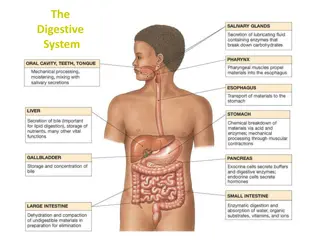
Understanding the Digestive System Processes
The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown, absorption, and elimination of food. It involves processes such as ingestion, propulsion, mechanical and chemical digestion, absorption, and defecation. Starting from the mouth with salivary glands and oral cavity, it progresses through the esop
3 views • 38 slides
Understanding Food Spoilage: Causes and Effects
Food spoilage is the deterioration of food to the point where it is no longer safe or suitable for consumption. It can occur due to various factors such as insect damage, physical injury, enzymatic degradation, microbial growth, temperature fluctuations, and more. Different types of spoilage can be
0 views • 24 slides
Protein Digestion and Metabolism in Ruminants and Non-Ruminants
Digestion and metabolism of protein in both ruminants and non-ruminants involve enzymatic breakdown of proteins into polypeptides and amino acids in the stomach and intestines. Key enzymes such as pepsin, trypsin, and chymotrypsin play important roles in protein digestion. Gastric digestion in the s
3 views • 14 slides
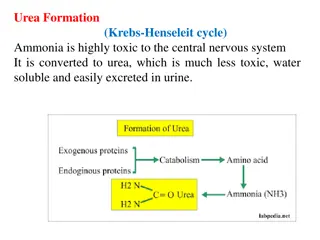
Urea Biosynthesis and the Krebs-Henseleit Cycle in the Liver
Urea is synthesized in the liver through a series of enzymatic steps known as the urea cycle or Krebs-Henseleit cycle. This process involves converting toxic ammonia into urea, a less toxic and water-soluble compound that can be easily excreted in urine. The liver plays a crucial role in urea biosyn
1 views • 20 slides
Understanding Water Activity and Mass Transfer in Food Engineering
Water activity (aw) plays a crucial role in microbial activity, chemical and physical changes in foods, and the dehydration process. Maintaining water activity below specific levels can prevent microbiological spoilage and deterioration reactions, while also affecting texture, aroma, and overall qua
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Enzyme Function: The Key Steps and Importance of Cofactors
Enzymes play a crucial role in catalyzing biochemical reactions by forming enzyme-substrate complexes and facilitating changes in substrate molecules to product molecules. The process involves four steps: proximity of enzyme and substrate, binding at the active site, catalysis leading to substrate a
0 views • 39 slides
Quantitative Estimation of Glucose by Enzymatic Method in Blood Samples
Estimation of blood glucose levels is crucial for diagnosing and managing conditions like diabetes mellitus. This practical involves using the enzymatic method with glucose oxidase to quantitatively determine glucose levels in serum. The enzymatic reaction converts glucose to gluconic acid and hydro
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Enzymatic Browning in Food Chemistry
Enzymatic browning is a chemical reaction that causes fruits and vegetables to turn brown when exposed to oxygen. This process, driven by enzymes like polyphenol oxidase (PPO), leads to the formation of brown pigments called melanins. Discover how enzymatic browning happens, its impact on various fo
0 views • 20 slides
Investigating Amylase Activity in Starch Digestion
An investigation on amylase activity involving the digestion of starch was conducted, with methods for controlling temperature, calculating digestion rates, and improving data precision discussed. The effects of temperature on enzymatic activity and precision enhancement techniques were explored.
