Understanding the Brain and Behavior in Fall 2016
This content delves into the intricacies of the brain and behavior, covering topics such as the organization of the brain, the nervous system, brain stem functions, disorders of the cerebellum, and the forebrain components. It provides a detailed exploration of the hindbrain and midbrain structures, highlighting their roles in regulating various physiological and cognitive processes. Additionally, the content discusses the thalamus and hypothalamus within the forebrain and their involvement in important regulatory functions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
INTRODUCTIONTO BRAINAND BEHAVIOR Fall 2016 Hana Kuwabara Andrea Mejia 1
TOPICSFOR TODAYS LECTURE The Organization of the Brain Protecting the Brain 2
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Central Nervous System Brain and Spinal Cord Brain stem and forebrain Peripheral Nervous System Somatic and Autonomic 3
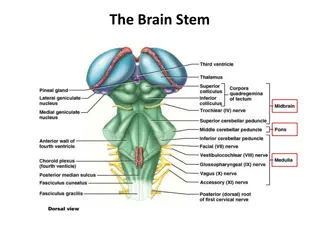
THE BRAIN STEM Hindbrain Midbrain 4
THE BRAIN STEM: THE HINDBRAIN Lowest part of brain stem Medulla Regulates many automatic activities e.g., breathing, heartbeat, digestion Area Postrema Pons Message station between the cortex and the cerebellum Cerebellum Motor coordination of on going movements 5
DISORDERS OF THE CEREBELLUM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5eBwn22Bnio https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dox3_ox8C2U
THE BRAIN STEM: THE HINDBRAIN 7
THE BRAIN STEM: THE MIDBRAIN Coordinates movement with sensory input Tectum Visual reflexes and reaction to moving stimuli Old /primitive visual system Tegmentum Reticular formation Periaqueductal gray matter Red nucleus Ventral tegmental area Substantia Nigra Communicate with the caudate nucleus in the Basal Ganglia 8
THE BRAIN STEM: THE MIDBRAIN 10
THE FOREBRAIN Diencephalon = thalamus and hypothalamus Telencephalon = cortex, basal ganglia, and limbic system Limbic system = amygdala and hippocampus
THE FOREBRAIN: THE THALAMUS & HYPOTHALAMUS Involved in regulating behavior and emotion Thalamus Grand Central Station for sensory information Hypothalamus The basic drives of the four F s : Fight/Flight response Feeding (hunger/thirst) Fornicating (sexual drive) 12
THE FOREBRAIN: THE THALAMUS & HYPOTHALAMUS 13
THE FOREBRAIN: THE LIMBIC SYSTEM Hippocampus + Amygdala Amygdala Emotional experiences Negative emotions Impulse control Involves Emotional behavior, activation of ANS, and hormonal activation Hippocampus Memory consolidation center Memories are not stored here Plays a bigger role in declarative memory Verbal and conscious 14
THE FOREBRAIN: THE LIMBIC SYSTEM 15
THE FOREBRAIN: THE BASAL GANGLIA Includes caudate nucleus, substantia nigra Believed to control motor activity Substantia nigra implicated in Parkinson s Disease Less dopamine https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aOSB6ytMk20 16
THE FOREBRAIN: THE BASAL GANGLIA 17
THE FOREBRAIN: THE CEREBRAL CORTEX Temporal Parietal Occipital Frontal > 80% of all neurons in central nervous system 18
THE FOREBRAIN: THE CEREBRAL CORTEX Divided into two hemispheres Connected by corpus callosum Left hemisphere Verbal processes, other cognitive processes Right hemisphere Perceiving our world, creating images 19
THE FOREBRAIN: THE CEREBRAL CORTEX Temporal Lobe Recognizing sights and sounds Long-term memory storage Parietal Lobe Touch sensation Monitoring body positioning 20
THE FOREBRAIN: THE CEREBRAL CORTEX Occipital Lobe Processing visual information Frontal Lobe Deciding how we respond to environment Personality, impulse control Prefrontal Cortex Thinking, reasoning, planning 21
PROTECTINGTHE BRAIN Meninges Cerebrospinal fluid / Ventricular System Blood-Brain Barrier 22
PROTECTINGTHE BRAIN: THE MENINGES Tough protective covering around brain and spinal cord Consists of 3 layers ( PAD ) 23
PROTECTINGTHE BRAIN: THE MENINGES Tough protective covering around brain and spinal cord Consists of 3 layers ( PAD ) Pia mater Follows surface very closely Very delicate, you can barely see it 24
PROTECTINGTHE BRAIN: THE MENINGES Tough protective covering around brain and spinal cord Consists of 3 layers ( PAD ) Arachnoid membrane Middle/Inner layer Weblike appearance Soft and spongy 25
PROTECTINGTHE BRAIN: THE MENINGES Tough protective covering around brain and spinal cord Consists of 3 layers ( PAD ) Dura mater Hard mother Outer layer Thick, tough, unstretchable 26
PROTECTINGTHE BRAIN: CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF) Fluid in and around the brain Functions: Reduce pressure on base of brain Absorb shock caused by sudden head movement Removal of waste products Continually manufactured and circulated through brain via ventricles Hollow, interconnected chambers 27
PROTECTINGTHE BRAIN: CEREBROSPINAL FLUID 28
PROTECTINGTHE BRAIN: THE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER Produced by cells in walls of the brain s blood vessels Semi-permeable Water, glucose (sugar = energy) can cross Many other molecules cannot 29
PROTECTINGTHE BRAIN: THE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER Functions: Protect brain from harmful chemicals Regulate brain s chemical balance 30

 undefined
undefined