Arkansas Concurrent Challenge Scholarship Program Details
The Arkansas Concurrent Challenge Scholarship Program provides eligible high school juniors and seniors with financial assistance for up to two concurrent credit courses per semester. Students can receive $125 per course, with a maximum of four courses per year. The program aims to offer equal acces
5 views • 6 slides
Coplanar Forces and their Classification
Coplanar forces are forces that lie in the same plane and can be classified into concurrent, parallel, non-concurrent, and non-parallel systems. These forces can be reduced to a single force or a couple for analysis. Understanding these force systems is essential in engineering and physics to determ
6 views • 20 slides
Central and Non-Central Forces in Physics
Newton's laws of motion introduced the concept of forces, leading to the classification of fundamental forces like gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear forces. Central forces act toward or away from a fixed center, while non-central forces are affected by additional param
2 views • 7 slides
Van der Waals Forces and Intermolecular Interactions
Van der Waals forces encompass London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding, influencing interactions between atoms and molecules. London dispersion forces are the weakest and present in all molecules, dipole-dipole forces involve permanent dipoles, and hydrogen bonding, the
16 views • 9 slides
Forces in Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Prof. Madhuri Reddy, an Assistant Professor at Hope Foundation's International Institute of Information Technology, explains the characteristics of forces, systems of forces, and the concept of resultant force and composition of forces in mechanics. Forces are defined as agents that produce or destr
3 views • 11 slides
Forces and Mass
Forces, such as contact and non-contact forces, interact with objects to cause motion or deformation. Mass is the amount of matter in an object, measured in kilograms. Learn about applied force, normal force, frictional force, air resistance, spring force, tensile forces, compressive forces, and she
5 views • 29 slides
Comprehensive Overview of Concurrent Enrollment Program at RRCC
Explore the essentials of the Concurrent Enrollment Instructor Program at RRCC, covering topics such as program intent, benefits, class expectations, course alignment, HLC accreditation, and collaboration with RRCC liaisons. Learn about the collective intent of concurrent enrollment, differences in
6 views • 24 slides
Force Diagrams and Balanced/Unbalanced Forces
Explore the concepts of force diagrams, balanced forces, and unbalanced forces through visual examples and explanations. Learn how balanced forces keep objects stationary or at a constant speed, while unbalanced forces cause movement and changes in direction. Practice calculating resultant forces an
4 views • 11 slides
Discovering Techniques for Detecting Deadlock Bugs in Concurrent Programs
This analysis delves into various bug detection techniques for concurrent programs, focusing on deadlock bugs. It explores model checking and testing techniques, discussing their precision, error detection capabilities, and scalability challenges. The prevalence of deadlock bugs in real-world applic
4 views • 35 slides
Rely-Guarantee-Based Simulation for Concurrent Program Transformations
Explore a rely-guarantee-based simulation approach for verifying concurrent program transformations, including compilers for concurrent programs, fine-grained implementations, and software transactional memory. Learn about defining correctness, compositionality, and verification aspects in the conte
4 views • 25 slides
Intermolecular Forces and Dispersion Forces in Molecules
Particle diagrams of liquids, solids, and gases reflect distinct arrangements due to intermolecular forces. The existence of substances as gases, liquids, or solids at room temperature is attributed to the forces between molecules known as intermolecular forces (IMF), with dispersion forces being th
3 views • 30 slides
Pediatric Concurrent Care: Enhancing Support Through Hospital Teams
Gain insights into pediatric concurrent care at Seattle Children's Hospital with Sue Ehling ARNP and Anne Anderson RN. Discover the importance of connecting with hospital teams for improved communication and support. Learn from a case study and lessons learned to enhance care for young patients faci
1 views • 31 slides
Concurrent Capable Program Review: Creating Trauma-Informed Services
In this program review developed by the Provincial Addiction and Mental Health Practice Supports Team, the focus is on creating welcoming, trauma-informed, and recovery-oriented services for individuals and families with concurrent mental health and substance use disorders or behavioral addictions.
