The American Revolution: Causes, Events, and Consequences
The American Revolution was sparked by British government control over the colonies and imposition of taxes without representation. Key events such as the Boston Massacre and Boston Tea Party further fueled the revolt. The war ended in victory for America and led to the birth of a new nation. Explor
2 views • 7 slides
The Declaration of Independence and its Impact on the American Revolution
The American colonies' journey to independence during 1775-1776 is highlighted, from initial hopes for reconciliation to the eventual Declaration of Independence. The document's significance is explored, focusing on the response it garnered, the process leading to its approval, and the outlined righ
3 views • 15 slides
Attitudes Toward Sports Among Colonial Settlers in the New World
The attitudes of European colonial settlers towards sports in New England, the Middle Colonies, and the South were deeply influenced by their religious backgrounds. While Puritans in New England were generally against play, Quakers and Dutch Calvinists in the Middle Colonies were more accepting. In
0 views • 19 slides
Evolution of North American Law: From Common Law to Unique Legal Tradition
The historical origins of North American law trace back to the early 17th century, marked by the influence of English common law on the colonies. Over time, the American legal system evolved, absorbing elements from both the English legal tradition and local statutes. The development of the United S
0 views • 19 slides
The Monroe Doctrine: A Declaration of American Independence
The Monroe Doctrine asserts that the American continents are not to be colonized by European powers and considers attempts to extend European systems into the hemisphere as dangerous. The United States declares its non-interference with existing European colonies or dependencies.
0 views • 8 slides
Education in Colonial Times: A Historical Overview
Education in colonial times varied across different regions in America. The Northern colonies emphasized education with schools like Harvard College, while the South lacked formal education laws pre-Civil War. In the middle colonies, education was deemed important but left to families until laws wer
0 views • 10 slides
Latin American Revolutions: Causes, Events, and Impact
Latin American Revolutions from 1791 to 1825 marked a period of significant upheaval as colonies in the Western Hemisphere sought independence from Spanish rule. Driven by factors like inspired by other successful revolutions, Spanish mercantilist policies, and unequal wealth distribution, these rev
1 views • 12 slides
Forming the United States: From Colonies to a New Government
Explore the journey of the 13 colonies as they came together to form the United States of America. Learn about the creation of the Constitution, the fears of the founders regarding the abuse of power, and the transition from the weak Articles of Confederation to a stronger central government followi
0 views • 29 slides
Causes and Impact of the French and Indian War on the American Revolution
The French and Indian War was caused by disputes over land and power between France and Great Britain, leading to a nine-year conflict that began in 1754. Tensions escalated as both countries claimed the Ohio River Valley, a key frontier region. The war had significant immediate and long-term impact
0 views • 17 slides
Washington Irving: Father of American Fiction and Pioneer of American Romanticism
Washington Irving, an influential American author of the early 19th century, is revered as the Father of American fiction. Known for iconic works like "The Legend of Sleepy Hollow" and "Rip Van Winkle," Irving played a crucial role in establishing American literature as an independent art form. His
1 views • 14 slides
The Path to American Independence: Lessons from History
Explore pivotal moments in American history from the Continental Congress forming the Continental Army to the drafting and approval of the Declaration of Independence. Learn about key figures like George Washington, Thomas Paine, and Thomas Jefferson who played crucial roles in shaping the course of
0 views • 13 slides
Causes and Reactions of the American War of Independence
The American War of Independence was fueled by various causes, including taxation without representation, economic restrictions on trade imposed by Britain, and defiance through protests like the Boston Tea Party. The colonies fought for their independence, culminating in the Declaration of Independ
0 views • 4 slides
Exploring American Colonial History Through Images
Explore the early American colonial period and independence through a collection of visual resources depicting key events such as Christopher Columbus's exploration, the first colonies in Jamestown, interactions between colonists and Native Americans, Thanksgiving celebrations, and political develop
0 views • 36 slides
Colonial Resistance and Key Events in American History
