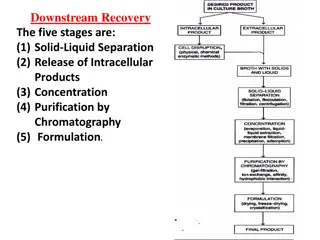
Comparison of CDOM Absorption Coefficients Using Different Filters and Instruments
This study conducted on July 13, 2011, analyzed the absorption coefficients of CDOM using various filters and instruments in different sample sources like open ocean, dockside, and Biscay pond dilution series. The comparison included measurements with ac-9 and ac-s filters of varying sizes, along with slope comparisons, standard error analysis, and concentration-related functions. The results highlight the importance of filter selection and measurement accuracy in determining CDOM absorption coefficients.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ac-9/ac-s absorption (a tube) and beam attenuation (c tube) Measuring CDOM absorption coefficients July 13, 2011
Things we are comparing: sample sources, instruments, filters Open ocean Dockside Biscay pond, and Biscay pond dilution series ac-9 (0.2 m Sartoris plastic filter) ac-9 (0.7 m Whatman GF/F) ac-s (0.7 m Whatman GF/F)
Table of slope comparisons (absorption, using Excel) Open ocean Dockside Biscay Pond ac-9 (0.2 m filter) 0.0113 0.008 0.011 ac-9 (0.7 m filter) 0.0155 0.009 0.0101 ac-s (0.7 m filter) NaN 0.0124 0.0138 aCDOM ( ) = aCDOM ( REF) e SCDOM( - REF)
Standard error Biscay Pond ac-9 0.2 filter 412 nm 532 nm 676 nm 4.02 +/- 0.019 0.801 +/- 0.0043 0.195 +/- 0.003 Propagated error was low
Is (a) a function of concentration? 4 412 3.5 440 488 y = -0.3607x + 3.0371 R = 0.8401 3 510 532 2.5 555 650 absorption y = -0.2205x + 1.8891 R = 0.8447 676 2 715 Linear (412) 1.5 Linear (440) y = -0.115x + 1.0114 R = 0.8693 Linear (488) 1 Linear (510) Linear (532) 0.5 Linear (555) Linear (650) 0 Linear (715) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Dilution ac-s ac-s ac-9 #1 ac-9 #2