Comprehensive Overview of Female Genital Organs and Ovarian Function
Explore in-depth insights into the anatomy and functions of female genital organs, focusing on the ovaries, uterus, uterine tubes, and associated structures. Delve into the maturation of follicles, ovulation process, and hormonal regulation. Gain a clear understanding of the intricate mechanisms involved in ovum production and the menstrual cycle.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
GENITAL ORGANS Semmelweis University, Faculty of Pharmacy 1st year 2nd semester Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology 2020.04.01.
Female genital organs Female genital organs - - overview overview Uterine tube Uterus Ovary Vagina Clitoris Vestibule of vagina Labium major Labium minor
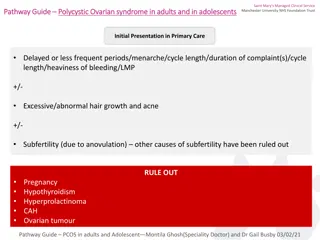
Ovary Ovary Function: production of ovum secretion of female sex hormones: estrogen and progesterone (menstrual cycle)
Follicle maturation Follicle maturation Primary oocytes remain in the first meiotic division until puberty. End of the first meiotic division: ovulation End of the second meiotic division: fertilization Follicular epithelial cells: Granulosa cells Theca cells Follicle maturation is influenced by FSH (follicule- stimulating hormone) from the hypophisis (pituitary gland). After ovulation (14th days of the menstruatic cycle) under the influence of LH (luteinizing hormone) the follicular epithelium transform into a corpus luteum and begins to secrete progesteron.
tertier follicle stroma germinal epithelium corpus luteum primer follicle secunder follicle primer oocyta theca folliculi athretetic follicles zona pellucida
Uterine tube Uterine tube Isthmus Isthmus Ampulla Ampulla Infundibulum Infundibulum Mesosalpinx Mesosalpinx Function: transport of ovum from ovary to uterus kinocilia peristaltic muscular activity
Uterus Uterus Fundus Uterine tube Body Ovary Isthmus Supravaginal part of cervix Vaginal part of cervix Vagina
anteflexion cervix-body angle anteflexion ( 60o) Position of the uterus Position of the uterus anteversion cervix-vagina angle anteversion ( 60o) Anteflexion of uterus Anteflexion of uterus Anteversion of uterus Anteversion of uterus Retroflexion retroversion of uterus Retroflexion - - retroversion of uterus
Position of the uterus Position of the uterus rectum ovary utherus vagina bladder vesicouterine pouch vesicouterine pouch rectouterine pouch (Douglas) rectouterine pouch (Douglas)
Ligaments of the uterus Ligaments of the uterus Ligaments: broad ligament mesometrium mesosalpinx mesovarium Ligaments: broad ligament of uterus mesometrium mesosalpinx mesovarium of uterus Suspensory ligament (a. and v. ovarica) round ligament of uterus (ligament of ovary) round ligament (ligament of ovary) of uterus Broad ligament parametrium: lateral cervical ligament parametrium: lateral cervical ligament uterosacral ligament pubovesical ligament uterosacral ligament pubovesical ligament mesosalpinx mesovarium mesometrium Ovarian ligament
Ligaments of the uterus (see below) Ligaments of the uterus (see below) sacrum sacrocervical ligament sacrocervical ligament rectum rectouterine pouch rectouterine pouch parametrium (cardinal ligament) parametrium (cardinal ligament) cervix pubovesical ligament + vesicouterine ligament = pubocervical ligament pubovesical ligament + vesicouterine ligament = pubocervical ligament bladder symphysis
Ligaments of uterus (see lateral) Ligaments of uterus (see lateral) Uterus Uterus Sacrocervical ligament Sacrocervical ligament Urinary bladder Urinary bladder Rectum Rectum Pubocervical ligament Pubocervical ligament Transverse cervical ligament Transverse cervical ligament
Bimanual examination of the uterus Bimanual examination of the uterus Colposcopic photographs (portio vaginalis cervicis) vaginal examination Uterine cavity Spatula Speculum Uterine portion rectal examination
Hystology and structure of the uterus Hystology and structure of the uterus ENDOMETRIUM ENDOMETRIUM MYOMETRIUM MYOMETRIUM stratum submucosum stratum vasculare stratum supravasculare PERIMETRIUM PERIMETRIUM
The menstrual cycle changes of the endometrium The menstrual cycle changes of the endometrium regeneration regeneration proliferative phase proliferative phase secretory phase secretory phase menstruation menstruation epithel stroma tubular glands
Position of the uterus during pregnancy Position of the uterus during pregnancy Placenta Mucous plug in the cervical canal Situs of abdominal internal organs shortly before the end of pregnancy
