Understanding Cell Reproduction and the Cell Cycle
Explore the process of cell reproduction, DNA structure, chromosomes, and the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell cycles. Learn about binary fission, mitosis, and cytokinesis in the context of cellular growth and division. Understand the significance of genes, DNA organization into c
5 views • 56 slides
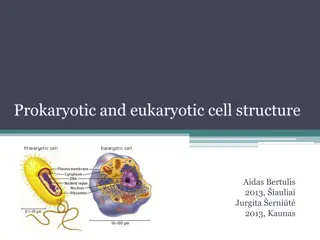
Understanding Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Structure
This comprehensive guide explores the structures and characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Learn about the differences and similarities between these cell types, including features like cell wall composition, membrane-bound organelles, nucleus presence, DNA structure, ribosomes, and m
7 views • 20 slides
Exploring the Basics of Genetics and Inheritance
Understanding the fundamentals of genetics and inheritance, this content covers topics such as Mendelian genetics, gene inheritance, chromosomes, alleles, and Gregor Mendel's pioneering work. It delves into genetic outcomes related to multiple traits, linkage, dominance, Hardy-Weinberg equations, an
0 views • 87 slides
Understanding Animal Genetics: A Comprehensive Overview
Animal genetics is the study of heredity, inheritance of traits from parents to offspring, genetic material like DNA, chromosomes, genes, alleles, and nucleotides. It involves the understanding of chromosomes in different livestock species, DNA as the carrier of genetic information, genes as units o
0 views • 67 slides
Unraveling the Mystery of Traits and Genes
Explore the fascinating world of traits and genes, understanding how they are passed down from parent to offspring through chromosomes. Delve into the role of genes in controlling various traits such as hair color, eye color, and even unique characteristics like detached earlobes and widow's peak. D
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Transcription Factors and Regulatory Sequences in Gene Expression
Transcription factors play a crucial role in gene expression by controlling the recruitment of RNA polymerase. Promoter regions contain sequences like CAAT box and TATA box that regulate transcription by binding proteins. Consensus sequences are conserved patterns in the genome with various biologic
2 views • 10 slides
Understanding Sex-Linked Inheritance: Key Concepts and Examples
Sex-linked inheritance refers to the transmission of genetic traits determined by genes located on the sex chromosomes. This type of inheritance differs from autosomal inheritance due to the unique characteristics of the X and Y chromosomes. In organisms with XX/XY sex determination, genes on the X
1 views • 21 slides
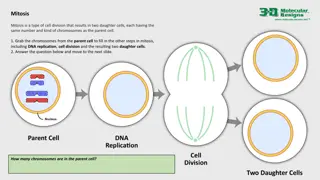
Cell Division Processes: Mitosis and Meiosis Explained
Mitosis and meiosis are two types of cell division processes with distinct outcomes in terms of chromosome numbers. Mitosis results in two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis produces four gamete cells with half the chromosome number. This explanation
2 views • 5 slides
Understanding Recombinant DNA Technology and Cloning Vectors in Genetics Engineering
Exploring the fundamentals of recombinant DNA technology and gene cloning, this content delves into the key concepts and basic steps involved. It covers various cloning vectors such as plasmids, bacteriophages, and artificial chromosomes, highlighting their common features and applications in geneti
0 views • 12 slides
Lampbrush and Polytene Chromosomes: Structures and Functions
Lampbrush chromosomes, found in growing oocytes of vertebrates, display large loops of DNA during the diplotene stage, with high gene expression levels. Polytene chromosomes, giant interphase chromosomes in insects, contain multiple strands with distinct banding patterns. Chromocenter serves as the
0 views • 14 slides
Giant Chromosomes: Lampbrush and Polytene Chromosomes
Giant chromosomes, such as lampbrush and polytene chromosomes, are significantly larger in size compared to normal chromosomes. Lampbrush chromosomes are found in oocytes of various vertebrates, while polytene chromosomes are common in dipteran flies like Drosophila. These specialized chromosomes pl
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Human Chromosomes and Genetics in Health and Disease
Human chromosomes play a crucial role in genetics, ranging from heredity to disease. Cytogenetics studies their structure and behavior, essential for diagnostics like prenatal testing and identifying genetic disorders. The coiling and folding of DNA within chromosomes, along with the mitotic cell cy
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Karyotypes and Chromosomal Abnormalities
Karyotypes are photographic inventories of an individual's chromosomes, helping determine genetic sex and detect abnormalities. Common chromosomal conditions like Down syndrome, Klinefelter's syndrome, and Turner's syndrome are discussed, along with the impact of abnormal sex chromosomes on characte
0 views • 10 slides
Posttranscriptional Modification of RNA Overview
A primary transcript is the initial RNA copy of a transcription unit, subject to posttranscriptional modifications like cleavage and further alterations to form functional tRNAs, rRNAs, and mRNAs. In eukaryotic cells, pre-rRNAs and pre-tRNAs undergo processing by ribonucleases to yield mature RNA sp
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Cloning Vectors and Recombinant DNA Technology
Genetics Engineering Lecture-2 delves into the concept and basic steps of recombinant DNA technology and gene cloning, highlighting different types of cloning vectors like plasmids, bacteriophages, bacterial artificial chromosomes, yeast artificial chromosomes, and mammalian artificial chromosomes.
