Understanding Financial Markets: Mechanisms and Efficiency
Financial markets play a crucial role in connecting borrowers and lenders, facilitating the flow of funds for optimal allocation. Different financial phases involve borrowing, saving, and investing. Transfers of funds occur directly or through intermediaries. Efficiency in financial markets ensures optimal resource utilization and quick adjustment to new information. Various types of financial markets cater to the diverse needs of participants, including money vs. capital markets, debt vs. equity markets, primary vs. secondary markets, and derivatives markets. Stock markets, such as NYSE and NASDAQ, function as secondary markets for trading securities.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
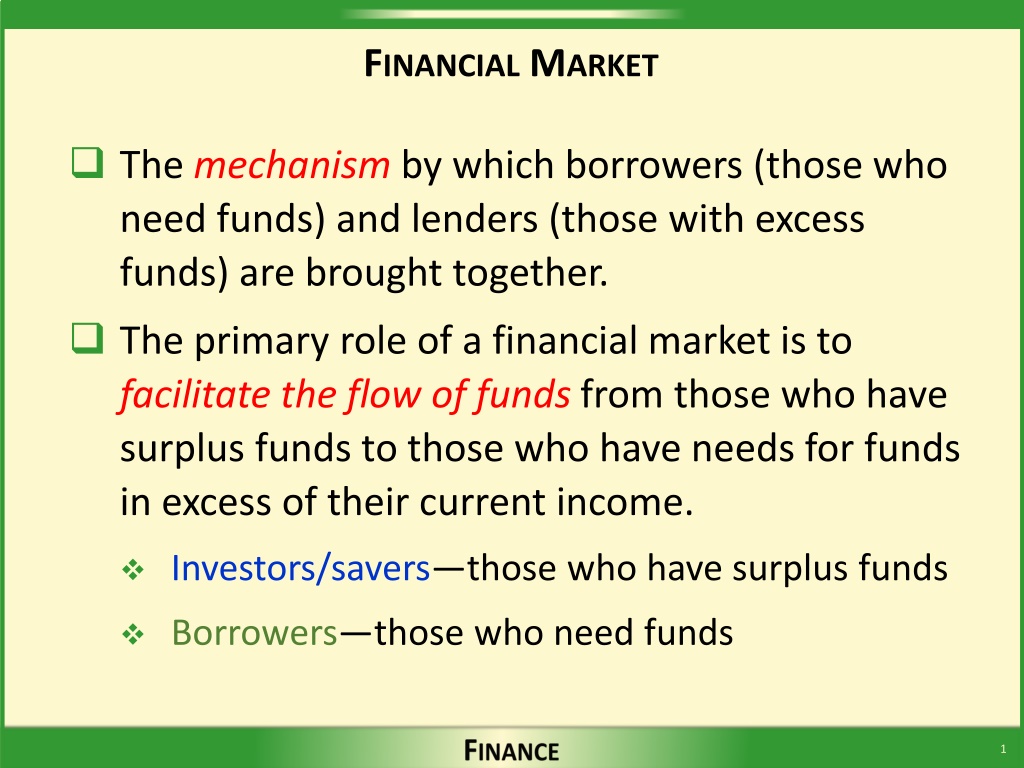
FINANCIAL MARKET The mechanism by which borrowers (those who need funds) and lenders (those with excess funds) are brought together. The primary role of a financial market is to facilitate the flow of funds from those who have surplus funds to those who have needs for funds in excess of their current income. Investors/savers those who have surplus funds Borrowers those who need funds 1
FLOWOF FUNDS Three financial phases Young adults borrow Older working adults save Retired adults use savings from prior years Funds transferred from savers to borrowers Direct transfer Investment banking house Financial intermediary 2
TRANSFEROF FUNDS Direct Transfers Securities (stocks or bonds) Borrower (Business) Saver (Investor) Dollars Indirect Transfers through an Investment Banker Securities Securities Borrower (Business) Saver (Investor) Investment Banker Dollars Dollars Indirect Transfers through a Financial Intermediary Borrower (Business) Intermediary Dollars (Loans) Intermediary Securities Business Securities Saver (Investor) Financial Dollars (Deposits) 3
EFFICIENCYOF FINANCIAL MARKETS Economic Efficiency funds are allocated to their optimal use at the lowest costs Informational Efficiency investment prices are adjusted quickly to reflect current information o Weak-form all information contained in past price movements is reflected in current market prices o Semistrong-form current prices reflect all publicly available information o Strong-form current prices reflect all pertinent information, both public and private 4
TYPESOF FINANCIAL MARKETS Different financial markets exist because savers and borrowers have different needs. Types of financial markets o Money versus capital markets o Debt versus equity markets o Primary versus secondary markets o Derivatives markets 5
STOCK MARKETS Stock markets are secondary markets. Physical stock exchanges versus the over-the- counter (OTC) market: o NYSE o NASDAQ o Electronic Communications Networks (ECNs) o Competition 6
INVESTMENT BANKING Investment banking house An organization that acts as a middleman to help firms and governments raise funds by issuing financial instruments. Helps corporations design securities attractive to investors. Generally buys the securities from the corporation and then resells them to investors (underwriting). 7
