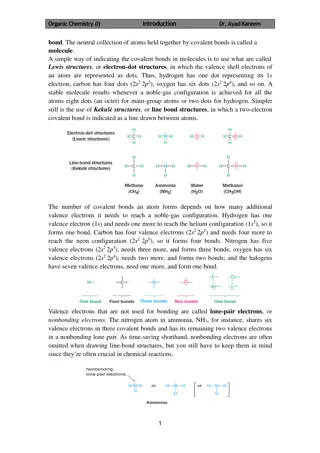
Understanding Molecular Polarity and Electronegativity in Chemistry
Explore the concept of molecular polarity, electronegativity, and bonding in chemistry through engaging visuals and discussions. Learn how the unequal sharing of electrons between atoms leads to polarity in molecules and discover the role of electronegativity in attracting shared electrons. Delve into the different types of bonds based on electron sharing and transfer, and investigate the direction and strength of dipoles between atoms. Get ready to work in pairs for hands-on activities that enhance your understanding of these fundamental chemical principles.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Living By Chemistry SECOND EDITION Unit 2: SMELLS Molecular Structure and Properties
Lesson 43: Polar Bears and Penguins Electronegativity and Polarity
ChemCatalyst Consider this illustration: 1. If the penguin represents a hydrogen atom and the polar bear represents a chlorine atom, what does the ice cream represent in the drawing? What do you think the picture is trying to illustrate 2. Would HCl be attracted to a charged wand? Explain your thinking.
Key Question What makes a molecule polar?
You will be able to: explain what causes polarity and polar molecules describe the different types of bonding that correspond to different combinations of electronegative atoms predict the general direction and strength of a dipole for any two atoms, using the periodic table
Prepare for the Activity Work in pairs.
Discussion Notes The tendency of an atom to attract shared electrons is called electronegativity. Electronegativity: The tendency of an atom to attract the electrons that are involved in bonding.
Discussion Notes (cont.) Dipole: A polar molecule or a polar bond between atoms. A crossed arrow is used to show the direction of a dipole. The crossed end of the arrow indicates the partial positive (+) end of the polar bond, and the arrow points in the direction of the partial negative ( ) end.
Discussion Notes (cont.) Bonds that involve sharing or transferring electrons fall into three categories.
Wrap Up What makes a molecule polar? Polarity in a molecule is caused by unequal sharing of electrons between atoms. Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract shared electrons. Anytime two atoms with different electronegativity values share electrons, there will be a partial negative charge on one atom and a partial positive charge on the other atom.
Wrap Up (cont.) Bonds are classified as nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, and ionic as the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms in the bond increases.
Check-In Consider hydrogen iodide, HI. 1. Is HI a polar molecule? Explain your reasoning. 2. How would the atoms be portrayed in the comic strip as polar bears, penguins, or both? Explain.