Risk-Based Environmental Monitoring for Listeria Surveillance at Retail
Explore the importance of risk-based environmental monitoring and decision-making in detecting Listeria contamination in retail food settings. Learn about routine sampling plans, trends in positive samples, species distribution, and key locations of Listeria findings from 2010 to 2014. Discover why regulatory agencies like MDA focus on Listeria surveillance at retail establishments and the critical steps taken when Listeria contamination is detected.
- Listeria surveillance
- Environmental monitoring
- Retail food safety
- Risk-based decision making
- Foodborne pathogens
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
118th AFDO Annual Educational Conference, Denver, CO Risk-Based Environmental Monitoring and Decision Making June 23, 2014 Listeria Surveillance, Decision Making, and Corrective Actions at Retail Carrie Rigdon, PhD Rapid Response Team Supervisor Dairy & Food Inspection Division
Routine Sampling Plan Why: Identify issues in potentially risky foods & environments What: Food and environmental samples at retail and manufacturing When: New assignments 2 to 4 times a year
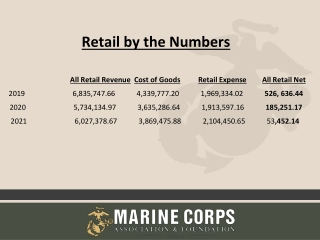
Micro Samples by Year All Sampling 900 820 800 700 600 500 462 457 Samples Positive 400 332 300 200 144 133 100 63 14 14 8 7 3 0 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 3.0% 7.5% 1.5% 10.5% 2.4% 2.0% % Positive:
Positives by Year All Sampling 70 59 60 50 40 Salmonella Listeria 30 26 20 14 10 10 7 4 4 3 1 0 0 0 0 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014
Listeria Positives by Year Environmental Sampling 350 315 300 264 250 231 200 Samples Positives 141 150 133 106 100 41 50 25 14 7 3 0 0 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 0% 13.0% 2.6% 10.5% 10.8% 2.1% % Positive:
Listeria Species Environmental Sampling 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 2010 18 23 2011 0 7 2012 3 11 2013 9 16 2014 1 2 L. mono. Other Listeria
Locations of Listeria 2010-14 Condenser pan 1 Inside service case 4 Door hadle/seal 5 Floor-Wall juncture 5 Mat 6 Table 8 Cart Wheels 12 Floor 14 Drain 35 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Why does MDA look for Listeria at Retail? Monitor operator s control for risks where RTE PHF are prepared, handled, or stored Prevent adulteration and possibility for adulteration
What happens when Listeria is found? Assess whether firm has lost control of their process Bring operator back into compliance adulteration statues Minn. Stat. 34A.02 (Adulteration), Minn. Stat. 31.02 (Prohibited Acts), and Minnesota Administrative Rule Chapter 4626.0015 (Food Safety under Food Code) Corrective Action Plan best guidance for accomplishing this
Firm Actions: Cleaning, CAP, and Verification Intensely clean and sanitize Assess causes and contributing factors Write a Corrective Action Plan (CAP) Cleaning and Sanitizing how? where? Equipment and employee flow Repairs to equipment or structure Employee training Verify that actions have been effective = firm sampling
MDA Actions Provide guidance but not act as their QA Review CAP Confirmatory sampling Visit operator to observe whether control measures were implemented
Questions? Carrie Rigdon carrie.rigdon@state.mn.us 651-201-6453