1 views • 13 slides
Understanding DNA: A Journey from Friedrich Miescher to Genes and Function
DNA, the hereditary basis of life, was first discovered by Friedrich Miescher in 1869. It consists of chromosomes, plasmids, and organellar DNA, collectively known as the genome. Genes, sequences of DNA, encode proteins and RNA, essential for an organism's functions. The genome is divided into chrom
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding DNA, Chromosomes, and Chromatin Structure
DNA is made up of genes, chromosomes, and chromatin. Genes carry vital information for protein synthesis, while chromosomes are condensed DNA required for cell division. Junk DNA are non-coding regions, and sister chromatids are identical DNA copies. Homologous chromosomes have matching structures,
1 views • 17 slides
Understanding Chromosomal Karyotypes: An Overview
Explore the world of chromosomal karyotypes with this detailed guide covering definitions, structures, identification methods, staining techniques, and the importance of karyotyping in genetic analysis. Learn about chromosome labeling, obtaining samples for karyotyping, and the process of arranging
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Chromatin Organization and Chromosome Structure in Molecular Biology
Chromosomes are the carriers of genetic information in cells, containing genes made of DNA. Chromatin, composed of DNA wrapped around histone proteins, plays a crucial role in organizing genetic material. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, and the Human Genome Project aims to map the human genome.
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Chromosome Territories in the Nucleus
Chromosome territories refer to specific regions in the nucleus where chromosomes are organized. While chromosomes appear as condensed structures during cell division, they have a different appearance in non-dividing cells like neurons. Scientists have used microscopy to study chromosome organizatio
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Genes, Chromosomes, Alleles, and Mutations in DNA
Explore the intricate world of genetics through genes, chromosomes, alleles, and mutations. Delve into the fundamental structures of DNA, such as nucleosomes and eukaryotic chromosomes. Gain insights into key genetic terms like genes, alleles, and genome composition. Learn about mutations, including
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Meiosis: The Key Processes and Concepts
Meiosis is a crucial process in genetics where the number of chromosomes is halved through two divisions, resulting in the formation of haploid cells from diploid cells. This process involves key concepts such as homologous chromosomes, crossing over, alleles, and the distinction between diploid and
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Human Chromosome Nomenclature and Structure
In humans, each cell typically contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, with 22 autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. Chromosomes can be classified based on their structure, centromere position, and banding patterns. The location of the centromere on each chromosome is important for gene mapping and i
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Polytene Chromosomes in Botany: Study Material for B.Sc. Part II Hons. Paper IV
Polytene chromosomes, giant chromosomes found in salivary glands of insects like fruit flies, exhibit unique banding patterns consisting of bands and interbands. Researchers like Balbiani have studied these chromosomes, noting over 5000 bands in Drosophila. The uncoiling of chromomeres in bands form
0 views • 14 slides
An Overview of Genetics and Cellular Components
Explore the fundamental concepts of genetics, including cell types, genetic material, heredity, and genetic terminology. Learn about prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, chromosomes, DNA, genes, and the study of heredity. Discover the significance of genetic information stored in the nucleus and its ro
0 views • 13 slides
Genetic Algorithm for Attribute Selection in Data Mining
Genetic algorithm (GA) is a powerful method for attribute selection in data mining as it efficiently explores numerous attribute combinations. By choosing the most important features and ignoring the rest, GA can enhance the data analysis process through methods like feature extraction and artificia
0 views • 41 slides
Understanding Chromosomes, Genes, and DNA in Genetics
This educational material explores the fundamentals of chromosomes, genes, and DNA, highlighting how genetic material is inherited from parents, determining traits such as eye color, blood type, and more. It explains the relationship between chromosomes, genes, and DNA, emphasizing their importance
0 views • 14 slides
Overview of Cell Division in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotic Cells
Cell division plays a crucial role in the growth and reproduction of all organisms. In prokaryotic cells, binary fission is the primary mode of division, while eukaryotic cells undergo a more complex process involving cell growth, DNA replication, chromosome distribution, and cytokinesis. The cell c
