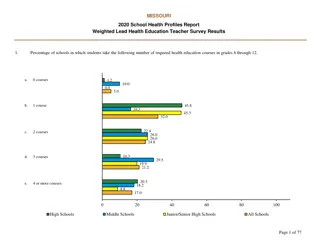
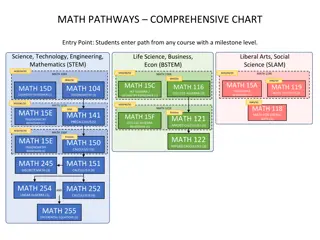
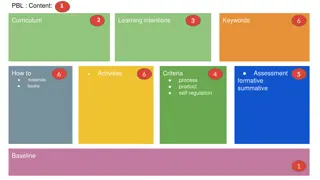
Creating High-Impact Learning Experiences: Designing Courses for Lasting Knowledge
Dive into the world of course design basics with a focus on significant learning domains, aspirational goals, and effective learning goals inventory. Explore the integration of foundational knowledge, application, and human dimensions to enhance the learning experience. Learn how to develop skills, critical thinking abilities, and self-directed learning approaches that foster long-term impact and meaningful connections in education.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
COURSE DESIGN BASICS OR BETTER, SEXY TITLE Designed by GA-CTL Workgroup: Mary Carney, Darryl Hancock, Laura Lynch, Deborah South Richardson, Washella T. Simmons
THE BIG PICTURE: ASPIRATIONAL GOALS Think-Pair-Share What would I like the impact of the FLC to be on participants 2 years down the road? What would distinguish people who have participated in this FLC from people who have not?
SIGNIFICANT LEARNING Significant Learning Domain Goal Foundational Knowledge Application of Learning Integration Understanding and remembering key concepts, terms Applying knowledge to real situations so that foundational knowledge becomes useful Making connections between ideas, learning experiences, and realms of life context learning more powerful Enhance significance of learning by recognizing social and personal implications of the learning for self and others Develop interests, feelings, values that help learners care about learning energy to learn more and make part of own life Learn about process of learning, including how to become self-directed and maximally effective learner Human Dimension Caring Value Learning How to Learn L. Dee Fink. 2013. Creating Significant Learning Experiences: An Integrated Approach to Designing College Courses.
EXAMPLE: LEARNING GOALS INVENTORY: FOUNDATIONAL KNOWLEDGE DOMAIN Answer each question on a Likert Scale: High Moderately High Moderately Low Low Not Applicable As a result of participation in the course, students should develop: 1. Knowledge of central facts in the subject area 6. Recognition of difference between fact and opinion related to this subject area From Learning Assessment Techniques by Barkley & Major
EXAMPLE: LEARNING GOALS INVENTORY: APPLICATION DOMAIN Answer each question on a Likert Scale: High Moderately High Moderately Low Low Not Applicable As a result of participation in the course, students should develop: 11. Writing skills 15. Critical thinking skills From Learning Assessment Techniques by Barkley & Major
EXAMPLE: LEARNING GOALS INVENTORY: INTEGRATION DOMAIN Answer each question on a Likert Scale: High Moderately High Moderately Low Low Not Applicable As a result of participation in the course, students should develop: 24. The ability to connect a concept to other concepts within this course. 27. The ability to connect course concepts to concepts in other disciplines or fields. From Learning Assessment Techniques by Barkley & Major
EXAMPLE: LEARNING GOALS INVENTORY: HUMAN DOMAIN Answer each question on a Likert Scale: High Moderately High Moderately Low Low Not Applicable As a result of participation in the course, students should develop: 31. The ability to work productively with others. 36. A commitment to their own emotional health and well- being. From Learning Assessment Techniques by Barkley & Major
EXAMPLE: LEARNING GOALS INVENTORY: CARING (VALUE) DOMAIN Answer each question on a Likert Scale: High Moderately High Moderately Low Low Not Applicable As a result of participation in the course, students should develop: 38. Openness to new ideas in the subject area. 41. A commitment to success in learning. From Learning Assessment Techniques by Barkley & Major
EXAMPLE: LEARNING GOALS INVENTORY: LEARNING HOW TO LEARN DOMAIN Answer each question on a Likert Scale: High Moderately High Moderately Low Low Not Applicable As a result of participation in the course, students should develop: 49. Study skills and strategies. 52. The ability to self-assess their performance. From Learning Assessment Techniques by Barkley & Major
INTEGRATED COURSE DESIGN Learning Outcomes Fink, L. (2003). Creating significant learning experiences : An integrated approach to designing college courses.
+ Significant Learning Feedback Assessment Teaching and Learning Activities Learning Outcomes
CREATING SIGNIFICANT LEARNING EXPERIENCES
DESIGN PHASES INITIAL PHASE Build Strong Primary Components INTERMEDIATE PHASE Assemble the Components into a Coherent Whole FINAL PHASE Finish Important Remaining Tasks
INITIAL DESIGN PHASE BUILD STRONG PRIMARY COMPONENTS 1. Identify important situational factors 2. Identify important learning goals and outcomes 3. Formulate appropriate feedback and assessment procedures 4. Select effective teaching/learning activities
that impact the design of the learning experience SITUATIONAL FACTORS
SITUATIONAL FACTORS THAT MAY IMPACT YOUR FLC Factor Context Examples Number of participants, frequency of meetings, medium (f2f, distance, hybrid) Expectations of external groups Your Provost, University System Characteristics of participant colleagues Schedule, available time, motivation, prior experience Characteristics of facilitator -- YOU Experience, confidence, interest, motivation
INTEGRATED COURSE DESIGN Learning Outcomes
TRANSLATING GOALS TO OUTCOMES What, specifically, should learners be able to do as a result of participating in the FLC? What will learners be able to do if the goal is achieved?
Integrated Course Design Learning Outcomes
EDUCATIVE ASSESSMENT: FIDELITY FEEDBACK Feedback should be Frequent Immediate Discriminating (based on criteria and standards) Done lovingly (supportively) performance revision feedback
TEACHING AND LEARNING Focus on pedagogy ACTIVITIES
Integrated Course Design Learning Outcomes
EBOOK FROM MANY USG LIBRARIES The LATs are activities that might be incorporated into a course design. Useful for developing learning outcomes and assessments Extends Fink s materials with concrete help
LEARNING ASSESSMENT TECHNIQUES Significant Learning Domain Foundational Knowledge Entry and Exit Tickets; Team Tests Application Learning Prediction Guide; Triple Jump (through real world examples) Integration Concept Maps; Case Study Human Dimension Free Discussion; Ethical Dilemma Caring Value Three-Minute Message; Issue Awareness Ad Learning How to Learn Student Generated Rubrics; What? So What? Now What? Journal Examples of LATs From Learning Assessment Techniques by Barkley & Major, which details 7 10 activities for each significant learning domain.
OTHER TOPICS BEYOND FOUNDATION Structuring a course strategy for increasing complexity and challenge (i.e., scaffolding the learning experience). Developing a grading system Preparing a learner-centered syllabus Planning an evaluationof the course and of the instructor s teaching
WHAT YOU COULD DO WITH AN FLC FOCUSED ON COURSE DESIGN Work with group to design courses Take all the pieces of this day and incorporate into an FLC on course design Just about anything you want to and you could design your own courses and your FLC -- according to these principles.