Understanding Gas Laws in Atmospheric Sciences
Explore the fundamental gas laws governing the behavior of gases in the atmosphere. Discover key parameters such as temperature, pressure, density, and volume, and how they are interrelated through Boyle's Law and the Law of Charles and Guy Lussac. See practical applications of these laws in our dai
6 views • 38 slides
Understanding the States of Matter: Solids, Liquids, and Gases
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass, consisting of tiny particles like atoms and molecules. Solids have closely packed particles, liquids have less densely packed particles that can flow, and gases have spread out particles. Solids retain their shape, liquids take the shape of their
7 views • 11 slides
Understanding Properties of Gases and Gas Laws
Gases exhibit unique properties compared to solids and liquids, including compressibility and variable densities. Pressure is defined as force per unit area, with common pressure units like atm, mmHg, and torr. Gas laws such as Gay-Lussac's Law, Boyle's Law, and Charles's Law describe the relationsh
4 views • 33 slides
The Role of Sunlight, Ozone, and Plant Life in Earth's Atmosphere
Sunlight plays a crucial role in the formation of ozone from oxygen, leading to the protection of plant life against harmful UV radiation. The ozone produced by sunlight helps in the photosynthesis process of plants, which in turn release oxygen, absorb CO2, and contribute to the overall balance of
7 views • 23 slides
Understanding Atmosphere Composition and Structure in Climatology
The study of climatology, focusing on the atmosphere, is presented by Dr. Banashree Saikia, covering topics such as atmospheric composition, insolation, temperature variations, atmospheric pressure, wind systems, atmospheric moisture, climatic classification, cyclones, and monsoons. The atmosphere,
1 views • 9 slides
Understanding Kinetic Theory of Gases: Key Concepts and Equations
Exploring the kinetic theory of gases, this content covers essential concepts such as ideal gas behavior, molar mass, the equation of state, and isobaric/isothermal processes. Discover the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature in gases, along with practical examples and calculations
0 views • 49 slides
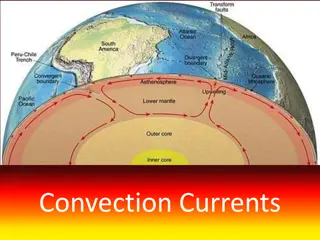
Understanding Convection Currents in Earth's Systems
Convection currents refer to the movement of heat by fluids like liquids and gases, transferring heat from one place to another. They play a significant role in the geosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere of the Earth, influencing phenomena such as plate tectonics, winds, and ocean currents. In the g
0 views • 12 slides
Types of Gases in Tunnelling & Gas Monitoring Sensors in TBM
Understanding the types of gases encountered in tunnelling is crucial for safety. Gases like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, methane, and hydrogen sulfide are common in TBM environments. Proper gas monitoring sensor placement inside the TBM is essential to detect hazardous gas leve
0 views • 11 slides
Gas Laws and Properties: Understanding the Behavior of Gases
Gas laws govern the behavior of gases and their properties in various conditions. From the total pressure of gas mixtures to calculating partial pressures, understanding the relationship between pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas is crucial. Effusion and diffusion play key roles in how
0 views • 16 slides
Exploring Properties of Matter: Solids, Liquids, and Gases
Dive into the characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases through engaging visuals and key vocabulary. Understand the behavior of particles in different states of matter and learn about the properties that define each state. Explore examples of solids, liquids, and gases with a focus on their uniq
0 views • 19 slides
Electrical Breakdown in Gases, Solids, and Liquids: Understanding the Phenomenon
Exploring the intricate dynamics of electrical breakdown in various mediums such as gases, solids, and liquids. From the criteria for breakdown in gases to factors affecting breakdown strength in liquid dielectrics, this study delves into the mechanisms, equations, and practical implications of thes
0 views • 15 slides
Chemical Properties and Bonding in Xenon: A Study of Noble Gases
Noble gases, including xenon, exhibit unique chemical properties due to their stable electron configurations. Xenon forms compounds like xenon difluoride, xenon tetrafluoride, and xenon hexafluoride, showcasing various hybridization states and geometries. These compounds illustrate the reactivity of
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Activity and Fugacity in Gases
Fugacity of real gases can be measured, defining standard states in terms of fugacity. The relation between fugacity, activity, and molar concentration is explored, highlighting the ideal behavior of gases at standard states. Activity coefficients and deviations from ideal gas behavior are also disc
0 views • 30 slides
Insight into Kinetic Theory of Gases and Maxwell Velocity Distribution