1 views • 32 slides
Concurrent Broadcast for Information Dissemination
Concurrent broadcast facilitates the efficient dissemination of information across network nodes through message contention and transmission. This method finds applications in adaptive routing and communication networks, aiding in the collection and distribution of global network status information
3 views • 21 slides
Performance Analysis of Synchronization Methods in Concurrent Data Structures
Explore the impact of synchronization methods on the performance and behavior of concurrent data structures in multithreaded applications. The study involves developing and implementing concurrent data structures, analyzing coarse-grain locking, fine-grain locking, lock-free mechanisms, and assessin
4 views • 25 slides
Newton's Laws of Motion: Inertia, Forces, and Acceleration
Delve into the fundamentals of Newton's first and second laws of motion, exploring concepts such as inertia, the relationship between forces and acceleration, and the procedure for solving force problems. Discover how objects behave when left to themselves, and grasp the significance of forces in ch
1 views • 21 slides
Succinct Representation of Concurrent Trace Sets in Program Synthesis
This work focuses on representing concurrent trace sets efficiently in program synthesis. It addresses the problem setting of concurrent programs with specifications and provides solutions for avoiding assertion violations, including adding locks, barriers, and wait-notifies. The synthesis loop ensu
5 views • 25 slides
Forces and Equilibrium in Physics
Forces in physics can be categorized into contact forces and field forces, measured in units like Newtons (N). Inertia, mass, weight, and equilibrium are fundamental concepts in understanding the behavior of objects under different conditions. An object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by
1 views • 15 slides
Sequentializing Concurrent Programs for Efficient Analysis
This talk discusses the use of verification tools meant for sequential programs to analyze concurrent programs. It explores the idea of simulating concurrent programs using sequential programs and highlights the efficiency of various solutions developed for sequential programs. The talk also delves
4 views • 23 slides
Lock-Free and Wait-Free Algorithms in Concurrent Data Structures
Illustration of lock-free and wait-free algorithms compared to blocking algorithms, with insights on concurrent object execution, blocking vs. non-blocking algorithms, definitions, comparisons between locks, lock-free, and wait-free approaches, and explanations on making algorithms wait-free. Exampl
1 views • 23 slides
Dynamic Verification for Hybrid Concurrent Programming Models
This content discusses dynamic verification for hybrid concurrent programming models, focusing on shared memory, transactional memory, message-passing, and data-flow models. It explores the motivation, proposed solutions, and ongoing work in this field. The importance of testing and verification in
3 views • 15 slides
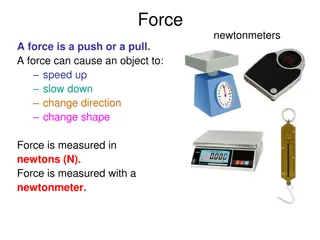
Forces and Their Applications
Forces are pushes or pulls that can cause objects to speed up, slow down, change direction, or shape. They are measured in newtons (N) using a newtonmeter. Various types of forces include contact, tension, electrostatic, friction, and gravitational forces. Forces always occur in pairs, with equal an
4 views • 46 slides
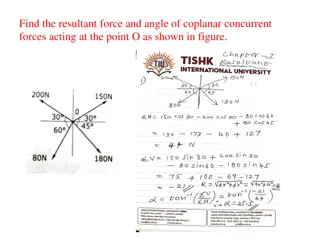
Calculate Resultant Force and Angle for Coplanar Concurrent Forces
Determine the resultant force and angle of coplanar concurrent forces acting at point O in the figures provided. Solve for the magnitude, direction, and location of the resultant force in various force systems. Different scenarios of forces acting on particles are analyzed to find the overall result
0 views • 5 slides
Analysis of Concurrent Programs Code Coverage
This article delves into the importance of code coverage-based testing for concurrent programs, emphasizing coverage metrics, test generation techniques, and the impact on testing effectiveness. It explores concurrency code coverage metrics, their role in fault detection, and strategies to generate
1 views • 98 slides
Coverage-based Testing of Concurrent Programs: Analysis & Metrics
This analysis delves into the importance of coverage-based testing for concurrent programs, exploring code coverage metrics, test generation techniques, and the impact of concurrency coverage metrics on testing effectiveness. It discusses how concurrency coverage metrics derive test requirements, ov
4 views • 36 slides
Compositional Verification of Termination-Preserving Refinement in Concurrent Programs
This research explores the compositional verification of termination-preserving refinement in concurrent programs, focusing on correctness, optimizations, and the application of new simulation as meta-theory. Contributions include a rely-guarantee-based program logic and the verification of lineariz
1 views • 34 slides
Concurrent Lines, Medians, and Altitudes in Geometry
