Bidding Procedures and Contract Types in Engineering Works
Understanding the standard bidding documents, types of tenders, and bid qualification procedures in engineering works and service contracts is crucial for effective project procurement. The significance of standard bidding procedures, scope and value of contracts, types of tenders, and bid qualification procedures are explained in detail in this chapter.
Uploaded on Jul 31, 2024 | 1 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CHAPTER TWO BIDDING PROCEDURES AND CONTRACT TYPES Learning Objectives: At the end of this Chapter , students should be able to: Explain the bidding procedures for engineering works and service contract Mention the different types of tendering List the different types of service and works contract. Understand the major components of contract document 1
STANDARD BIDDING DOCUMENT The significance of having standard bidding procedure, specially for public funded projects is: To simplify the drafting of a specific bidding document for Procurement of Works by procurement staff; To minimise the time required by the Tender Committee to approve Bidding Documents prior to release; To reduce Bidders time and effort in the preparation of Bids; To facilitate and simplify the evaluation and comparison of bids and Contract award by the Procuring Entity To ensure this, for instance, the Ethiopian government established an agency (PPA) that supervises procuring entities and sets procedures of public procurement [proclamation no. 430/2005] 2
SCOPEAND VALUEOF CONTRACT This SBD is suitable for a standard contract, where the works have been fully designed by or for the Procuring Entity (Employer), prior to bidding, and the Contractor will be responsible for construction only. It is suitable for works valued at up to US$10 million. This SBD for the Procurement of Works is not suitable for the following situations: Complex works under US$10 million, such as large water treatment plants; Works over US$10 million; Works designed by the Contractor, including turnkey contracts. 3
TYPESOFTENDER Things Bidders Geographical Procurement Procurement Bases Procured Coverage Coverage Awareness Steps Types Goods Competitive International General PN Single Services Negotiated Regional Specific PN Two Staged Works National Pre Qualification Local Post - Qualification 4
Bid Qualification Procedure Competitive Bid Negotiative Bid Financial Proposal Short-Listed Bid Open Bid Financial Pr. One-Stage Procedure Two-Stage Procedure Financial Proposal Pre-Qualification Post Qualification 5 Technical Proposal Financial Proposal Financial Proposal Technical Proposal
TYPESOF TENDER Based of things to be procured tenders can be classified as: Consultancy/ Service o Services means the consultancy services to be performed by the Supplier as described in the contract. E.g. Design, Supervision, Contract administration Works o The Works are what the Contract requires the Contractor to construct, install, and turn over to the Employer, as defined in the Special Conditions of Contract. Goods o Goods means all of the commodities, raw materials, machinery and equipment, and/or other materials that the Supplier is required to supply to the Procuring Entity under the Contract. 6
BIDDINGPROCEDUREFOR SERVICE CONTRACT Selection of Bidders; Preparation and Issue of RFP Documents; Bidding Period and Receipt of proposal; Proposal Opening; Proposal Evaluation; and Bid Acceptance, Contract Award and Signing. 7
SELECTIONOF BIDDER Under the Request for Proposals method, the Procuring Entity will normally publish a notice seeking expressions of interest, so that all potential bidders have the opportunity to participate. The notice must be published in a newspaper of wide international circulation or in a relevant trade publication or technical or professional journal of wide international circulation. The Procuring Entity will then evaluate the expressions of interest received and develop a shortlist of between three and seven bidders. The RFP document should be accompanied by a letter of invitation 8
PREPARATIONAND ISSUINGOF RFP DOCUMENTS The Procuring Entity is responsible for the preparation and issue of the RFP The Procuring Entity must use the standard RFP or other appropriate standard document issued by the Public Procurement Agency, as this is a mandatory requirement for contracts to be funded by the Government of the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia. In deciding the deadline for proposal submission the PE should allow Bidders sufficient time for obtaining and studying the RFP, preparing complete and responsive proposals and submitting the proposals. 9
BIDDING PERIODAND RECEIPTOF PROPOSALS The Bidder is responsible for proposal preparation and the submission of its proposal. During the bidding period, the Procuring Entity shall: Hold any pre bid meeting, if one is required, and issue minutes promptly; Promptly respond to requests for clarifications from Bidders; Issue amendments to the RFP if necessary; Receive and record sealed proposals from Bidders or make a Bid Box available up to the deadline for proposal submission; Close bidding at the precise date and time of the deadline and ensure that no late proposals are received; Keep all proposals received secure until the time for proposal opening. 10
