Automated Mobile App QoE Diagnosis with Cross-layer Analysis
This work presents the QoE Doctor, a solution for accurate and repeatable QoE measurements and analysis in mobile apps. By introducing UI automation, it enables the replay of user behavior to measure UI layer QoE metrics without modifying app source code. The QoE Doctor also supports multi-layer dia
3 views • 28 slides
Layer 2 Token Marketing Services
Layer-2 token marketing promotes tokens built on scalable layer-2 solutions, highlighting benefits like faster transactions and lower fees. Get connected with our experts today and launch a lucrative \ntoken platform.
0 views • 3 slides
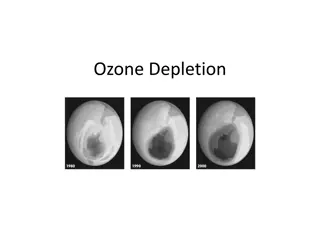
Understanding Ozone Depletion: Causes and Impact
The ozone layer, found in the stratosphere at 15 to 40 km altitude, plays a crucial role in absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation. However, due to the use of Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), the ozone layer has been depleted, leading to the formation of the ozone hole. This depletion is caused by chemi
0 views • 27 slides
Understanding Boundary Layers in Fluid Dynamics
A boundary layer forms when a fluid flows over a solid surface, with viscous forces present close to the surface. It can be laminar or turbulent, determined by the Reynolds number. Flow separation occurs in adverse pressure gradients, affecting lift and causing drag. Efforts to delay separation incl
1 views • 19 slides
Understanding Multi-Layer Perceptrons in Neural Networks
In this lecture by Dr. Erwin Sitompul at President University, the focus is on Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLP) in neural networks, discussing their architecture, design considerations, advantages, learning algorithms, and training process. MLPs with hidden layers and sigmoid activation functions enabl
2 views • 17 slides
NASA Platform Layer Updates for the CAELUM (7.0) Release
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) discusses platform layer updates for the CAELUM (7.0) release of the Core Flight System in the 2021 Flight Software Workshop. The platform layer consists of the Operating System Abstraction Layer (OSAL) and Platform Support Package (PSP), whic
1 views • 20 slides
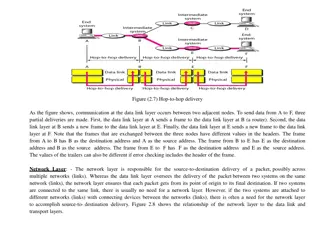
Understanding Communication Layers in Computer Networks
Communication in computer networks is facilitated through different layers such as the data link, network, and transport layers. Each layer has specific responsibilities in ensuring data delivery from one point to another. The data link layer handles communication between adjacent nodes, the network
3 views • 7 slides
Understanding Boundary Layer and Drag Forces in Fluid Dynamics
Boundary layer module explains the presence of viscous forces near a surface due to fluid flow, leading to laminar or turbulent boundary layers. Flow separation occurs when a boundary layer detaches from a surface, impacting lift and drag forces. Adverse pressure gradients and flow separation phenom
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Paper and Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) in Biochemistry
Chromatography techniques are used in laboratories to separate and identify components of mixtures. Paper chromatography is a type where a developing solution travels up a filter paper, separating compounds based on their affinity to the stationary phase. Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) is a similar
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding the OSI Model and Layered Tasks in Networking
The content highlights the OSI model and layered tasks in networking, explaining the functions of each layer in the OSI model such as Physical Layer, Data Link Layer, Network Layer, Transport Layer, Session Layer, Presentation Layer, and Application Layer. It also discusses the interaction between l
1 views • 41 slides
Bedforms in Unidirectional Flow: Characteristics and Formation
Bedforms in unidirectional flow exhibit various characteristics such as sediment layer thicknesses, boundary layer dynamics, presence of ripples and dunes, and the interplay between flow velocity and sediment deposition. These bedforms, including ripples and dunes, form due to interactions between t
3 views • 13 slides
Understanding RARP and Transport Layer in Computer Networking
Exploring Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) for mapping physical addresses to logical addresses in networking, along with insights on the Transport Layer's role in providing communication services to application processes. Learn about RARP packet formats, encapsulation, and the significance
0 views • 41 slides
Understanding Internet Transport Layer Services and Protocols
In the realm of networking, exploring the principles of transport layer services is crucial. This involves concepts like multiplexing/demultiplexing, reliable data transfer, flow control, and congestion control, which are facilitated by protocols such as UDP and TCP. The transport layer acts as a br
0 views • 56 slides
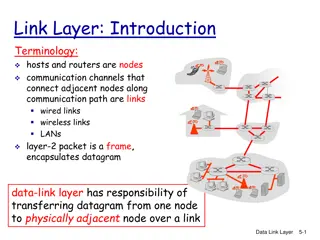
Understanding Data Link Layer Communication in Computer Networks
Exploring the data link layer in computer networks, this lecture discusses the node-to-node communication, services provided, such as framing, flow control, error control, and congestion control. Through a series of images, the concept of links and nodes, as well as the responsibilities of the data
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Data Link Layer in Computer Networking
