Approaches in Studying Human-Environment Relationship
Explore different approaches to understanding the dynamic relationship between humans and their environment, including deterministic, teleological, possibilistic, and economic deterministic perspectives. These approaches shed light on how human actions and interactions with the environment have evol
1 views • 9 slides
Evolution of Robot Localization: From Deterministic to Probabilistic Approaches
Roboticists initially aimed for precise world modeling leading to perfect path planning and control concepts. However, imperfections in world models, control, and sensing called for a shift towards probabilistic methods in robot localization. This evolution from reactive to probabilistic robotics ha
2 views • 36 slides
Understanding Machine Learning Concepts: Linear Classification and Logistic Regression
Explore the fundamentals of machine learning through concepts such as Deterministic Learning, Linear Classification, and Logistic Regression. Gain insights on linear hyperplanes, margin computation, and the uniqueness of functions found in logistic regression. Enhance your understanding of these key
6 views • 62 slides
Overview of Distributed Systems: Characteristics, Classification, Computation, Communication, and Fault Models
Characterizing Distributed Systems: Multiple autonomous computers with CPUs, memory, storage, and I/O paths, interconnected geographically, shared state, global invariants. Classifying Distributed Systems: Based on synchrony, communication medium, fault models like crash and Byzantine failures. Comp
9 views • 126 slides
Understanding Information Systems in Organizational Management
Management in organizations is divided into three levels: operational, tactical, and strategic. Each level requires different information systems to support various activities. Operational systems focus on routine transactions and control processes, while middle-level systems aid in semi-structured
9 views • 39 slides
Enhanced Scheduling Method for Low Latency Traffic in IEEE 802.11-24/0091r1
This document presents an enhanced scheduling method for handling low latency traffic in IEEE 802.11 networks. It focuses on supporting deterministic and event-based latency-sensitive traffic, addressing challenges in scheduling and resource allocation. The proposed method aims to improve the reliab
8 views • 12 slides
Solving Fitch's Paradox of Knowability Using Fractal Mathematics
Explore how to tackle Fitch's Paradox of Knowability through the use of fractal mathematics, DSI (Deterministic Search of Infinity) algorithm, and interstellar data compression. By understanding the scopes of knowability and employing innovative solutions, such as compressing massive amounts of data
0 views • 9 slides
Evolution of Wi-Fi and Cellular Technologies for Next Generation
The document discusses the initiation of a new study group for the next generation of Wi-Fi following IEEE 802.11be, emphasizing objectives like deterministic operation, increased throughput, and capacity. It outlines a timeline for the launch of new mainstream PHY/MAC generations every four years.
6 views • 12 slides
Understanding Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) in Regular Language Theory
An exploration of Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) in the context of Regular Languages, covering their definition, functioning, application in recognizing input strings, and building a DFA for a specific language. The Chomsky Hierarchy and the significance of Regular Languages are also briefly di
0 views • 41 slides
Understanding D Latches and Flip-Flops in Digital Systems
Digital systems rely on storage elements like D latches and flip-flops to store key information from the past. These structures can hold values of 1 or 0 based on certain control signals, ensuring deterministic behavior. Clock signals are essential for regulating when these storage elements can upda
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Pushdown Automata and Language Acceptance
Pushdown Automata (PDA) provide a theoretical framework for recognizing context-free languages. In PDA, the acceptance of a language depends on reaching a final state or having an empty stack. This concept is illustrated through examples and the distinction between deterministic and non-deterministi
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Different Types of Recommender Systems
Recommender systems play a crucial role in providing personalized recommendations to users. This article delves into various types of recommender systems including Collaborative Filtering, Content-Based, Knowledge-Based, and Group Recommender Systems. Collaborative Filtering involves making predicti
0 views • 7 slides
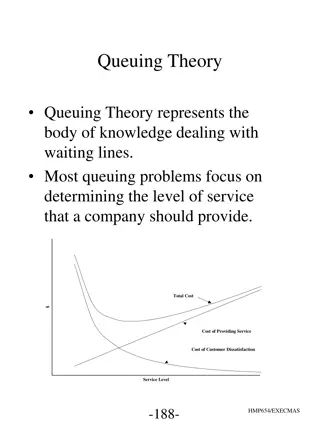
Understanding Queuing Theory and its Characteristics