Explore the growing colonial resistance during the Townshend Acts, the Writ of Assistance, the Boston Massacre, and the Boston Tea Party. Learn about key figures like Samuel Adams, John Adams, and Crispus Attucks who played significant roles in the fight against British taxation and injustice in the
0 views • 9 slides
The Colonists' Struggle for Rights and Unity: A Timeline
Colonists in the American colonies resisted British control and policies that they saw as violations of their rights, leading to organized opposition and boycotts. Events such as the Townshend Acts, the Boston Massacre, and the Tea Act of 1773 fueled tensions, prompting figures like Samuel Adams to
0 views • 10 slides
American Revolution Key Events and Reactions
The journey of the American Revolution unfolds through key events such as the French and Indian War, British taxation policies, colonial resistance, and the push for independence. Each step led to escalating tensions between the colonies and Britain, culminating in acts of defiance and the start of
0 views • 13 slides
George Washington: An American Revolutionary
George Washington, the first president of the United States, led a remarkable life from his early days in Virginia to commanding the Continental Army during the American Revolution. His military experience and leadership were instrumental in securing independence for the colonies despite facing chal
0 views • 33 slides
Impact of British Empire and Commonwealth on Migration: Unpacking Immigration Stories
Explore the historical impact of the British Empire and Commonwealth on British migration through six immigration stories. Understand how relations with former colonies have shaped diversity in Britain and influenced British immigration patterns. Key terms like migration, emigration, empire, and col
0 views • 23 slides
History of European Colonization in America
The visual content and text describe the early colonization of America by Europeans, focusing on the establishment of colonies like New Sweden and New Netherland. It illustrates the interactions between European settlers and Native Americans, the competition for land, and the growth of colonies at t
0 views • 14 slides
Insights into Fruit Bats: Behavior, Growth, and Senses
Fruit bats, also known as flying foxes, exhibit a wide variation in size, with some as small as two inches and others over 16 inches long. They are equipped with excellent vision and sense of smell, aiding in finding food sources and avoiding danger. Fruit bats have unique feeding habits with sharp
0 views • 9 slides
Causes of the Spanish-American War: Imperialism, Cuba, and Yellow Journalism
The Spanish-American War was fueled by imperialism, particularly the desire for colonies, as well as the unrest in Cuba against Spanish rule. American economic interests in Cuba, coupled with yellow journalism's sensationalized reporting, further escalated tensions leading to the conflict.
0 views • 25 slides
American Colonial Unrest and Revolutionary Actions
American colonies faced a series of challenges and oppressive acts from the British government, triggering unrest and paving the way for revolutionary actions. This period saw events such as the Proclamation Line of 1763, Quartering Act, Stamp Act tax, and the formation of groups like the Sons of Li
0 views • 15 slides
The Duel for North America: France's Colonization Efforts
France, like England and Holland, was a latecomer in the race for North American colonies. King Louis XIV took an interest in overseas territories, leading to the establishment of Quebec in 1608. Samuel de Champlain played a key role in French colonization efforts, forging alliances with Native Amer
0 views • 20 slides
The American Revolution: Early Years and Conflict
The American Revolution began with the Colonies declaring independence, leading to a war where Patriots faced many challenges against the better-equipped British forces. Loyalists, including African Americans, played complex roles in the conflict. Despite disadvantages, Americans had strengths like
0 views • 10 slides
Root Causes of the American Revolution: England's Actions and Colonists' Reactions
England's strained relationship with the American colonies intensified due to policies like the Proclamation of 1763, tax laws, trade regulations, the Sugar Act, and the Stamp Act. Colonists resisted through petitions, boycotts, and protests, leading to growing tensions that ultimately sparked the A
0 views • 13 slides
Exploration and Colonization in the New World: Chapters 1-2 Review
European exploration and colonization of the New World were driven by factors such as the search for new trade routes, desire for wealth, and spreading of religion. The consequences of exploration included the spread of disease, slave trade, and cultural exchanges between the Eastern and Western hem
0 views • 12 slides
Colonial America Founders and Colonies Overview