The discussion delves into the kinetic theory of gases, highlighting the deviations from ideal gas behavior and the derivation of the Maxwell velocity distribution. It explores the intricacies of molecule-wall collisions, Maxwell's assumptions, the Gaussian distribution, and the concept of reversibl
0 views • 8 slides
The Noble Gases: Properties, Sources, and Uses
The noble gases, including helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon, and Oganesson, are characterized by their low reactivity due to a complete electron configuration. They have diverse applications, such as forming inert atmospheres, medical treatments, and lighting technologies. Naturally occurr
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding the States of Matter and Properties of Gases
Matter can be classified into gas, liquid, and solid based on particle arrangement, shape, and motion. Gases in pharmacy are crucial for various applications like anesthesia and aerosols. Properties of gases include compressibility, pressure exertion, diffusion, and expansion. Gas laws such as Boyle
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Pressure Variations at Different Altitudes
Atmospheric pressure varies with altitude due to the weight of the air column above. This activity explores how Otto von Guericke's experiments with vacuum systems demonstrate the power of air pressure. Theoretical concepts of atmospheric pressure are discussed, highlighting its relation to gravity
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Gases and Plasmas in the Atmosphere
Delve into the concepts of gases and plasmas in the atmosphere, exploring topics such as fluid pressure, buoyancy, and the unique properties of gases compared to liquids. Discover how the balance between kinetic energy and gravity determines the thickness of our atmosphere and why it is essential fo
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Gases in the Earth's Atmosphere
Explore the composition and layers of the Earth's atmosphere, including the significance of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, and carbon dioxide. Learn how human activities impact atmospheric composition and how changes in temperature and pressure affect weather predictions. Discover the rol
0 views • 13 slides
Cutting-Edge Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Research at Barcelona Supercomputing Center
Conducted by the Atmospheric Composition Group at Barcelona Supercomputing Center, this cutting-edge research focuses on atmospheric chemistry modeling using advanced tools and frameworks like HERMESv3 and MONARCH. The team's approach integrates various modules to study complex processes influencing
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding the Greenhouse Effect and Its Impact
The greenhouse effect is the trapping of the sun's warmth in a planet's lower atmosphere, primarily by greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor. These gases absorb and re-emit infrared radiation, which leads to an increase in temperatures. While carbon dioxide and water vapor are signifi
1 views • 13 slides
Understanding Kinetic Theory of Gases and Thermodynamics
Explore the fundamental principles of the kinetic theory of gases, including the five postulates and the relationship between macroscopic properties and microscopic phenomena. Delve into the concept of entropy and thermodynamics, along with the behavior of ideal and real gases. Gain insights into th
0 views • 116 slides
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics: Historical Laws and Principles
This lecture explores the historical overview of thermodynamic laws, including Boyle's Law, Charles' Law, and Gay-Lussac's Law. It delves into the relationships between pressure, temperature, volume, and amount in ideal gases, providing useful insights for meteorologists and atmospheric scientists.
0 views • 23 slides
Overview of Alternative Gases and Pressure Gas Welding in Oxyfuel Welding
Alternative gases to acetylene in oxyfuel welding, such as MAPP, propane, and natural gas, offer different characteristics and applications. Pressure gas welding (PGW) is a fusion-welding process that uses oxyacetylene gas and pressure to join metal parts without filler metal. The advantages, limita
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Earth's Atmosphere: A Detailed Overview
The Earth's atmosphere is a vital layer of gases that encircles our planet, providing the necessary conditions for life to thrive. It consists of several distinct layers, each with unique characteristics and functions. From the troposphere closest to the surface to the thermosphere extending to grea
0 views • 29 slides
Understanding Intermolecular Forces and Dispersion Forces in Molecules
Particle diagrams of liquids, solids, and gases reflect distinct arrangements due to intermolecular forces. The existence of substances as gases, liquids, or solids at room temperature is attributed to the forces between molecules known as intermolecular forces (IMF), with dispersion forces being th
0 views • 30 slides
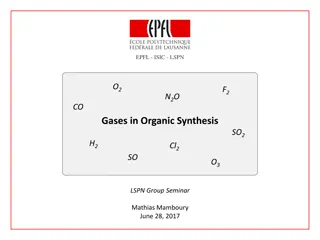
Role of Gases in Organic Synthesis: A Comprehensive Overview
The presentation delves into the significance of gases in organic synthesis at standard temperature and pressure, focusing on reactions with atom incorporation for the synthesis of useful organic molecules. It covers various gases such as H2, O2, O3, CO, NO, N2O, SO2, Cl2, F2, discussing their advan