PROPOSAL OPENING The Tender Committee is responsible for the Proposal Opening, which is a critical event in the procurement process. Conduct the Proposal Opening strictly following the procedures specified in the ITB Sub-Clause 20 for all proposals received on or prior to the date and time of the proposal submission deadline. Ensure that all proposals that were received on time are accounted for, before starting the Proposal Opening, as proposals that are not opened and read out at Proposal Opening shall not be further considered. Ensure that only technical proposals are opened and that financial proposals are kept sealed and removed to a secure place after the opening. 11
CONTINUED Agree before the Proposal Opening on the details to be read out Not reject any proposal at Proposal Opening, except for late proposals received after the date and time of proposal submission deadline. Examine the proposals at Proposal Opening in accordance with the provisions of ITB Sub-Clause 17 12
PROPOSAL EVALUATION For Consultancy services, proposal evaluation will be conducted in two stages and Tender Committee approval of the technical evaluation report must be obtained before opening financial proposals and conducting the financial evaluation. The Tender Committee shall: Maintain the evaluation process strictly confidential Reject any attempts or pressures to distort the outcome of the evaluation, including fraud and corruption 13
CONTINUED Strictly apply only and all of the evaluation criteria specified in the RFP to determine the proposals which proceed to the financial evaluation and subsequently to make a recommendation for award of contract to the Tender Committee. For consultancy services, negotiations are often held with the recommended Bidder, to finalise all technical details, prior to placing the contract. 14
BID ACCEPTANCEAND CONTRACT AWARD The following procedure is required for bid acceptance and award of the contract The head of the Procuring Entity makes a contract award decision. The Procuring Entity notifies all Bidders of the results of the evaluation. After a period of five working days, if no complaint has been received by the Procuring Entity, the PE awards the contract by either issuing a Letter of Acceptance to the successful bidder or signing a contract (which is often done following the successful conclusion of any negotiations). Where a Letter of Acceptance is issued, the contract will be confirmed by issue of a full conformed Contract Document. 15
SUMMARYOF BP FOR SERVICE CONTRACT Preparation of Terms of Reference (TOR) Preparation of Cost Estimate Advertize for expression of interest Prepare short list Prepare and issue Request for Proposal (RFP) Evaluate Technical proposal Notify Unsuccessful Bidder Notify bidders (passing technical Requirements) about the date of financial opening Open financial opening in public Evaluate financial proposal Negotiate price and sign contract 16
CONTINUED The TOR normally consist of Background of the project; Objectives of the Assignment; Scope of work; Transfer of knowledge; List of reports, schedule of deliveries, period of performance; Data, local services, personnel, and facilities to be provided by the borrower; and Institutional arrangements. 17
TYPESOF SERVICE CONTRACTSBASEDON METHODOFEVALUATIONOFPROPOSAL 1. Competitive Selection Process Quality v Cost based (QCBS): Financial proposal and Technical proposal is evaluated(Sf = 100 x Fm/F Two envelope system used (S = (St x T%) + (Sf x P%) Financial proposal opened in public, Example 100,000.00 Birr project. 2. Competition on quality (QBS) Technical Evaluation Only Negotiations on Price 3. Selection under fixed budget (SFB) Technical and financial proposals in two separate envelopes Financial proposals to be within specified fixed budget Technical evaluation (quality) first Public opening of financial proposals Rejection of proposals exceeding fixed budget Highest rated technical proposal (within fixed budget) selected Least Cost Selection (LCS) Financial Proposal will be ranked The lowest priced proposal will be recommended for contract award, subject to satisfactory negotiations. 4. 18
TYPESOF SERVICE CONTRACTSBASEDONMODE OFPAYMENT lump-sum planning and feasibility studies, environmental studies, Design etc. Contents, duration, and output clearly defined. payments linked to outputs only. II. Time-based Quality Control, supervision, Contract administration, technical assistance. payments linked to inputs, agreed staff rates and reimbursable items. Example: AAHDPO III. Percentage contracts The consultant will paid based on a percentage of the works being executed (Cost plus %) or % of the project cost V. Indefinite delivery contracts specialized services on call I. 19
BIDDINGPROCEDUREFORWORKS The relevant parts of the bidding process are summarised here as follows: Selection of Bidders; Preparation and Issue of Bidding Documents; Bidding Period and Bid Receipt; Bid Opening; Bid Evaluation; and Bid Acceptance, Contract Award and Signing. 20
SELECTIONOF BIDDERS Open tendering without pre-Qualification The PE must publish an Invitation to Bid notice, so that bidding is open to all interested bidders The notice must be published in at least one national newspaper of general circulation Where tendering is international, the notice must also be published, in a newspaper using the same language as the notice and of sufficient circulation to attract foreign competition Notices should also be published on the internet, wherever possible. PEs should also ensure that bidding documents are finalised and approved before publishing the Invitation to Bid notice, to avoid any delays in the process. a. 21
