Exploring the Wonders of Oceania's Islands
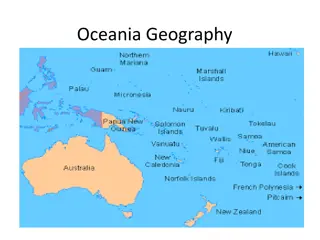
Delve into the captivating world of Oceania's diverse islands, from continental to volcanic formations. Understand the unique characteristics of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia, home to over 20,000 islands. Explore the differences between continental islands, like New Guinea and New Caledonia, and volcanic islands, such as Guam and CNMI. Discover the formation of low islands and the intricate ecosystem of coral reefs. Prepare to embark on a fascinating journey through the Islands of Oceania.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Group Presentation Rules No less than15 Slides Titles No less than 40 font size Information, No less than 30pt font size
Presentation notes Make Your Titles Headlines, Not Descriptions Let the Titles Tell the Story Layout Counts, Be consistent Never include 2 -3 slides of photos
Presentation notes Pace your presentation, too fast is not good for the audience No more than 2 or 3 points per slide Visual Media is recommended Stick to primary, bright, clear color combinations
OBJECTIVES Distinguish the different areas of Oceania Compare a continental island and a volcanic island Identify how coral survive and form Report how volcanoes form islands
Oceania Groups of islands Micronesia Melanesia Polynesia Home to over 20,000 islands Island is formed by plate movement or volcanic activity Sometimes Australia, New Zealand (is included in this textbook), and the Malay Peninsula are included
Continental Islands Largest type of island Have wide variety of plants or animals and can support more people than volcanic islands Examples of Continental Islands New Guinea New Caledonia
Volcanic Islands Built by volcanoes rising from the sea floor to above the surface Examples of a volcanic island Guam CNMI Volcanoes in the CNMI are still active Why volcanos sink Rising sea level Cooling of the volcano
Low islands Some volcanic islands that have been worn down nearly to sea level Many islands in the Northwest Hawaiian islands are some examples
Coral Reefs Life forms like mollusks, algae, and other life forms create coral reefs Two kinds of coral reproduction Asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction Algae and coral live in symbiosis Algae extract calcium from the water Coral gives the algae animal waste which is plant fertilizer
Coral Reefs Animals that use the reef as a home Sharks lobsters anemones Octopus clams Moray eels starfish Crabs slugs
Coral polyp 4 parts: skin, several stinging tentacles, an all-purpose cavity and the skeletal cup Secrete lime to make hard bony cups outside their bodies Eat plankton (tiny floating plants and animals) Sexual reproduction depends on species, some are hermaphrodites (producing both sperm and egg) When they die their body dissolve but skeleton remain. New coral builds on top of skeletons of the dead coral
Atoll Lagoon is usually sand from broken coral parts No rivers Flat island rarely more than 15 feet above sea level Similar to reef islands No variety of landforms Size and shape and number of islands can vary
Reef Islands Vulnerable to typhoons and heavy seas Can form on any type of reef fringing, barrier, patch, or atoll. Reef islands collect sand and other debris Sand is made from pieces of coral broken down by the waves Limestone is the compacted dead coral of the reef itself Rain is soaked up by the land, through the limestone and end up above the saltwater
Reef Islands Because the fresh water stays above the sea level, a convex lens and can be dug up to provide wells of fresh water. 4 ways plants can get on an island seeds that float for hundreds of miles birds that eat seeds, don t digest and leave it on the land in their droppings seeds blown by the wind people bring plants
Formation of volcanic islands https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RMtuTfAqAbo New island emerges https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9md0q29ED5w