ENAMEL
Enamel, the hardest calcified tissue in the human body, forms a protective covering over the teeth, adapting them for mastication. Its thickness varies across different surfaces of the teeth, with maximum thickness found on cusps. The structure of enamel makes it brittle, especially when it loses su
2 views • 46 slides
Understanding the Development of Occlusion and Dentition
Exploring the stages of tooth development, eruption, theories, and keys to normal occlusion. Learn about primary and permanent dentition, dental formulae, dental lamina, odontogenic cells, and enamel organ formation in the process of tooth development.
6 views • 108 slides
DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES
The developmental history of a tooth is segmented into distinct stages, namely the bud, cap, and bell stages. Each stage represents critical morphological changes in tooth development, from the initial formation of tooth buds to the differentiation of enamel organs and dental papilla. Understanding
6 views • 33 slides
Understanding Enamel Caries: Zones and Histopathology
Enamel caries is examined through histopathology, revealing four distinct zones - Translucent, Dark, Body, and Unaffected. Each zone presents unique characteristics, such as pore formation and light absorption. Understanding these zones is crucial for identifying and describing enamel caries accurat
1 views • 16 slides
Mammalian Dentition and Tooth Structure Exploration
Understanding dentition in mammals sheds light on their evolution, classification, age approximation, and dietary habits. The arrangement of teeth, tooth structure, development, and types of mammalian teeth are discussed, highlighting unique features like thecodont attachment, enamel coating, and de
2 views • 16 slides
Dental Developmental Stages: Bud, Cap, and Bell Stages Explained
The developmental history of a tooth is intriguingly divided into distinct morphologic stages - the bud, cap, and bell stages. Each stage represents a crucial phase in tooth development, from the initial formation of tooth buds to the intricate differentiation of enamel organs and dental papilla. Un
1 views • 40 slides
Formation of Hertwig's Epithelial Root Sheath in Tooth Development
The formation of Hertwig's Epithelial Root Sheath (HERS) is crucial in determining the shape, length, and number of roots in teeth. It initiates the formation of radicular dentin, marking the beginning of root development after enamel and dentin formation. HERS consists of outer and inner enamel epi
0 views • 29 slides
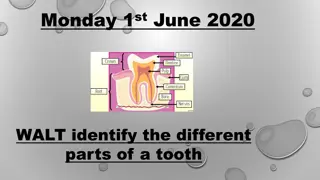
Understanding the Different Parts of a Tooth
Explore the structure of a tooth by learning about its various parts such as enamel, dentine, pulp, and more. Discover the difference between the crown and root, and engage in interactive activities like labeling diagrams and creating models to enhance your understanding. Watch a video for a detaile
0 views • 7 slides
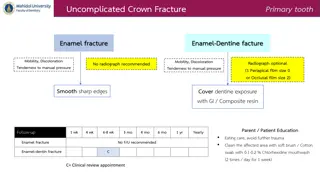
Pediatric Dental Crown and Root Fractures Management Guidelines
Guidelines for managing pediatric dental crown and root fractures are provided based on the type and severity of the fracture, along with treatment recommendations, follow-up schedules, and parent/patient education tips. The content covers uncomplicated crown fracture, primary tooth enamel-dentine f
2 views • 9 slides
Development Stages of Inner Enamel Epithelium
The life span of cells in the inner enamel epithelium can be divided into six stages: Morphogenic, Organizing, Formative, Maturative, Protective, and Desmolytic. Differentiation of ameloblasts occurs in various regions of the tooth germ. Amelogenesis, the enamel formation, takes place during the for
0 views • 48 slides
Root Development in Tooth Growth Process
Root formation plays a crucial role in the development of teeth, starting after enamel and dentin formation at the cementoenamel junction. Hertwig's epithelial root sheath (HERS) molds the shape of roots, initiating radicular dentin formation. The cervical loop forms an epithelial diaphragm, narrowi
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Fluorosis: A Critical Health Concern in Endemic Regions
Fluorosis, a prevalent condition in parts of India, China, Tanzania, and South Africa, affects millions due to high fluoride levels in drinking water. It manifests as dental and skeletal fluorosis, causing various symptoms based on exposure levels. Dental fluorosis leads to enamel discoloration and