In geometry, concurrent lines intersect at a single point called the point of concurrency. Theorems state that perpendicular bisectors of triangle sides and angle bisectors are concurrent. The circumcenter, incenter, and centroid are points of concurrency with specific properties. Medians and altitu
40 views • 12 slides
Concurrent Programming and Language Support
Concurrent programming involves executing multiple activities simultaneously without interference unless programmed to communicate. The importance of concurrency lies in various application areas which benefit from organizing programs into independent parts, running faster on parallel machines, and
3 views • 35 slides
Consistency Framework for Iteration Operations in Concurrent Data Structures
This research explores a consistency framework for iteration operations in concurrent data structures, addressing challenges in concurrent data sharing among threads/processes. It delves into algorithmic design, defining consistent iterations in a concurrency context, and presents examples and resea
1 views • 27 slides
Concurrent Enrollment Program Overview & Accreditation Information
Learn about the program overview, roles, expectations, and accreditation details of the Concurrent Enrollment Program. Discover the partnerships, faculty mentor requirements, high school instructor guidelines, and NACEP standards for accreditation. Get insights into the National Alliance for Concurr
22 views • 12 slides
IEEE 802.11-24 Multi-AP Coordinated Concurrent Transmission Protocol
In the IEEE 802.11-24 document, the Multi-AP Coordinated Concurrent Transmission Protocol is discussed to enhance throughput in multi-BSS environments. The protocol aims to support Coordinated SR and Coordinated BF methods for concurrent transmission, improving network performance. Various interfere
6 views • 18 slides
Concurrent Algorithms: A Review of Multiprocessor Programming Concepts
Delve into the world of concurrent algorithms with this comprehensive review of Maurice Herlihy and Nir Shavit's "Concurrent Algorithms: The Art of Multiprocessor Programming". Explore topics like concurrent computation, memory object management, and correctness in concurrent objects, along with a q
3 views • 27 slides
Concurrent Programming with Thread Coordination and Lock Implementation
Explore the structured approach to concurrent programming with threads by synchronizing shared objects in C. Learn about the challenges and mechanisms like flags, locks, condition variables, and semaphores. Understand mutual exclusion, critical sections, and atomic operations in coordinating concurr
0 views • 31 slides
Concurrent Programming Challenges and Solutions at Millersville University
Explore the complexities of concurrent programming at Millersville University, learning about classical problem classes like races, deadlock, livelock, and fairness. Delve into iterative servers and understand the challenges faced by clients in a concurrent environment.
3 views • 34 slides
Lazy-CSeq: Tool for Sequentializing Concurrent C Programs
Lazy-CSeq is a tool for the sequential analysis of non-deterministic concurrent C programs, offering approaches for reduction to sequential analysis and conversion. It provides solutions for analyzing concurrent programs, unrolling, inlining, and refactoring, as well as testing with various tools li
1 views • 11 slides
Understanding Concurrent Programming Challenges at Carnegie Mellon
Delve into the complexities of concurrent programming at Carnegie Mellon with insights on the difficulties posed by races, deadlock, and data race issues. Explore the nuances of managing shared variables in a concurrent environment and the implications of classical problem classes in programming sys
1 views • 73 slides
Concurrent Enrollment Updates and Discussion at Academic Leadership Conference
Stay informed about the latest developments in faculty credentialing, concurrent enrollment, and advisory boards discussed at the 2016 Academic and Student Affairs Leadership Conference. Updates include HLC extension applications, NACEP accreditation, pricing structure changes, and more. Explore the
2 views • 17 slides
Concurrent Multi-Party Quantum Computation and Secure MPC Simulator Insights
Explore the complexities of concurrent multi-party quantum computation and secure multi-party computation simulator in the real and ideal worlds. Delve into known results and limitations in both classical and quantum settings, along with the challenges and potential solutions for achieving secure MP
3 views • 25 slides
Understanding Central Forces in Physics
Explore the concept of central forces in physics, including gravitational and electromagnetic interactions, characteristics of central and non-central forces, and their impact on the motion of particles. Learn about the fundamental forces shaping interactions between matter and how central forces di
1 views • 7 slides
Understanding Transactions in Concurrent Programming
Learn about transactions in concurrent programming, including the importance of atomicity, ACID properties, and the challenges of concurrent programming. Discover how transactions simplify concurrent programming and provide guarantees for serial equivalence. Explore the use of SQL syntax for impleme
0 views • 41 slides