Understanding Nucleic Acids and RNA Molecules
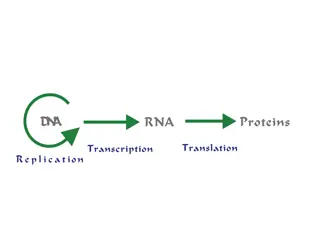
Nucleic acids are linear polymers composed of nucleotides, with DNA and RNA being the main types. RNA consists of messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), each playing a crucial role in protein synthesis. mRNA carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes, tRNA transfers amino acids during protein synthesis, and rRNA forms the structure of ribosomes. Understanding these components is essential in grasping the mechanisms of genetic expression.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
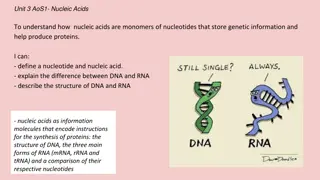
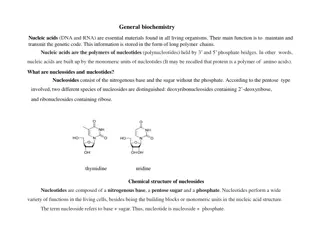
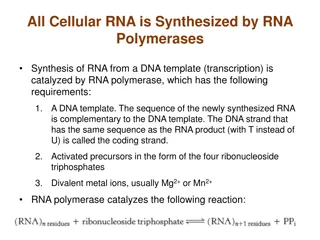
What are nucleic acid ? Linear polymers of nucleaotides.first isolated by Miescher (1871) Each nucleotide consist of 3 components 1. purine or pyrimidine nucleobase 2. Pentose sugar 3. Phosphate group Nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic Acid(DNA) and ribonucleic acid(RNA)
Types of RNA In all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms ,three main classes of RNA molecules exist: Messenger RNA (m RNA) Transfer RNA (t RNA) Ribosomal RNA (r RNA)
mRNA mRNA is translated from DNA in the nucleus and posted out to the ribosomes for translation. Codonsare complementary to DNA triplets specifies one amino acid. mRNA is single stranded. Accounts for only 5% of total RNA. 5 end is capped with guanosine triphosphate nucleotide While 3 end has ply-A tail.
rRNA rRNA are found in the ribosomes and account for 8O% of total Rna in cell. Ribosome consist of large subunit called the 50S and small subunit called 30S. Ribosomesare the site for protein synthesis. It is also single stranded but may be variously folded and show complementary base pairing at fold.
tRNA tRNA is the smallest of the 3 types of RNA It is an essential component of translation : transfer of amino acids during protein synthesis. Each of 20 amino acids have specific tRNA. tRNA have a clover leaf like structure which is stabilized by strong H- bond between nucleotides. Hair pin model : Hoagland Clover leaf model: Holle