0 views • 10 slides
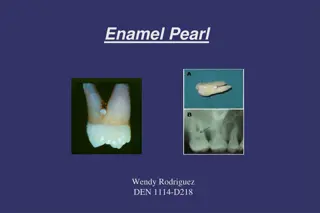
Understanding Enamel Pearl Anomaly in Dentistry
Enamel Pearl is a developmental anomaly where small nodules of enamel form below the cemento enamel junction, mainly on permanent teeth. This anomaly, detected radiographically, can lead to bacterial accumulation, periodontal issues, and inflammation if left untreated. Dental hygienists play a cruci
0 views • 8 slides
Mammalian Tooth Structure: Vertical Section Overview
Mammalian teeth consist of hard tissues (enamel, dentine, cementum) and soft tissue (tooth pulp). The enamel is the hardest, dentine surrounds the pulp cavity, and cementum covers the dentine and connects to the alveolar bone. Tooth pulp provides support, nourishment, and defense mechanisms. Support
1 views • 7 slides
Oral Health Tips During Pregnancy
Taking care of your oral health during pregnancy is crucial for both you and your baby. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are recommended, and it's safe to visit the dentist for most procedures, especially during the second trimester. Understanding how pregnancy impacts oral health, safe dental
0 views • 27 slides
Enhance Your Smile with Dental Treatments
Explore how dental procedures like bonding, veneers, crowns, enamel shaping, orthodontics, and teeth whitening can transform your smile. Improve the appearance of your teeth through these cosmetic dentistry options to boost your confidence and oral health.
0 views • 17 slides
Phylogenetic Signals in Phytosaur Tooth Enamel Microstructure
This study explores phylogenetic signals in phytosaur tooth enamel microstructure and their implications for Newark Supergroup phytosaurs. It discusses the traditional phylogenetic position, recent interpretations, key features, identification challenges, ideal fossils, localities, and the evolution
0 views • 27 slides
Histological Structure of Digestive System in Domestic Animals
The histology of the digestive system in domestic animals, specifically focusing on the teeth and their structures, including short (brachydont) and long (hypsodont) types. Details include the composition of enamel, dentine, cementum, and dental pulp, highlighting the differences in tooth morphology
0 views • 14 slides
Mammalian Dentition and Tooth Structure
Dentition refers to the arrangement of teeth in the upper and lower jaw of mammals. Most mammals have specialized teeth, with some exceptions like the Platypus and Baleen whales. The structure of a mammalian tooth includes the crown, root, and neck, made up of dentine, enamel, and cement. Tooth deve
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Enamel Pearls and Fluorosis: Dental Abnormalities Explained
Enamel pearls are small spherical projections on root surfaces that can lead to plaque retention and gum disease if left untreated. They are caused by abnormal enamel formation during tooth development. On the other hand, fluorosis is marked by enamel hypomineralization due to excessive fluoride ing
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Enamel: Structure, Formation, and Properties
Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body, formed by ameloblast cells during tooth development. Chemically, it consists mostly of inorganic matter, primarily hydroxyapatite. Mature enamel lacks organic matter, is avascular, and not renewed. Its structural unit is the enamel rod, surrounded b
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Neoplasia and Odontogenic Tumors in Dentistry
Neoplasia refers to abnormal tissue growth surpassing normal growth, persisting excessively even after the initial stimulus. Odontogenic tumors are classified by the WHO in 1992 into benign and malignant categories, with various subtypes described. Ameloblastoma is a true neoplasm of enamel organ ti
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Dentin: Structure, Properties, and Functions
Dentin is a vital component of teeth, featuring various structural units such as dentinal tubules. This calcified tissue determines tooth shape, hardness, and radiolucency. It plays a significant role in supporting enamel, cementum, and pulp, with dentinal tubules housing odontoblast processes. Dent
0 views • 29 slides