The Data Link Layer (DLL) is the second layer of the OSI model, responsible for error detection and correction, framing, addressing, synchronization, flow control, and multi-access protocols. It deals with logical link control and media access control, addressing destination hardware, avoiding data
0 views • 49 slides
Enhancements to International Survey of Herbicide Resistant Weeds and Website Overhaul Plan
In 2019, Ian Heap, Director of the International Survey of Herbicide Resistant Weeds (HRAC), is leading an initiative to enhance the survey and overhaul the website to target completion by year-end. The website will undergo a three-tiered redesign focusing on presentation layer, application layer, a
0 views • 11 slides
Insights into the Low-Latitude Boundary Layer in Mercury's Magnetosphere
Study focuses on the low-latitude boundary layer (LLBL) in Mercury's magnetosphere, analyzing magnetosphere and magnetosheath plasma characteristics such as reconnection rates, IMF/magnetic shear, and plasma beta. Results show anti-correlation between LLBL and non-LLBL regions, with different reconn
0 views • 11 slides
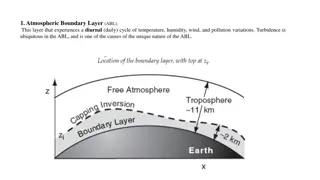
Understanding Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Static Stability
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer (ABL) undergoes daily variations in temperature, humidity, wind, and pollution with turbulence being a key factor. Static stability in the environment determines the behavior of air parcels, leading to categorizations of stable, unstable, and neutral conditions based o
0 views • 13 slides
Meridian: An SDN Platform for Cloud Network Services
Meridian is an SDN platform developed by Mohammad Banikazemi, David Olshefski, Anees Shaikh, John Tracey, and GuohuiWang at IBM T. J. Watson Research Center. The platform focuses on providing cloud network services efficiently. It encompasses an architecture that enables faster and more convenient n
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding ZFS: Structure and Operations
Explore the comprehensive structure and operations of ZFS, covering aspects like MOS layer, object-set layer, Dnode, Block Pointer, and TRIM operations. Learn about the meta-object set (MOS), dataset and snapshot layer (DSL), and storage pool allocator (SPA) modules within ZFS. Understand how ZVOLs,
0 views • 10 slides
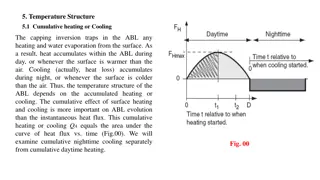
Understanding Temperature Structure and Cumulative Heating/Cooling in Atmospheric Boundary Layer
The temperature structure in the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) is influenced by cumulative heating or cooling effects from the surface. During the day, heat accumulates within the ABL, while cooling occurs at night. The cumulative heating or cooling is more crucial for ABL evolution than instanta
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding the Planetary Boundary Layer in Atmospheric Science
The Planetary Boundary Layer (PBL) plays a crucial role in atmospheric dynamics, divided into surface, mixed, stable, and residual layers. During the day, the mixed layer experiences convective motions due to surface heating, while the stable layer dominates during the night. Understanding these lay
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
This content delves into the concepts of Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), exploring their origins, application in web security, and protocol stack integration. It covers the TLS/SSL handshake process, key derivation, data transfer mechanisms, and the significance of the
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Modular Layer 2 in OpenStack Neutron
Modular Layer 2 (ML2) is a new core plugin in OpenStack Neutron that enables interface with various network mechanisms and types for enhanced flexibility and efficiency. It replaces deprecated plugins like Open vSwitch and Linuxbridge, offering a more modular and feature-rich approach for managing l
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Earth's Atmosphere: A Detailed Overview
The Earth's atmosphere is a vital layer of gases that encircles our planet, providing the necessary conditions for life to thrive. It consists of several distinct layers, each with unique characteristics and functions. From the troposphere closest to the surface to the thermosphere extending to grea
0 views • 29 slides
Developing Sustainable Infrastructures Amid Climate Change and Global Disasters
Prof. H.A. Odeyinka's keynote paper discusses the importance of developing sustainable infrastructures amidst declining economic resources in the face of climate change and global disasters. It highlights the concepts of climate change, sustainable development, atmospheric layers, ozone layer, carbo
0 views • 25 slides
Ground Boundary Impact on Short Tower Turbines: A Conceptual Study
This conceptual study explores the impact of ground boundary on the production of short tower turbines. It investigates whether two turbines with the same rotor diameter but different hub heights can generate the same energy output. The study examines how the ground boundary influences the airflow p
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Application-layer Protocols in Computer Communication and Networks
Explore Chapter 2 of the course on Computer Communication and Networks, focusing on the application-layer protocols in the client-server paradigm, specific protocols like HTTP and SMTP, client-server architecture, peer-to-peer architecture, and addressing needs in the network application layer.
