Understanding Nutrition and Digestion for Optimal Health
Nutrients obtained from the environment are essential for growth, repair, and regulation in organisms. Macronutrients like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and water are needed in larger amounts, while micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals are required in smaller quantities. Carbohydrates serve as a quick energy source, with functions ranging from energy provision to structural support in cells and tissues. Essential nutrients, including fatty acids, amino acids, minerals, vitamins, and water, must be supplied through diet as our bodies cannot synthesize them. Overall, maintaining a balanced intake of nutrients plays a crucial role in sustaining optimal health and well-being.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Nutrition &Digestion Ass.Prof.Dr. Suhad Faisal Hatem
Nutrients : substances obtained from the environment that organisms need for growth ,repair ,regulation and survival. Six type of nutrients help to maintain homeostasis Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Most energy is provided by carbohydrates and fats Cells rely on a supply of energy to maintain their activities,Nutrients that supply energy are lipids, carbohydrates, proteins. Energy in food is measured in a unit called a Calorie Broken down by digestion to their subunits, which are used during cellular respiration,Energy from these subunits is released and is captured in ATP
Macronutrients : Nutrients the body needs in relatively large amounts are called macronutrients. They include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and water Micronutrients : Nutrients the body needs in relatively small amounts are called Micronutrients. They include vitamins and minerals.
1-Carbohydrates Functions 1. Energy source for plants and animals 2. Source of carbon in metabolic processes 3. Storage form of energy 4. Structural elements of cells and tissues 5. One gram of carbohydrates provides 4 Calories of energy.
1-Carbohydrates a source of quick energy glucose, sucrose (simple carbohydrate ) polysaccharides, long chains of sugar molecules Cellulose, starch, and glycogen are polysaccharides composed of glucose chains (complex carbohydrate) Cellulose - structural component of plant cell walls Starch -storage material of plants Glycogen - used by animals for short-term energy storage.it is converted glucose by body
Essential Nutrients Provide raw materials Our cells can synthesize most of the molecules our bodies require, but they cannot synthesize certain raw materials, called essential nutrients, which must be supplied in the diet Essential Nutrients for humans include certain fatty acids, amino acids, a variety of minerals, vitamins, water
Lipdes Essential Fatty Acids:Certain fatty acids are essential in the human diet Fats and oils provide a source of energy and essential fatty acids Similar to carbohydrates but include less O2 and not dissolved in water They help us absorb fat-soluble vitamins, are important in cell division, fetal development, and immune response Sources of essential fatty acids are fish oils, canola oil, soybean oil, flaxseed, walnuts One gram of lipids provides 9 Calories of energy
Protein Function Protein from food is broken down into its amino acid subunits, which can be used to synthesize new proteins.Composed from C ,H,O,N to form amino acids used for the growth and repair of the body s cells and tissues Protein functions in the body -*: enzymes, receptors on cell membranes, oxygen transport molecules, structural proteins, antibodies, muscle proteins Protein-rich foods - meat, milk, eggs, corn, beans, soybeans One gram of proteins provides 4 Calories of energy Essenssial amino acids Proteins are composed of chains of amino acids. Your body can make only 12 of the 20 amino acids it needs to build proteins. The other 8, called essential amino acids, must come from the food you eat. Food such as meat, cheese, and eggs contain all eight essential amino acids.