Queuing Theory is the study of waiting lines and service levels in businesses. It involves analyzing customer arrival patterns, service configurations, and queuing processes such as FIFO vs. LIFO disciplines. Characteristics include the generation of customers, homogeneity of populations, and determ
1 views • 25 slides
Polynomial-time Pseudodeterministic Construction of Primes and Motivational Challenges
Exploring the challenges and advancements in generating prime numbers, particularly focusing on a pseudodeterministic construction method within polynomial time. The discussion includes reviewing previous approaches, fundamental computational problems related to primes, motivational problem statemen
0 views • 40 slides
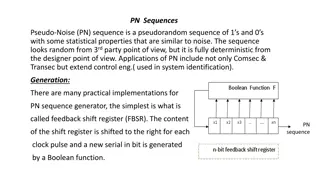
Understanding Pseudo-Noise Sequences and Applications
Pseudo-Noise (PN) sequences are deterministic yet appear random, with applications in various fields such as communication security, control engineering, and system identification. Generated using shift registers, they exhibit statistical properties akin to noise. Linear and nonlinear feedback shift
1 views • 19 slides
Using Chaos to Send Secret Messages
Chaos is a fundamental concept in creating secret messaging systems using deterministic systems with sensitive initial conditions. By implementing chaotic behavior in electrical circuits known as the "Talker" and "Copycat," messages can be encoded and decoded based on chaotic attractors and synchron
0 views • 21 slides
Introduction to Embedded Systems Design
Embedded Systems Design, Chapter 1 provides an insightful overview of embedded systems, distinguishing them from general-purpose computers. The chapter delves into the characteristics of embedded systems, their design considerations, and the various types of embedded computers such as general-purpos
1 views • 7 slides
Understanding Deterministic Turing Machines
Detailed explanation of Deterministic Turing Machines, their constituents, formal definition, determinism, and special statuses such as Start, Accept, Reject, and Loop. Includes visual representations and key concepts of deterministic Turing machines.
0 views • 14 slides
Distributed Algorithms for Leader Election in Anonymous Systems
Distributed algorithms play a crucial role in leader election within anonymous systems where nodes lack unique identifiers. The content discusses the challenges and impossibility results of deterministic leader election in such systems. It explains synchronous and asynchronous distributed algorithms
2 views • 11 slides
Concurrent Revisions: A Deterministic Concurrency Model
Exploring a deterministic concurrency model proposed by Daan Leijen and Sebastian Burckhardt, focusing on concurrent programming, threads, locks, futures, promises, transactions, and the resolution of conflicts in parallel performance.
0 views • 36 slides
Overview of Computational Complexity Theory: Savitch's Theorem, PSPACE, and NL-Completeness
This lecture delves into Savitch's theorem, the complexity classes PSPACE and NL, and their completeness. It explores the relationship between time and space complexity, configuration graphs of Turing machines, and how non-deterministic space relates to deterministic time. The concept of configurati
0 views • 67 slides
Understanding Issues in Context-Free Grammar: Ambiguity, Precedence, Associativity, and More
Delve into the complexities of context-free grammar, exploring concepts such as ambiguity, precedence, associativity, left recursion, and left factoring. Learn about the challenges posed by left recursion and the differences between ambiguous and unambiguous, as well as deterministic and non-determi
0 views • 7 slides
Information Systems in Organizations: Overview and Implementation
Information systems play a crucial role in organizations, encompassing transaction processing systems, functional area information systems, and enterprise resource planning systems. This content delves into the purpose of transaction processing systems, the support provided by information systems ac
0 views • 30 slides
Enhancing Replay Interface Efficiency in System Debugging
Efforts by researchers at Microsoft Research Asia and MIT focus on enhancing replay interface efficiency for system debugging. The motivation stems from the non-determinism challenges caused by time, user input, network I/O, and thread interleaving. The study observes that only certain parts of a pr
0 views • 26 slides
Compiler Data Structures and NFA to DFA Conversion
Compiler data structures play a crucial role in the compilation process, handling lexical analysis to code generation. Understanding the conversion from non-deterministic finite automata (NFA) to deterministic finite automata (DFA) is essential for efficient language processing and optimization.