The content provides details about important founders and key characteristics of the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies in Colonial America. It covers founders like William Penn, Duke of York, Lord Baltimore, and James Oglethorpe, as well as information on staple crops, religious groups, pla
0 views • 7 slides
Contrasting Early Colonial Regions in America
Early New England, Middle, and Southern colonies differed in economics, geography, culture, government, and relations with American Indians. New England focused on subsistence farming and democratic town meetings. The Middle colonies benefited from fertile land and trade along rivers. The Southern c
0 views • 13 slides
British Class System and Migration to Former Colonies
The British class system categorizes individuals based on wealth, education, and occupation into working class, middle class, and upper class. Migration to former colonies like Canada played a significant role in shaping the demographics and cultural richness of these countries. The decision to immi
0 views • 13 slides
The Evolution of Postcolonial Literature in English
The exploration delves into the evolution of postcolonial literature in English, contrasting the experiences of settler colonies and invaded colonies in adopting and adapting the English language. It discusses the impact of historical impositions and themes of identity, exile, and displacement acros
0 views • 15 slides
Immigration and Slavery in the American Colonies (1607-1765)
The American colonies experienced significant immigration, with English, Irish, and German settlers seeking a new beginning. Many English immigrants were indentured servants, while Irish and German immigrants faced push factors like war and religious persecution. Additionally, the slave trade played
0 views • 42 slides
American Literature Through the Ages
Explore the rich tapestry of American literature covering American Indian culture, New England Puritanism, the 18th century American Enlightenment, and the American Renaissance. Discover the oral traditions of American Indian tribes, the puritanical values of New England, the democratic origins of A
0 views • 17 slides
From Protest to Revolution: The Spark of American Independence
The chapter details the brewing tensions between the American colonists and British authorities leading up to the American Revolution. It covers the Tea Act, the Boston Tea Party, the Intolerable Acts imposed by Parliament, the support from other colonies, and the events at Lexington and Concord tha
0 views • 7 slides
The Story of New England Colonies: Pilgrims, Puritans, and Plymouth Colony
Explore the history of the New England colonies including Plymouth, Massachusetts Bay, Rhode Island, Connecticut, and New Hampshire. Discover the impact of geography on their development, the differences between Pilgrims and Puritans, and the founding of Plymouth Colony by the Pilgrims led by Willia
0 views • 24 slides
Colonial America in Review
Explore key aspects of Colonial America through a test review covering the founding of colonies, influential figures like William Penn, significant locations such as New Orleans, and concepts like pacifism and debtors' colonies.
0 views • 35 slides
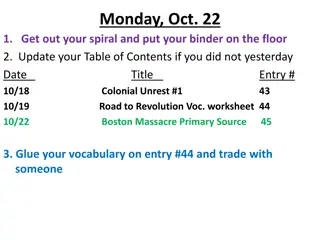
Life in the Colonies: A Detailed Exploration
Explore what life was truly like in the colonies through a series of tasks involving homework, updating tables of contents, analyzing newspaper articles, and reflecting on various aspects such as farming, city life, rights of colonists, African American experiences, religion, education, colonial fam
0 views • 4 slides
Settling the Northern Colonies: Religious Transformation and Colonization
The Protestant Reformation led to the emergence of Puritanism in the Northern Colonies, with figures like Martin Luther and John Calvin shaping religious beliefs. The Massachusetts Bay Colony stood as a beacon of self-government and religious ideals, while dissenters like Anne Hutchinson and Roger W
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding the Impact of the French and Indian War on American History
The French and Indian War, lasting from 1754-1763, had significant consequences on the American colonies. It intensified the rivalry between Britain and France, led to Britain acquiring French territory, and resulted in major debt for Britain. The war's aftermath saw the end of salutary neglect and
0 views • 7 slides
Explore the 13 Colonies: History, Charts, and Maps
Dive into the fascinating world of the 13 Colonies, understanding their origins, characteristics, and significance. Discover the New England, Middle, and Southern Colonies through detailed charts, maps, and insightful information about their establishment, economies, and societal structures. Uncover
0 views • 23 slides
Exploring the 13 Original Colonies of Early America
Uncover the historical significance of the 13 original English colonies in early America. Dive into when they were founded, who established them, and the motives behind their creation. Engage in map activities to understand the colonization process and recognize the lasting impacts of European settl
0 views • 23 slides