INVESTMENT BANKING Flotation costs issuing costs Setting the offering price (rate) Seasoned issues IPOs initial public offerings o Maintaining a market Shelf registration 8
EFFECTSOF FLOTATION COSTS Peach Software must raise $575 million to fund its growth. Peach plans to issue new common stock to raise the needed funds. Peach s investment banker will charge the firm 8 percent of the total amount issued to help raise the funds. How much stock must Peach issue to net $575 million after flotation costs. The secret to solving a word problem: Take the words out of the problem! 9
EFFECTSOF FLOTATION COSTS Needed funds = $575 million Flotation costs = 8 percent of the amount issued If Peach issues 8 percent more stock than the amount of needed funds (i.e., $575 million), will it have enough to support its growth? NO! If it issues 8 percent more stock: $3.68 Issue amount = $575(1.08) = $621 If $621 million is issued, flotation costs will be: Flotation costs = $621(0.08) = $49.68 Net proceeds = $621 $49.68 = $571.32 = $621(1 0.08) 10
EFFECTSOF FLOTATION COSTS The net amount received by the firm when it raises funds is: Net proceeds = Amount of issue (Amount of issue)(F) OC + NP OC (1 F) Amount of Issue = F = investment banking flotation costs stated in decimal form OC = other issuing/flotation costs, such as legal fees, printing, etc. NP = net proceeds, which is the amount the firm wants/needs after paying flotation costs 11
EFFECTSOF FLOTATION COSTS Needed funds = $575 million Flotation costs = 8 percent of the amount issued $575+0 (1-0.08) Amount= of Issue =$625 = If the firm issues $625 million, the net proceeds will be: Flotation costs = $625(0.08) = $50 Net proceeds = $625 $50 = $575 = $625(1 0.08) 12
FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES Organizations that generally take deposits and use the money to generate returns by creating loans or other investments. Manufacture a variety of financial products. Facilitate the transfer of funds from those who have funds (savers) to those who need funds (borrowers). Types of intermediaries Improve the standard of living in an economy. 13
FOREIGNVERSUS U.S. FINANCIAL MARKETS For the most part, U.S. financial markets/intermediaries face greater restrictions than in other countries. o Branching o Services, especially non-financial More participants (institutions) in U.S. markets. o More independent financial intermediaries in the United States than in other countries. U.S. financial markets are considered more efficient. 14
CHAPTER 3 QUESTIONS 1. What is a financial market? What is the role of a financial market? 2. Why is it important for financial markets to be somewhat efficient? 3. Why are there so many different types of financial markets? 4. What is an investment banking house? What role do investment bankers play in the financial markets? 5. What is a financial intermediary? In what ways do financial intermediaries improve the standard of living in an economy? 6. How do financial markets and financial intermediaries in the United States differ from financial markets in other parts of the world? 15