Vermicompost Cost Analysis for Organic Farming
This analysis details the cost breakdown of producing vermicompost, showcasing input costs such as cow dung, labor charges, earthworms, and other expenses. It also calculates the expected output and net income for a single tank of vermicompost, providing insights for sustainable agricultural practices. Recommendations include researching subsidies, adhering to marketing regulations, and monitoring market prices for effective business management.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
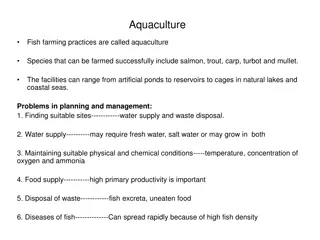
MODULE 14 Vermicompost Cost Analysis
VERMICOMPOST COST ANALYSIS Input cost per tank 1. Cow dung cost(3000kgs) ---------- Rs.1,200 (In one pit we require 1.5 tractor load cow dung.1 tractor load cow dung = 2000kg approx.) 2. Labour charges to load the cow dung---------- Rs.450 3. Labour charges to fill the tank ---------- Rs.750 4. Labour charges for maintenance ---------- Rs.600 5. Earthworms cost (1kg=500/-) 7kgs -------- Rs3,500 (1ft3of volume we require 28.3 gm of earthworms) 6. Other charges per pit(gunny bags, cement bags)-Rs.1,000 7. Actual input cost per tank ---------- Rs.7,500 8. Output expected per tank ----- 2,500 kg Vermicompost 9. Cost of 1kg Vermicompost---- Rs.12 Therefore, 2,500 x 12= Rs.30,000 (30,000/- income generate for one pit) Net income= Gross income- Expenditure = Rs.30, 000 7,500 = Rs. 22,500
5. Collect information related to various subsidies/funds offered by the Government, authorized state units and other financial institutions involved with the promotion of the producer. 6. Comply with relevant regulations in marketing of the produce. 7. Track information related to wholesale and retail price of the produce
8. Record daily sell and purchase of items in designated log books, register. 9. Record quantity, quality, date of manufacture and batch number of every produce accurately. 10. Identify appropriate marketing channels related to the produce considering requirements and constrain