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Ploidy and Chromosome Numbers in Organisms
Ploidy refers to the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, impacting the number of possible alleles. Humans are diploid, with 2 sets of 23 chromosomes each from parents, totaling 46 chromosomes. The haploid number for humans is 23, and the monoploid number is also 23. Variations in ploid
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Genetics: Chromosomes, Genes, and Inheritance
Genetics encompasses the study of chromosomes, genes, and inheritance patterns. Chromosomes are bar-like structures carrying DNA, with homologous pairs determining traits. Autosomes and sex chromosomes play roles in genetic makeup. Genes are hereditary units determining individual traits, with allel
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Cell Reproduction: Chromosomes, Cell Cycle, and Division
Explore the fascinating world of cell reproduction, from the structure of chromosomes and the role of histones to the process of mitosis and meiosis. Learn about diploid and haploid cells, the significance of homologous chromosomes, and the stages of the cell cycle. Discover how different types of c
0 views • 14 slides
Genetics II Jeopardy: Linked Genes, Genetic Mapping, and Sex Chromosomes
Explore the world of genetics with Genetics II Jeopardy, covering topics such as linked genes, genetic mapping, sex chromosomes, and inheritance patterns. Discover the significance of gene location on chromosomes, the concept of recombination frequency, and the role of specific genes like SRY in mal
0 views • 26 slides
Comparison of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells in Cell Biology
Cells are the fundamental units of life, but viruses are an exception as they lack cells. Eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus with a nuclear membrane housing chromosomes, while prokaryotic cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles. Eukaryotic cells are larger, containing membrane-
0 views • 9 slides
Cell Division Mechanisms in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells divide through binary fission, while eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis with nuclear division and cytokinesis. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and divide by replicating DNA and forming two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotic chromosomes, associated with histone proteins, undergo co
0 views • 56 slides
Cell Observation Lab for Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Explore the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells through a hands-on lab. Observe, sketch, and label organelles in bacteria (yogurt), protists (pond water), fungi (yeast), and plant cells (onion and anacharis). Learn to differentiate cellular structures and understand the characterist
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology - DNA, Chromosomes, and Gene Regulation
Delve into the intricate world of molecular biology as we explore the central dogma, from DNA structure and replication to gene regulation and chromosomal organization in eukaryotic cells. Discover the fundamental principles governing genetic information flow and genome evolution, offering insights
0 views • 32 slides
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: A Comparative Overview
Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack membrane-bound organelles, reproducing through binary fission. Eukaryotic cells are more complex, larger, with a nucleus enclosed in a nuclear envelope. They have various organelles and a cell wall. The plasma membrane defines cell boundaries, regulating the pa
0 views • 13 slides
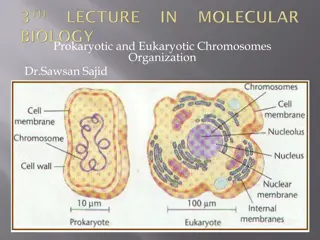
Understanding Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Chromosome Organization
Chromosomes are vital structures in cells, holding genetic material. Prokaryotic cells have a nucleoid containing DNA while eukaryotic cells have DNA enclosed in a nucleus. Proteins like H-NS, HU, FIS, and IHF play crucial roles in maintaining chromosome structure and gene expression. Unlike eukaryo
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Genes and the Genetic Code for Protein Synthesis
Explore the structures of genes, the degeneracy of the genetic code, and the process of protein synthesis through transcription, RNA processing, and translation. Delve into the role of exons, introns, promoters, and operators in gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Learn why the genetic code is dege
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Gene Structure and Splicing in Eukaryotic Cells
Explore the intricate world of gene structure and splicing in eukaryotic cells, covering topics such as exon-intron organization, central dogma, protein synthesis, genetic codes in translation, and protein 3D structure. Gain insights into the fundamental processes that regulate gene expression and p
0 views • 16 slides