0 views • 60 slides
Understanding Transport Layer Services and Challenges
The transport layer provides essential services for reliable communication between end-hosts, including error detection, recovery, and timing preservation. Different transport service models, connection paradigms, and challenges like packet delay, reordering, and loss are discussed in comparison to
0 views • 22 slides
Enhancing Bitcoin Network Through Trust Extraction and Blockchain Scalability
Explore methods to extract trust from the blockchain and enhance scalability through Layer 1 and Layer 2 changes, including parameters adjustment, consensus algorithm modifications, sharding, payment networks, and side chains. Learn about payment channels, Bitcoin throughput, and strategies to incre
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding ARP, ICMP, and DHCP in TCP/IP Protocol Stack
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) plays a crucial role in bridging the Layer 2/Layer 3 addressing boundary in the TCP/IP protocol stack, allowing IP to be agnostic about layer 2 addressing while still using layer 2 for packet delivery. Machines ARP for MAC addresses within their local network, where
0 views • 39 slides
Understanding the Low Velocity Layer (LVZ) in Subduction Zones
The presence of a Low Velocity Layer (LVZ) at the top of subducting plates in subduction zones has significant implications for imaging and potentially seismogenesis. This hydrated layer of oceanic crust, likely caused by dehydration reactions during subduction, affects seismic wave behaviors and ca
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding the Layers of Distributed Systems
This content delves into the intricacies of distributed systems, exploring concepts such as establishing communication with applications, managing channels for actual communication, bandwidth versus latency considerations, and the functions of physical, link, and network layers. From the physical la
0 views • 27 slides
Understanding the Link Layer in Computer Communication and Networks
The link layer, an essential component in computer networks, is implemented at every host through adapters like NICs or Ethernet/802.11 cards. It handles tasks such as frame encapsulation, error checking, and flow control to ensure reliable data transmission between nodes. Link layer services includ
0 views • 64 slides
Understanding Link Layer in Computer Networking
The link layer, also known as the data link layer, plays a crucial role in transferring data between adjacent nodes over communication links. This layer is responsible for framing, access control, reliable delivery, error detection and correction, flow control, and more. It is implemented in network
0 views • 34 slides
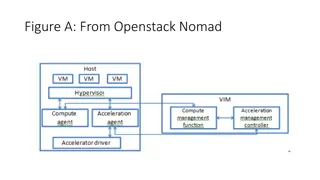
Acceleration Management Architectures in OpenStack Nomad and DPACC
The figures depict the architecture of Software Acceleration Layer (SAL), Acceleration Management Layer (AML), and other components in OpenStack Nomad and DPACC. They illustrate the interaction between Software Routing Layer (SRL), General Drivers (g-drivers), Hardware I/O Interface (hio), and more
0 views • 4 slides
Journey to the Earth's Layers
The Earth's structure consists of four main layers: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust is the thin, rocky layer we see on the surface, while the mantle is a solid layer that flows like a viscous liquid. The outer core is a hot, melted layer of iron and nickel, and the inner cor
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding the Network Layer in Computer Networking
The network layer is vital in computer networking, responsible for host-to-host delivery by carrying packets between computers. It enables internetworking, routing packets to their destinations, and ensuring unique addressing for global communication. This layer encapsulates data packets, fragments
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Layer 3 Switches: Functionality and Configuration
Layer 3 switches combine the features of Ethernet switches and routers, allowing them to process both MAC and IP headers. By configuring VLANs, trunking, and management interfaces, these switches can handle data forwarding across different subnets efficiently. This guide explains the basic principle
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Transport Layer Parameters and Examples
This content delves into the important parameters associated with the transport layer, such as the number of lanes per converter device, the number of converters per device, and the number of octets per frame. It provides examples of how these parameters are configured in different scenarios, showca
0 views • 8 slides