Blood supply of the internal genital organs Blood supply of the internal genital organs Pampiniform plexus of veins Pampiniform plexus of veins Uterine tube Ovarian artery and vein Ligament of ovary Ovarian artery and vein Uterus Isthmus Ampulla Ovarian and tubal branches Infundibulum Fimbriae Ovary Ureter Uterine plexus Uterine plexus Internal iliac artery Internal iliac artery Uterine artery Vaginal artery and Vaginal artery and vein vein Vaginal plexus Vaginal plexus Internal pudendal artery Internal pudendal artery Vagina
External genital organs External genital organs Mons pubis Mons pubis Prepuce of clitoris Prepuce of clitoris Labium majus Labium majus Clitoris (glans) Clitoris (glans) External urethral orifice External urethral orifice Labium minus Labium minus Orifice of vagina Orifice of vagina
External genital organs External genital organs Crus of clitoris Crus of clitoris Body of clitoris Body of clitoris Glans of clitoris Glans of clitoris Bulb of vestibule Bulb of vestibule Greater vestibular gland Greater vestibular gland
Muscles of the pelvis, perineum Muscles of the pelvis, perineum mons pubis DIAPHRAGMA UROGENITALE symphysis pubic bone anus m. gluteus maximus m. levator ani (DIAPHRAGMA PELVIS) coccygeal bone
The breast The breast subclavicular lymphnodes parasternal lymphnodes axillar lymphnodes
MALE GENITAL ORGANS Gonads: (production of germ cells; secretion of sex hormones) testes Genital tract: (transport of germ cells) epididymis ductus deferens Sex glands: seminal vesicle prostate bulbourethral gland External genital organs: penis scrotum
MALE GENITAL ORGANS Seminal vesicle Prostate Bulbourethral gland Penis Ductus deferens Epididymis Scrotum Testis
TESTIS AND EPIDIDYMIS Spermatic cord Head of epididymis Testis: 4-5 cm long plum-shaped Body of epididymis
TESTIS Structure: tunica albuginea connective tissue septa lobules (~200-300): convoluted seminiferous tubules: 30-60 cm long interstitium mediastinum: rete testis Function: production of sperm secretion of male sex hormone: testosterone
TESTIS Convoluted seminiferous tubules: Sertoli cell cells of spermatogenesis: spermatogonium primary spermatocyte secondary spermatocyte spermatid sperm Interstitium: Leydig cell
SPERMATOGENESIS Type A spermatogonium (2N, 2C) Spermatocytogenesis 16 --- Type B spermatogonium (2N, 4C) 32 ------------------------ Primary spermatocyte (2N, 4C) Meiosis 64 ---------------- Secondary spermatocyte (1N, 2C) 128 ----- Spermatid (1N, 1C) Spermiogenesis Sperm (1N, 1C)
SPERMATOGENESIS Meiosis: production of haploid germ cells: 46 23 chromosome Prophase I genetic variability: crossing-over separation of homologous chromosomes Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Prophase II Anaphase IITelophase II Metaphase II
SPERMATOGENESIS Spermiogenesis: spermatid sperm spermatid sperm
EPIDIDYMIS Spermatic cord Head of epididymis Testis Body of epididymis
EPIDIDYMIS Structure: head: ductuli efferentes testis: ~10-20 20 cm long body and tail: ductus epididymis: 4-6 m long Function: maturation of sperm storage of sperm
DUCTUS DEFERENS, SEMINAL VESICLE AND PROSTATE Ductus deferens Seminal vesicle Prostate Urethra Ductus deferens Seminal vesicle Ejaculatory duct Prosta te Urethra
DUCTUS DEFERENS Size and shape: 50-60 cm long 3-3.5 mm in diameter 0.5 mm lumen Structure: mucosa extremely thick muscular wall Function: transport of sperm during ejaculation
SEMINAL VESICLE Size and shape: 5-10 cm long highly folded tubular gland Structure: mucosa thick muscular wall
PROSTATE Size and shape: 4 cm wide, 2 cm a-p, 3 cm vertical chestnut-shaped Structure: stroma: smooth muscle fibroelastic connective tissue glands: mucosal submucosal main Prostatic hypertrophy Prostatic cancer
ACCESSORY SEX GLANDS Prostate Seminal vesicle Cowper s gland (bulbourethral gland) Semen: 2-6 ml 99% is produced by accessory glands alkaline pH >20 million (~100 million) sperm / ml >60% motile sperm
PENIS Erectile bodies: corpus cavernosum crus penis Parts: glans penis prepuce body root corpus spongiosum glans penis bulbus penis
PENIS Crus penis covered by: ischiocavernosus muscle Bulbus penis covered by: bulbospongiosus muscle
SCROTUM Coverings of the testis and spermatic cord: skin of scrotum tunica dartos septum external spermatic fascia cremasteric fascia cremaster muscle internal spermatic fascia tunica vaginalis Function: temperature of testes is maintained at 2-3 C below body temperature
MALE URETHRA Urinary bladder Internal urethral orifice Prostate Urogenital diaphragm Corpus spongiosum External urethral orifice
MALE URETHRA Size and shape: 20-25 cm long internal urethral orifice sphincter vesicae external urethral orifice Parts: prostatic part: urethral crest, seminal colliculus membranous part spongy part sphincter urethrae