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding P vs. NP: A Comprehensive Overview
Delve into the complexities of computational problem-solving with insights on P, NP, NP-complete, determinism, and non-determinism. Explore the distinctions between deterministic and non-deterministic algorithms and the implications they have on problem-solving capabilities. Gain a deeper understand
0 views • 22 slides
Parameterized Model for Doppler Spread in mmWave Systems
This document presents a parameterized model for Doppler spread in mmWave systems based on measurements with an 83 GHz channel sounder. The model is linked to the Quasi-deterministic (QD) propagation channel model adopted by the work group. It discusses Doppler frequency shift, channel sounder confi
0 views • 10 slides
IEEE 802.11-18/1951r0 ETSI CAM Generation Rules
ETSI EN 302.637.2 defines the structure and generation rules of Cooperative Awareness Messages (CAMs) for Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS). CAMs are essential for a variety of ITS use cases and must be backward compatible in NGV systems. The CAM messages are non-deterministic in time and siz
0 views • 7 slides
Overlay Networks and Consistent Hashing in Distributed Systems
Understanding the concept of overlay networks and consistent hashing in distributed systems is crucial for scalability and efficient data storage. Overlay networks like P2P DHT via KBR offer a decentralized approach for managing data while consistent hashing provides a balanced and deterministic way
0 views • 36 slides
Efficient Hardware Support for Disciplined Non-Determinism in Shared Memory Systems
DeNovoND presents a holistic approach to rethinking memory hierarchy, aiming to enhance hardware efficiency for disciplined non-determinism in shared memory systems. The work addresses limitations in deterministic programming, offering strong safety properties and simplified coherence and consistenc
0 views • 28 slides
Advances in Digital Humanities: CLARIN2020 Sessions Overview
Presentations at CLARIN2020 highlighted enhancements to research tools, reproducible annotation services, and the transition to more generalized repository systems. Discussions encompassed the optimization of Wittgenstein research tools, reproducibility in WebLicht workflows, and the implementation
0 views • 13 slides
Introduction to High-Level Petri Nets for Software Engineering
High-Level Petri Nets, an extension of classical Petri nets, offer a structured approach to system modeling with attributes, time considerations, and hierarchy. Sebastian Coope, a lecturer at Liverpool University, explores the practical applications and advantages of Petri Nets in software engineeri
0 views • 49 slides
Systematic Testing of Reactive Software - A Case Study on LG Electric Oven
Overview of a case study conducted on LG Electric Oven using systematic testing of reactive software with non-deterministic events. The study focused on detecting concurrency bugs in the software controller of the oven through an automated testing framework that generates event timing sequences. It
0 views • 32 slides
Understanding Cross-Device Tracking for Better Engagement
Delve into the world of cross-device tracking with insights on probabilistic vs. deterministic matching models, limitations of third-party cookies, reasons to engage in cross-device tracking, and the distinctions between probabilistic and deterministic matching methods. Explore how tracking across m
0 views • 41 slides
Time Distribution System R&D Update for Hyper-Kamiokande Experiment
In the February 2020 update, Stefano Russo from LPNHE Paris presented the progress on the time distribution system R&D for the Hyper-Kamiokande experiment. The focus is on implementing a bidirectional data exchange link with a large bandwidth capacity for synchronous, phase-deterministic protocol. T
0 views • 17 slides
Concurrent Revisions: A Model for Deterministic Concurrency
This content discusses a deterministic concurrency model called Concurrent Revisions, focusing on interactive applications with large shared data structures. It covers the challenges of conflicting tasks, conventional concurrency control methods, and proposes a programming model based on revisions a
0 views • 41 slides
Overview of Nested Data Parallelism in Haskell
The paper by Simon Peyton Jones, Manuel Chakravarty, Gabriele Keller, and Roman Leshchinskiy explores nested data parallelism in Haskell, focusing on harnessing multicore processors. It discusses the challenges of parallel programming, comparing sequential and parallel computational fabrics. The evo
0 views • 55 slides
Understanding Embedded Systems and Cyber-Physical Systems
Embedded systems are specialized computer systems embedded within larger systems, such as control systems and car controllers. This lecture covers real-time aspects, applications of Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), and examples like the Boeing 777/Airbus A380 cockpit. It discusses the design process of
0 views • 22 slides
Ensuring Orthogonal Security in Data Encryption Processes
Addressing the challenge of data confidentiality in untrusted server environments through the use of encryption techniques such as deterministic and non-deterministic encryption. The goal is to achieve full functionality independently of data encryption, allowing for secure processing of data querie
0 views • 21 slides
Shadow: Scalable and Deterministic Network Experimentation in Cybersecurity
The presentation discusses the concept of deterministic experimentation in cybersecurity, emphasizing the importance of experimental control and scalability in large distributed systems like Tor. It introduces Shadow, a network simulator designed to achieve repeatable and realistic experiments for r
0 views • 15 slides