.CONTINUED b. Restricted Tendering the bidders invited will be those included on the shortlist, who should be selected from among contractors registered in the contractors list. There is no need to publish an Invitation to Bid notice, but the bidding document should be accompanied by an invitation to bid letter the Procuring Entity may advertise the opportunity, to invite companies to express interest in being invited to bid. 22
PREPARATIONAND ISSUEOF BIDDING DOCUMENTS The Procuring Entity is responsible for the preparation and issue of the Bidding Document and must use the appropriate SBD, as this is a mandatory requirement for contracts to be funded by the Government. A record must be kept of the Bidders to whom Bidding Documents have been issued. Receipts must be issued for all fees paid 23
BIDDING PERIODAND BID RECEIPT During the bidding period, the Procuring Entity shall: Hold any pre bid meeting or site visit and issue minutes promptly; Promptly respond to requests for clarifications from Bidders; Issue amendments to the Bidding Documents if necessary; Receive and record sealed bids from Bidders or make a Bid Box available up to the deadline for bid submission; Close bidding at the precise date and time of the deadline and ensure that no late bids are received; and Keep all bids received secure until the time for bid opening. 24
BID OPENING Best Bid-Opening Practices to Observe Conduct the Bid Opening strictly following the procedures specified in the ITB Sub-Clause 23 for all bids received on or prior to the date and time of the bid submission deadline. Ensure that all bids that were received on time are accounted for, before starting the Bid Opening, Examine the bids at Bid Opening in accordance with the provisions of ITB Sub-Clause 19. 25
BID EVALUATION The Tender Committee shall: Maintain the bid evaluation process strictly confidential Reject any attempts or pressures to distort the outcome of the evaluation, including fraud and corruption Strictly apply only and all of the evaluation and qualification criteria specified in the Bidding Documents to determine the lowest evaluated bid and to make a recommendation for award of contract to the Tender Committee. 26
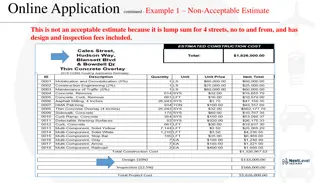
TYPESOF WORKS CONTRACT Type of contracts: 1. lump sum contract Such a contract might be used for the supply of a particular unit of process plant or material, or for a package deal in which the Contractor is responsible for both o Detailed design and o Construction. 2. Cost - reimbursable contract Cost- reimbursable contracts are used when the requirements of the promoter are vague or when it is desirable for design to proceed concurrently with construction. Such contracts are also used when the promoter wishes to be directly involved in the management of the contract or to reduce the financial risk to the contractor 27
TYPESOF WORKS CONTRACT 3. Cost - plus contract A cost-plus contract is the extreme form of the cost reimbursable type and is so called because The contractor is reimbursed for all costs incurred during the fulfillment of the contract, Plus an agreed fee to cover overheads and profit. The fee may be defined as a percentage of the agreed actual cost or as a fixed amount 4. Admeasurements Contracts The most common types of construction contract which facilitate competitive tendering but Which incorporate some mechanism for the introduction and evaluation of changes in the work content of the contract. 28
TYPESOF WORKS CONTRACT Bill of quantities :Bidders are required to enter unit prices against the estimated quantities of many items of completed work Activity Schedule : This types of contract is similar to the bill of quantities, but the estimated quantities of work items which are expected to be less accurate than those given in the bill of quantities. a) b) 5. Target Contracts: A promoter may introduce additional incentives into a contract by offering the contractor a bonus payment for the achievement of some previously defined target in terms of Time, Cost, or Performance 29
PROVISIONSOF CONTRACT/CONTRACT DOCUMENT For works contract include: Invitation to Bid; Construction Agreement and its Appendices; Letter of Acceptance; Signed form of Bid of the Contractor, Appendices and Annexes ; Particular Conditions of Contract General Condition of Contract; Priced Bill of Quantities; Drawings; Technical Specifications and Methods of Measurement; The Standard Instructions and Information to Bidders for Building Construction Works and the Particular Project Information and Instruction thereto; l. Any other documents required to form part of the Contract. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. 30
COMMENCEMENTOFSITE SUPERVISION As per sub clause 41.1 of the GCC of FIDIC 1987 edition, the Contractor shall commence the Works as soon as is reasonably possible after the receipt by him of a notice to this effect from the Engineer, which notice shall be issued within the time stated in the Appendix to tender after the date of the Letter of Acceptance Hence, the supervision service of the Engineer will commence in parallel 31