0 views • 47 slides
Understanding Enzymes: Nature, Classification, and Mechanism of Action
Enzymes are biocatalysts synthesized by living cells. They are protein in nature and specific in their action. This article delves into the definition of enzymes, classification based on enzymatic action, enzyme class reactions, structure, and mechanism of enzyme action, highlighting how enzymes pla
1 views • 19 slides
Overview of Secondary Metabolites: Alkaloids, Flavonoids, Steroids, and Glycosides
Exploring the diverse world of secondary metabolites, this content delves into the composition, chemistry, biosources, therapeutic uses, and commercial applications of various compounds such as Alkaloids, Flavonoids, Steroids, Glycosides, and more. It discusses the structural characteristics, biolog
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Sucrose Hydrolysis and Reducing Sugars in Carbohydrate Chemistry
This content delves into the mechanisms of sucrose hydrolysis through non-enzymatic and enzymatic processes, highlighting disaccharides like sucrose, lactose, and maltose. It explores the significance of glycosidic bonds in carbohydrate structures and discusses the reducing capacity of sugars such a
7 views • 16 slides
Understanding Enzyme Inhibition in Biochemistry
Enzyme inhibition plays a crucial role in pharmacology and biochemistry by regulating enzymatic reactions. Inhibitors can be reversible or irreversible, affecting enzyme activity differently. Competitive, uncompetitive, and noncompetitive inhibition types are explained along with examples like diiso
0 views • 20 slides
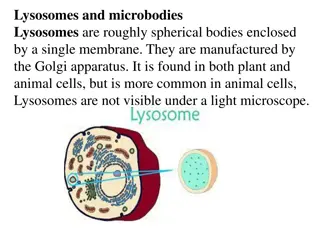
Understanding Lysosomes: Functions and Characteristics
Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles containing digestive enzymes that break down various biomolecules. They maintain an acidic internal environment, protecting the cell from enzymatic activity. Lysosomes play a crucial role in cellular waste disposal, macromolecule digestion, and intracellula
0 views • 18 slides
Carbohydrate Digestion and Metabolism in Ruminants and Non-Ruminants
Digestion and absorption of carbohydrates play a crucial role in the overall metabolism of ruminants and non-ruminants. This process involves various enzymes like amylase, maltase, lactase, and sucrase that break down complex carbohydrates into simpler forms for absorption in the small intestine. Ru
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Meat Microbiology: Challenges and Growth Phases
Meat microbiology is a crucial aspect of food science, focusing on organisms present in red meat, poultry, fish, and their products. This field addresses both preventing food spoilage and protecting consumers against foodborne illnesses. Challenges arise from slaughtering to home consumption, where
0 views • 124 slides
Demonstration of Salivary Enzyme Amylase Action in B.Sc. Practical
Salivary enzyme amylase, also known as ptyalin, plays a crucial role in breaking down starch and glycogen into maltose. This practical session in the Zoology department explores the action of salivary enzyme amylase at a temperature of 37°C and pH of 6.6. By conducting experiments with starch, iodi
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Enzyme Inhibition in Acid Phosphatase Kinetics
In this experiment, the effect of inhibitors on enzymatic reactions, specifically acid phosphatase, is explored. Different types of inhibition (competitive, noncompetitive, uncompetitive) are examined, along with reversible and irreversible inhibitors. The study aims to determine the type of inhibit
1 views • 17 slides
Effective Produce Management in Culinary Practice
Understand the importance of quality produce, considerations for purchasing fruits, proper storage techniques, washing produce, preventing enzymatic browning, and cooking using both dry and moist heat methods.
0 views • 10 slides
Exploring the Chemistry and Culture of Tea: A Comprehensive Study
Delve into the intricate world of tea through its chemistry, processing techniques, types, and effects. Uncover the social rituals surrounding tea consumption and its diverse cultural significance. Enhance your knowledge with insights on oxidation, enzymatic transformations, and the health benefits
0 views • 21 slides
Non-enzymatic Antioxidant Responses of Maize Varieties to Water Stress
Introduction of maize as a crucial crop facing challenges from both biotic and abiotic factors like drought, leading to oxidative stress. Non-enzymatic antioxidants play a key role in combating reactive oxygen species (ROS) caused by drought, with crop landraces showing potential in stress adaptatio
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Key Concepts in Biology and Chemistry
Exploring the fundamentals of biology and chemistry, including methods for problem-solving, characteristics of life, organic compounds in organisms, and the role of enzymes in metabolism. Learn about cellular organization, reproduction, metabolism, homeostasis, heredity, response to stimuli, growth
0 views • 21 slides
Menthol: Synthesis, Structure, and Applications
Menthol is an organic compound found in mint oils, synthesized or derived from cornmint or peppermint. It has a waxy, crystalline form and is solid at room temperature. The biosynthesis of menthol involves several enzymatic steps starting from the terpene limonene. Various enzymes such as geranyl di
0 views • 12 slides
Microbiology Laboratory Experiments Overview
This overview showcases various microbiology laboratory experiments conducted to examine the physiology of bacteria, enzymatic activities, and biochemical reactions. It includes experiments on Phenol Red Dextrose Broth, Phenol Red Lactose Broth, Nitrate Broth, Tryptone Broth, and more. The provided
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Activity Diagrams and State Chart Diagrams
Activity diagrams describe the workflow behavior of a system by showing the sequence of activities performed, including conditional and parallel activities. Elements such as Initial Activity, Symbol Activity, Decisions, Signals, Concurrent Activities, and Final Activity are depicted in these diagram
