, and unbalanced forces through visual examples and explanations. Learn how balanced forces keep objects stationary or at a constant speed, while unbalanced forces cause movement and changes in direction. Practice calculating resultant forces an
1 views • 11 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion explain the relationship between forces and motion. The first law states that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a net force, while the second law describes how force is related to an object's mass and acceleration. The third law states that for every ac
0 views • 21 slides
Physics Concepts Review: Motion and Forces
Explore essential concepts in physics related to motion and forces, including forces acting against falling objects, gravitational forces, momentum, inertia, and more. Test your knowledge with questions on gravity, air resistance, satellite orbits, and the law of universal gravitation.
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Intermolecular Forces and Dispersion Forces in Molecules
Particle diagrams of liquids, solids, and gases reflect distinct arrangements due to intermolecular forces. The existence of substances as gases, liquids, or solids at room temperature is attributed to the forces between molecules known as intermolecular forces (IMF), with dispersion forces being th
0 views • 30 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion: Inertia, Forces, and Acceleration
Delve into the fundamentals of Newton's first and second laws of motion, exploring concepts such as inertia, the relationship between forces and acceleration, and the procedure for solving force problems. Discover how objects behave when left to themselves, and grasp the significance of forces in ch
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion describe how objects behave in response to external forces. The first law states that objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by a force, while objects at rest stay at rest. The second law relates force, mass, and acceleration, showing how they are interconnected
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Forces and Equilibrium in Physics
Forces in physics can be categorized into contact forces and field forces, measured in units like Newtons (N). Inertia, mass, weight, and equilibrium are fundamental concepts in understanding the behavior of objects under different conditions. An object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by
0 views • 15 slides
Laws of Motion and Forces Explained with Examples
Newton's Three Laws of Motion and key concepts regarding forces are discussed in this content. It includes explanations, visual aids, and quiz questions to test understanding. Topics covered range from object behavior at rest or in motion to calculations involving forces and accelerations. Additiona
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Motion and Newton's Laws
Explore the concepts of motion, distance, speed, and velocity as they relate to Newton's Laws of Motion. Learn about measuring motion, calculating speed, graphing motion on distance-time graphs, and understanding velocity. Discover how motion is constant and how relative motion is used. Practice cal
0 views • 36 slides
Understanding Dependent and Relative Motion in Dynamics
Dependent Motion and Relative Motion are fundamental concepts in Dynamics, providing the foundation for future analysis. Dependent Motion involves constraints like ropes or cables, while Relative Motion considers observers in motion. Dynamics involves applying a limited set of equations in diverse w
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Motion: Types and Physics
Motion refers to a body changing position with respect to its surroundings. Different types of motion include linear, rotatory, and oscillatory motion. The physics relating to motion is called Mechanics, which comprises Dynamics and Kinematics. Scalars and vectors play a crucial role in describing t
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Motion Perception in Computational Vision
In computational vision, the concept of motion opponency plays a crucial role in how the brain processes left and right motion inputs. By examining psychophysical results and the construction of motion opponent energy filters, we explore how the brain handles motion information. Additionally, the Ve
0 views • 23 slides
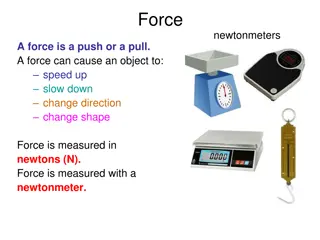
Understanding Forces and Their Applications
Forces are pushes or pulls that can cause objects to speed up, slow down, change direction, or shape. They are measured in newtons (N) using a newtonmeter. Various types of forces include contact, tension, electrostatic, friction, and gravitational forces. Forces always occur in pairs, with equal an
0 views • 46 slides
Understanding Motion in Physics: Definitions and Examples
An object is said to be in motion if it changes position with time, while rest implies no change. Learn about types of motion such as linear and circular, as well as vibratory motion and reference points. Explore how objects can be in motion relative to one reference point while at rest relative to
0 views • 4 slides