Vitamins It organic molecules that animals require in small amounts for normal cell function, growth, development and Help change carbohydrate and fats to energy Vitamins are required for the proper functioning of enzymes that control metabolic reactions in the body Vitamins are essential nutrients that the body cannot synthesize and must be obtained in the diet They are grouped into two categories: water soluble or fat soluble
Minerals Elements that play a role in animal nutrition and can only be obtained in diet or drinking water Calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus are components of bone and teeth Sodium, calcium, and potassium - needed for muscle contraction and nerve impulses Iron - hemoglobin in the blood Iodine - hormones produced by the thyroid gland Major Minerals includes Calcium, magnesium, phosphorus ,Sodium, and potassium Trace Minerals includes Iron, Iodine,Zinc,Copper
Water :The human body is about 60% water carries dissolved nutrients by our body and help in digesting food All metabolic reactions occur in solution, and water participates directly in hydrolysis reactions that break down proteins, carbohydrates, fats Water is the principal component of saliva, blood, lymph, extracellular fluid, and cytoplasmic fluid By sweating, evaporation of water , prevent over heating Urine, mostly water, is necessary to eliminate cellular waste products
Weight Gain and Obesity Any unused energy in food, whether it comes from carbohydrates, proteins, or lipids, is stored in the body as fat. An extra 3,500 Calories of energy results in the storage of almost half a kilogram (1 pound) of stored body fat. People who consistently consume more food may become obese. Obesity occurs when the body mass index is 30.0 kg/m2 or greater. Body mass index (BMI) is an estimate of the fat content of the body. It is calculated by dividing a person s weight (in kilograms) by the square of the person s height (in meters). Obesity increases the risk of health problems such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
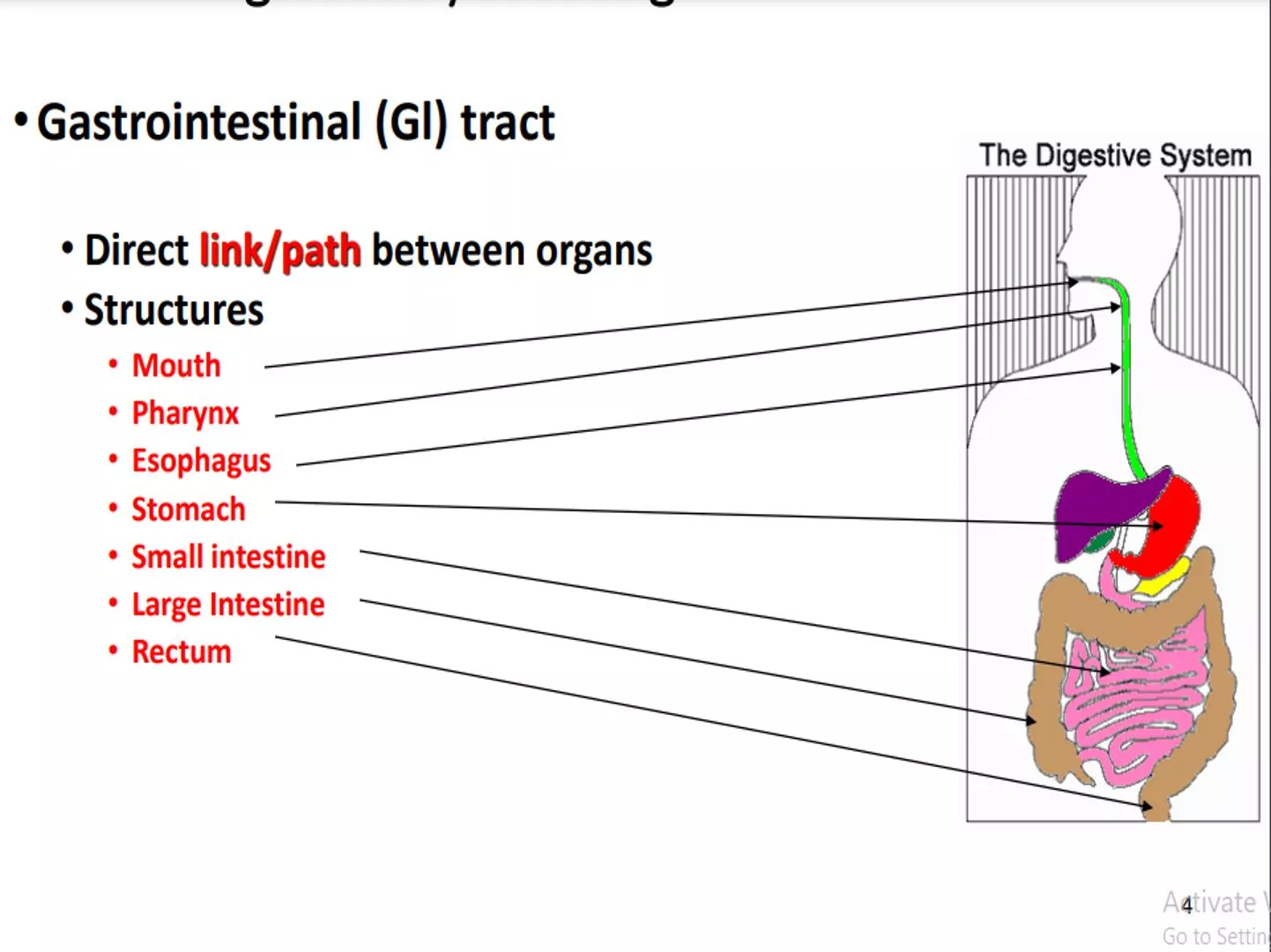
Digestion is the process by which the large complex molecules in food are broken down into smaller molecules that can be used by the body. The digestive system includes the gastrointestinal tract and the associated glands. Ingestion: the process of taking in food into the digestive tract through an opening, usually called a mouth is known as ingestion Digestionconsists of two types of processes 1- Mechanical breakdown: The process of breaking down food into smaller pieces by teeth and tongue mixed food with saliva (contains bacteria-killing enzyme and antibodies). Also the mucus help food to move from throat to stomach using muscle movement called peristalsis. 2- Chemical breakdown: The particles of food are acted upon by enzymes that break them down into simpler subunits.
