Wireless Communication Evaluation Results and Channel Characteristics Analysis
This content discusses TDCP evaluation results in Ericsson RAN1, comparing precoding based on reciprocity versus CSI feedback. It also explores autocorrelation versus Doppler shift, Doppler spread estimation based on channel peaks, and proposed descriptions for AltA and AltB methods. The analysis delves into the intricacies of understanding channel variability, Doppler shift calculations, and correlation profiles for optimal wireless communication system design.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
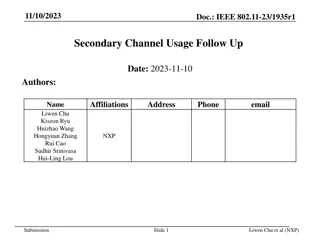
TDCP evaluation results Ericsson RAN1 #110
Use case 1 (left figure): Precoding based on reciprocity vs. CSI feedback Use case 2 (right figure): Precoding based on Type I vs. Type II CSI Switching point for both use cases are round 10 km/h
Autocorrelation vs. Doppler shift Maximum doppler shift would be the same for channels with vastly different channel variabilities, and it does not reflect how fast channel varies with time.
Autocorrelation vs. Doppler spread based on channel peaks To estimate the maximum Doppler shift based on channel peaks is very complex. This relies on the following steps 1. Identify channel peaks in the channel impulse response a. As best as possible given limited time resolution that merge multiple peaks into one b. As best as possible despite very limited or no resolution in angle of arrival which merges multiple peaks into one c. Avoiding side peaks and noise peaks 2. Match channel peaks identified at different time instances 3. Estimate the Doppler shift of each identified and matched peak 4. Calculate the maximum Doppler shift ???? as the largest Doppler shift estimated for any peak minus the smallest doppler shift estimated for any peak, divided by two.
Proposed description for AltA. and AltB. AltA. Based on Doppler profile o E.g., Doppler spread derived from the 2nd moment of Doppler power spectrum AltB. Based on time-domain correlation profile o E.g. correlation within one TRS resource, correlation across multiple TRS resources o note: the correlation over one or more lags of TRS resource may be condiered. The lags may be within one TRS burst or different TRS bursts