0 views • 23 slides
Addressing the Gas Crisis in Rome: Solutions and Strategies
The gas crisis at Centro Fermi in Rome on 4th July 2019 highlighted the need for reducing harmful gas emissions. Regulations have been in place since the 1990s to ban gases with high ozone depletion power. The European Community is progressively banning gases with high global warming power, leading
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Matter: Solids, Liquids, Gases, and Fluids
Matter exists in various states - solid, liquid, gas, and fluid. Solids have atoms closely packed, liquids have more freedom but still cohesion, gases have atoms spread out, and fluids flow like liquids or gases. Mass density characterizes matter based on atom proximity. Gas pressure results from mo
0 views • 22 slides
Exploring the Fascinating World of Gases and Plasmas in Chapter 14
Delve into the intriguing realm of gases and plasmas as we transition from liquids in Chapter 13. Understand the dynamics of fluid pressure, buoyancy, and the unique characteristics that differentiate gases from liquids. Explore examples illustrating the concepts and ponder over the mysteries of our
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Composition and Structure
The presentation covers fundamental concepts related to the Earth's atmosphere, including its composition, origin of oxygen, dry and moist layers, standard atmosphere layers, and temperature variations. Key topics discussed include the primordial atmosphere, atmospheric constituents, water vapor dis
0 views • 58 slides
Gas Absorption and Atmospheric Soundings: Principles and Applications
Gases in the atmosphere absorb radiation through various mechanisms such as changing rotational/vibrational energy and exciting electrons. This absorption plays a crucial role in remote sensing applications. The absorption principles differ for molecules like CO2 and H2O, influencing their vibration
0 views • 9 slides
Storage and Manipulation of Liquefied Gases with Dewars and Cryostats
Storage and manipulation of liquefied gases involve using specialized equipment like Dewars and Cryostats to minimize heat transfer and maintain low temperatures. Dewars, invented by James Dewar, are double-walled vacuum vessels designed to store liquefied gases with minimal losses. The use of vacuu
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding the Kinetic Theory of Gases and Ideal Gas Model
Explore the Kinetic Theory of Gases, the Molecular Model of Ideal Gases, and concepts like pressure, temperature, and heat capacity. Understand the fundamental properties of gases, including the distribution of molecular speeds and equations that describe gas behavior. Learn about the mole concept,
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding the Behavior of Gases: A Comparison of Real and Ideal Gases
This chapter delves into the behavior of gases, contrasting real gases with the ideal gas model. It explores the P-V-T relationships of gases, highlighting the differences between ideal and real gas behaviors based on molecular properties. The critical point where coexisting gas and liquid phases co
0 views • 40 slides
Understanding Electromagnetic Radiation and Solar Energy Interactions
The interaction between electromagnetic radiation and the Earth's atmosphere is crucial for powering atmospheric processes and sustaining life on our planet. From the Sun's energy production to the absorption patterns of different gases in the atmosphere, various laws like Planck's Law, Stefan-Boltz
0 views • 17 slides
GEOS-Chem Atmospheric Chemistry Model Overview
GEOS-Chem, developed by Daniel J. Jacob at Harvard University, is a global model of atmospheric composition used to understand human and natural influences on the environment. The model addresses various atmospheric chemistry issues on different scales, from local to global, and is regularly updated
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Pressure, Wind Variations, and Humidity in Weather Systems
The atmosphere is composed of various elements like gaseous molecules, water vapor, and dust particles. Key weather variables include atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity, wind, cloud cover, and precipitation. Atmospheric pressure is influenced by the weight of air above a point, with average
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Gases in the Environment and Their Impact on Earth
Gases such as CO, CO2, SO2, O2, and O3 play a crucial role in shaping our environment. This chapter delves into the properties of gases, the three states of matter, pressure exerted by gases, atmospheric pressure measurement methods, and units of pressure used in scientific fields.
0 views • 25 slides
Atmospheric Correction Techniques for Satellite Image Enhancement
Atmospheric correction is essential for improving the quality of Remote Sensing images captured by satellites. This process involves correcting for the effects of atmospheric gases such as scattering and absorption on the measured Top-of-Atmosphere (TOA) reflectance. Techniques like molecular correc
0 views • 8 slides