Understanding the Lifecycle of Building and Publishing Applications
Explore the comprehensive process of software development, from creating manifest files to deploying and certifying applications. Delve into topics such as application security, hosting, licensing, debugging, and more. Learn about mobile and web-based applications, differences between various platforms like Windows 8 and Windows 10, and the importance of application containers and packages.
- Software Development
- Application Lifecycle
- Mobile Applications
- Application Security
- Windows Development
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Software Developer MTA: Section 1
Topics Lifecycle of an Application Manifest File Security Hosting Licensing Building your App Debugging Testing Validating Certifying your App Publishing your App
Mobile applications Web based HTML5 etc Can run in any browser or OS Changes made on the server, no need to download Avoids app store charges Requires internet connection Mobile based No internet connection required Faster than web apps Specific to an OS and possibly device Richer functionality access to GPS, sensors, camera etc
Building an application in Windows Windows 8: Mobile operating system was called Windows RT or Windows RunTime Program in C# Need Visual Studio and Windows Phone 8 SDK Windows 10: Platform is now called UWP, Universal Windows Platform Main components of an application Services databases/APIs/ cloud Libraries pre-existing code to save duplicate writing Codebase the code written by the developer UIX - the user interface
Application container AppContainers are a sandbox mechanism which control what resources an app can access or not The sandbox is a separate controlled environment for each app This is a security concept and prevents badly written apps from overwriting other apps or the underlying OS
Application package This contains all the information required to make the app available on an app store You need: All the files required to run the app, zipped up (Android.apk, IOS.app, Windows.exe.msi) The apps capabilities The required device capabilities Pre-requisites Dependencies Compatibility Security This is all contained in a Manifest file eg Package.appxmanifest for Windows
Manifest file - XML IDENTITY OF THE APPLICATION (WHAT IT IS CALLED) Identify Name= MyCompany.MySuite.MyApp Version= 1.0.0.0 PUBLISHER OF THE APP Publisher= CN=MyCompany, O=MyCompany, L=MyCity, S=MyState, C=MyCountry > DISPLAY NAME <DisplayName>MyApp</DisplayName> PUBLISHER DISPLAY NAME <PublisherDisplayName>MyCompany</PublisherDisplayName> PATH TO LOGO IMAGE <Logo>images\icon.png</Logo>
Manifest file - XML PREREQUISITES (Minimum OS levels required before the application will be permitted to run) <Prerequisites><OSMinVersion>6.2.1</OSMinVersion><OSMaxVersionTested>6.2.1</OSMaxVersionTested> < /Prerequisites> DEPENDENCIES OF THE APP Other packages that this package requires <Dependencies> <PackageDependency Name="Microsoft.WinJS.1.0" Publisher="CN=Microsoft Corporation, O=Microsoft Corporation, L=Redmond, S=Washington, C=US" MinVersion="1.0.0.0"/> </Dependencies>
Manifest file - XML CAPABILITIES OF THE APP (WHAT IS IT GOING TO NEED PERMISSION TO ACCESS Eg. NETWORK. GEOLOCATION, PHONE CONTACTS, CAMERA ETC.) <Capabilities> <Capability Name="internetClient"/> <Capability Name="musicLibrary"/> <Capability Name="videosLibrary"/> <DeviceCapability Name="microphone"/> <DeviceCapability Name="webcam"/> </Capabilities> The app must ask permission to use these capabilities
Manifest file - XML Security: Permissions Permissions grant the ability for some code to execute other code The developer declares which trust level their application needs in order to be able to run This is known as "code access security". In the Microsoft .NET framework Full trust means that the application needs all rights that the .NET framework provides
Authentication Users can log in via a variety of methods determined by the programmer Windows Authentication : handled by Windows Database Authentication : handled by the programmer, eg via Login Anonymous : zero authentication
Licensing EULA End User License Agreement Is what you agree to before you start using an application (I agree to these terms...) Open Source Permissive (BSD, MIT, and Apache) Copyleft (GPL, LGPL, Eclipse Public License, Mozilla Public License, and Common Development and Distribution License). Copyleft enforces freedom of use (including all other rights) and grant subsequent users to modify, distribute, and use the software as they please.
IDEs (integrated development environments) IDE Development Platforms Source code editor Automated build process Debugger Examples Android Studio Xcode for IOS Visual Studio IntelliJ for Java Xamarin cross platform
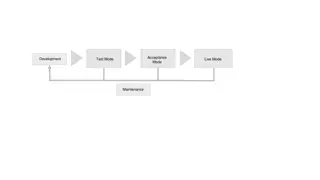
Software development lifecycle Analysis Design Build Test Release Ongoing Maintenance Documentation
Building the app Using an SDK Windows SDK for UWP (Universal Windows Platform) apps https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/downloads/windows-10-sdk Android SDK - Studio https://developer.android.com/studio/index.html IOS SDK - Xcode https://developer.apple.com
Debugging There are five parts to the debugging workflow: Discover. Identify a problem. Locate. Determine where in the code the problem occurs. Inspect. Examine the control flow and data structures of the running code to find the cause of the problem. Fix. Apply your insight into the cause of the problem to devise a solution and edit the code to suit. Confirm. After editing, run the app and check it with the debugger to be sure the fix was successful. Different Types of Errors Syntax Error Logical Error Exception
Debugging tools Set, activate or deactivate breakpoints Pause or resume execution of your code Step over; that is, execute the current line of code and, if the current line is a function or method, step out to the next line in the current file Step in; that is, execute the current line of code and, if the current line is a routine, jump to the first line of that routine Step out of a jumped-to routine; that is, complete the current routine and step to the next routine or back to the calling routine. Variable viewer Source editor
Testing and validating Testing Unit Testing Integration Testing System Testing Touch Screen Testing Can use mouse Touch events Can use an Emulator to simulate touch events Validating Your App W3C Page Validation https://www.w3.org/developers/tools/ http://ready.mobi/Unit Testing/
Certifying Windows App Certification Kit https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/mt637086%28v=vs.85%29.aspx?f=255&MSPPError=- 2147217396 https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/develop/app-certification-kit https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/mt674655(v=vs.85).aspx https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/uwp/debug-test-perf/windows-app-certification-kit https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/hardware/br230771(v=vs.85).aspx
Publishing Licensing Issues eg. EULA Publishing To The Windows Store https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/store/publish-apps Publishing To The Android Store https://developer.android.com/studio/publish/index.html https://developer.android.com/studio/publish/app-signing.html Publishing To The IOS Store https://developer.apple.com/library/content/documentation/IDEs/Conceptual/AppDistributionGuide/Su bmittingYourApp/SubmittingYourApp.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40012582-CH9-SW1 https://code.tutsplus.com/tutorials/how-to-submit-an-ios-app-to-the-app-store--mobile-16812 https://developer.apple.com/app-store/review/guidelines/