Understanding Nucleotide Biosynthesis and Nucleic Acids
Exploring the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines, essential components for DNA and RNA structures. Delve into the world of pyrimidines, purines, nucleosides, nucleotides, and adenosine derivatives like AMP, ADP, ATP, and cAMP, crucial for various biological processes. Unravel the significance of these molecules in the context of nucleic acids.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Nucleotide Biosynthesis Nucleotide Biosynthesis (Biosynthesis of Purines & (Biosynthesis of Purines & Pyrimidines) Pyrimidines) By Assist. Prof, Dr. Ali Aldeewan
Pyrimidines and Purines In order to understand the structure and properties of DNA and RNA, we need to look at their structural components. We begin with certain heterocyclic aromatic compounds called pyrimidines and purines.
Pyrimidines and Purines In order to understand the structure and properties of DNA and RNA, we need to look at their structural components. We begin with certain heterocyclic aromatic compounds called pyrimidines and purines.
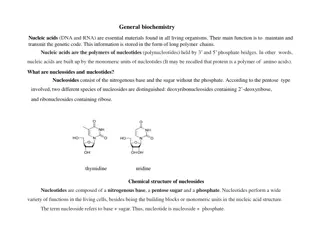
Nucleosides The classical structural definition is that a nucleoside is a pyrimidine or purine N-glycoside of D-ribofuranose or 2-deoxy-D-ribofuranose. Informal use has extended this definition to apply to purine or pyrimidine N-glycosides of almost any carbohydrate. The purine or pyrimidine part of a nucleoside is referred to as a purine or pyrimidine base.
Nucleotides Nucleotides are phosphoric acid esters of nucleosides.
Adenosine 5'-Monophosphate (AMP) Adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP) is also called 5'- adenylic acid. NH2 N N O N N OCH2 4' HO P O 5' 1' HO 3' 2' HO OH
Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) NH2 N N O O N N OCH2 O HO P P O HO HO HO OH
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) NH2 N N O O O N N OCH2 O HO O P P P O HO HO HO HO OH
Adenosine 3'-5'-Cyclic Monophosphate (cAMP) Cyclic AMP is an important regulator of many biological processes. NH2 N N N N CH2 O O O P O OH HO
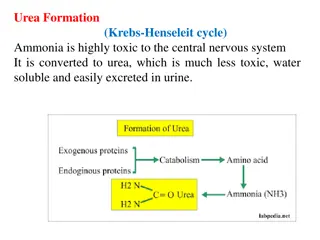
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are polymeric nucleotides (polynucleotides). 5' Oxygen of one nucleotide is linked to the 3' oxygen of another.
Fig. 27.22 NH2 N 5' OCH2 N O N N NH2 3' O OH OCH2 5' N P O O A section of a polynucleotide chain. N O O O 3' O OH OCH2 5' NH P O N O O O 3' O OH O P O O
For detailed description of this topic, please click on: http://www.easybiologyclass.com/nucleotide-biosynthesis-de-novo-salvage- purine-pyrimidine-nucleotides-cells/
Visit our website: www.easybiologyclass.com for: Lecture notes Video tutorials Biology PPTs Biology MCQs CSIR and GATE Study Materials Job Notifications Question Bank Many more Our sister concern: www.angiospermtaxonomy.com
For more information, please log on to: www.easybiologyclass.com easybiologyclass For video tutorials : Slideshare Download PPT : E-mail: easybiologyclass@gmail.com mail@easybiologyclass.com visit: www.easybiologyclass.com

 undefined
undefined