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Purine Degradation and Gout
Purine degradation pathway involves the breakdown of dietary nucleic acids, mainly from meat, into uric acid through specific enzymatic steps. Excessive uric acid production can lead to conditions like gout and hyperuricemia. Humans excrete uric acid in the urine as the final product, while other an
1 views • 12 slides
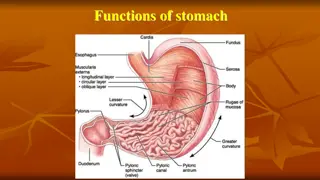
Functions and Secretions of the Stomach
The stomach plays crucial roles in digestion through its secretions such as stomach juice, hydrochloric acid, and mucus. These secretions aid in breaking down food components, promoting optimal enzymatic activity, and providing a protective barrier against bacteria. The stomach juice is composed of
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Metabolic Pathways and Regulatory Mechanisms
Metabolic pathways are a series of enzymatic reactions interconnected to form a flow of substrates and products. Irreversible steps, known as committed steps, determine pathway direction. Regulation, through positive or negative feedback, controls enzyme activity. Branched pathways share common inte
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Necrotic Tissue and Debridement in Wound Care
Explore the significance of necrotic tissue in impairing wound healing and learn about various therapeutic interventions for debridement, including mechanical, enzymatic, sharp, autolytic, and biologic methods. Discover how necrotic tissue color and consistency can indicate the severity of a wound,
0 views • 45 slides
Factors Affecting Polyphenol Oxidase Activity in Enzyme Reaction
Polyphenol oxidase (PPO) is a copper-containing enzyme with an optimal pH of 6.7 that catalyzes the oxidation of phenols, leading to color changes like browning in fruits and potatoes. This experiment aims to demonstrate PPO activity, its chemical nature, substrate specificity, and the effects of te
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Folate: Structure, Sources, and Bioavailability
Folate, also known as vitamin B9, plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. Folic acid and folate are different forms of the vitamin, with distinct sources and structures. Good food sources of folate include green vegetables, legumes, fruits, and fortified products. The bioavailability of fo
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Water Composition for Brewing Beer
The minerals and salts in brewing water significantly impact pH levels, particularly in all-grain brewing, affecting flavor contribution. Maintaining ideal mash pH and alkalinity is crucial for enzymatic activity during the brewing process. Alkalinity helps neutralize acids and influences various re
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding the Pentose Phosphate Pathway in Metabolism
The Pentose Phosphate Pathway, also known as the Hexose Monophosphate shunt, is an alternative route for glucose metabolism that plays a crucial role in NADPH synthesis, fatty acid production, antioxidant activity, and nucleotide formation. This pathway involves oxidative and non-oxidative phases, r
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) in Genetic Engineering
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a key enzymatic method in genetic engineering developed in 1983. It amplifies targeted regions of DNA, aiding in various applications like studying diseases, forensic analysis, and analyzing ancient DNA. PCR involves heating, denaturation, primer binding, and exten
0 views • 14 slides
Best Practices for Fresh Tissue Stability Testing
Establishing stability of fresh tissue samples is crucial for accurate residue analysis. Homogenization of tissue samples is recommended to ensure uniform distribution of analytes and prevent enzymatic activity. This process aids in maintaining sample integrity and minimizing freeze/thaw effects. Pr
0 views • 15 slides
Biochemical Methodology 530 - Lactate Dehydrogenase Extraction and Purification Experiment
This course focuses on the extraction and purification of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) using a series of procedures involving tissue preparation, centrifugation, and ammonium sulfate precipitation. The methodology includes detailed steps from preparing the extraction buffer to isolating LDH in differ
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Bilirubin Metabolism in Human Body
Bilirubin, a key pigment in bile, is derived from heme breakdown and plays a crucial role in the liver's detoxification process. This article explores the metabolism of bilirubin, its relationship with heme and globin, as well as its excretion steps involving enzymatic reactions and conjugation in h
0 views • 31 slides
Enzymatic Digestion of Fat by Pancreatic Lipase
The experiment focuses on studying the enzymatic digestion of fat by pancreatic lipase. It covers the structure of triglycerides, the role of lipase enzyme in hydrolyzing triglycerides to release fatty acids, and the general hydrolysis process. The aim is to investigate the effects of lipase enzyme
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding the Impact of Microorganisms on Food
Microorganisms play a vital role in food supply, either beneficial for food bioprocessing or undesirable causing food spoilage and foodborne diseases. They can be utilized for food preservation and probiotics, but their growth and enzymatic activities can also lead to food deterioration. This articl
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Calcium Homeostasis and Its Importance in the Body
Calcium homeostasis plays a crucial role in various physiological functions, including bone integrity, blood clotting, enzymatic regulation, hormonal secretion, neurotransmitter release, nerve excitability, and muscle contraction. Bones act as a major calcium reservoir, with blood containing 50% ion
0 views • 17 slides