4- Digestion in Stomach Stores food and releases it gradually into the small intestine, Stomach helps in the mechanical breakdown of large pieces of food and Chemical breakdown Gastric fluid includes: 1-Pepsinogen (inactive)------------ Pepsin -------Proteins --------Peptides. 2- HCL :Activates inactive pepsinogen into active pepsin. Kills bacteria. Makes the medium acidic which is suitable for pepsin to act on proteins. 3- The stomach secretes a layer of mucus to protect itself from its own acidic Sphincters : circular muscles help food movement in and out stomach (pyloric & cardiac) Digested juices and enzymes turn the partly digested food in the stomach into a semi liquid mixture called chyme food takes six hours to empty the stomach after a meal.water&alchohol will be absorbed in stomach
5- Absorption: The main function of small intestine is to digest food and absorb the digested food into the bloodstream with liver and pancreas. Absorption occur in small and large intestine Small intestine: include bile juice & pancreatic juice & digestive enzymes 1- bile juice Liver secretes bile which is stored in the gall bladder and released when needed through the bile duct, Bile helps in emulsification of fats. 2- pancreatic juice : neutralizes the acidic chyme and enzyme digests carbohydrates, proteins and lipids. Pancreatic proteases(trypsin): break down protein into peptides , Pancreatic lipases break down fats into fatty acid and glycerol. 3-Digestive Enzymes The walls of the small intestine secrete digestive enzymes to digest food. Peptidases to split small peptides into amino acids. Maltase acts on maltose and converts it into glucose. Sucrase acts on sucrose and converts it into glucose and fructose. Lactase acts on lactose and converts it into glucose and galactose. Lipases acts on lipids and convert it into fatty acid and glycerol.
The small intestine has numerous folds and projections (Villi ) that give it an internal surface area . Villi :Minute finger like projections cover the entire folded surface of the intestinal wall. Each individual cell of the villi bear microscopic projections called microvilli. Each villus of the small intestine is provided with a rich supply of blood capillaries that absorbed nutrient except large fat molecules and distribute them throughout the body Nutrients absorbed by the small intestine include water, monosaccharides, amino acids and short peptides, fatty acid produced by lipid digestion, vitamins and minerals.
6-Elimination/egestion: In digestable materials must be expelled from the body. The end of the large intestine is the rectum (short term storage which holds feces before it is expelled Large intestine It has two parts, colon and rectum. The large intestine has bacteria which live on unabsorbed food. The intestinal bacteria can synthesize vitamin B12, thiamin, riboflavin and Vitamin K. Cells lining the large intestine absorb these vitamins and water , salts and concentrate waste After absorption is complete, any remaining material is converted into semisolid feces.
Accessory gland 1-Pancrease: organ secreted enzyme &hormones Exocrine pancreas produces NaHCO, Amylase,Trypsin, lipase Endocrine pancreas produces insulin &glucagon 2-liver :organ effects on digestion by producing bile Regulate cholesterol by bile salts(green fluid) Detoxify blood , store iron , vitamins A D E K Convert excess food to form can be stored Filters out toxins and waste including drugs, alcohol and poisons 3-Gall bladder: Structure located near liver store the bile ,bile will break fats and make it emulsifies