Understanding Bread Making Process: Flour, Yeast, & Water
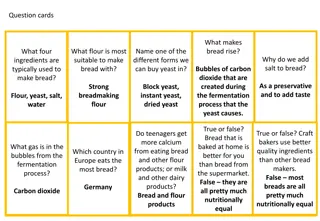
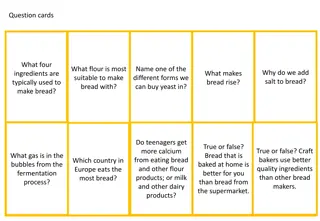
Strong plain flour, yeast, and water play crucial roles in bread making. The flour provides gluten for structure, yeast produces carbon dioxide for rising, and water activates fermentation. Together, they create an elastic dough that traps gas bubbles, resulting in a quality bread product.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Food Preparation Skills Food Preparation Skills Student Name: Class: Target Level:
Food Preparation Skills Food Preparation Skills Prepare, combine & shape Making dough pastry, bread, pasta Meat & fish Knife skills
Food Preparation: Binding, Coating & Glazing Binding: to hold ingredients together. Egg acts as a binding agent e.g. burgers. Water binds flour & fat in pastry. Potato and/or flour is used as a binding material in fish cakes & breadcrumbs are used in sausages. Coating: means adding an outer layer to a food e.g. breadcrumbs on fish cakes, batter on fish & chocolate on biscuits. Glazing: egg wash glaze has a golden, shiny finish on pastry & bread dough. Egg white has a crisp, golden texture good for sweet pastry dishes. Egg yolk gives a golden brown colour. Milk gives a golden brown glaze for scones, pastry & biscuits. Sugar & water gives a sweet, sticky glaze on enriched dough.
Food Preparation: Dough (bread, Pasta & Pastry) Bread dough: made with strong, plain flour due to its high gluten content. Gluten is made of two proteins called gliadin & glutenin. Gluten is made when water is added to the flour and a strong elastic dough is formed. The elasticity of the dough helps to trap CO2 which is produced by the yeast and makes the bread rise. Yeast is the raising agent that produced CO2 gas. It needs warm liquid to allow the yeast to grow & produce CO2. Salt adds flavour to the bread & helps the development of the gluten.
Describe the function of strong plain flour, yeast and water when making bread and explain how they work together to produce a quality product. [8]
Strong plain flour function: provides gluten, (formed by combining gliadin and glutenin, natural proteins in wheat) forms an elastic stretchy dough when mixed with a liquid gluten stretches to hold the carbon dioxide bubbles produced by the yeast provides structure to the cooked bread as it coagulates when cooked at high temperature enables dextrinization of starch: brown colour Yeast function: it uses both respiration and fermentation (mostly the latter) to develop it produces gas bubbles/carbon dioxide which is trapped by the dough and makes the bread rise it uses available sugar for growth Water function: binds dry ingredients together if warm provides suitable condition for yeast to activate/fermentation provides moist conditions for the yeast How the ingredients work together the flour (starch and sugar) provide food for the yeast the water provides moisture and warmth within the dough the yeast is distributed throughout the mixture during mixing as bread dough is kneaded, proteins in flour line up and strands of gluten form to create a matrix within the bread dough gluten becomes elastic when kneaded and can be pushed up by the carbon dioxide produced by the yeast in fermentation carbon dioxide expands when heated and releases alcohol which provides the aroma produced when bread is cooked the gluten entangles the bubbles of carbon dioxide and when heated sets giving bread its open texture heat causes the sugar to caramelize which gives the crust a good colour (dextrinisation)
Food Preparation: Pastry Used for sweet & savoury dishes: Shortcrust, choux, flaky/rough puff, suet, hot-water crust, filo, puff pastry. Shortcrust pastry: made using the rubbing-in method & used for pies & tarts. Made using half the amount of fat to flour (1:2). Plain flour is used for low gluten content. See food science / fats & oils for more info. Choux pastry: used for eclairs & profiteroles etc. Ingredients must be weighed accurately. Strong flour is used to form the structure, while fat & water are boiled together before adding flour to make a roux. Eggs are then beaten into the mixture before being cooked in a hot oven. The water in the mixture turns to steam in the hot oven & raises the dough while the protein in the eggs coagulate & sets the structure.
Food Preparation: Pasta Pasta is made form strong flour for its high gluten content. Olive oil or egg is added as liquid to form the dough. Spinach, tomato puree, squid ink or beetroot can be added to change the colour. The dough is kneaded to develop the gluten before being left to rest. The dough is then rolled using a pasta machine until thin & left to dry.
Questions What is the most suitable flour to use for choux pastry? What is the ratio fat:flour in shortcrust pastry? What are the names of the types of proteins in strong flour? Name two foods that can be added to pasta to change the colour? Write a set of accurate instructions to make choux pastry.
Homework Homework Choux pastry is used for a variety of decorative pastry recipes, such as choux swans, Croquembouche, beignets, Gateau St. Honore, churros and gougere. Investigate where these recipes come from and how they are made. If possible, have a go at making one of them to stretch your skills.