Understanding Government Systems and Democratic Principles
The content covers topics related to government branches, the roles of federal judges, law enforcement, and presidential advisors. It also explores concepts like economic security, state differences, democratic elections, and historical events like Shays' Rebellion. The visual aids and questions delve into the foundations of governance, civil rights, and national unity.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
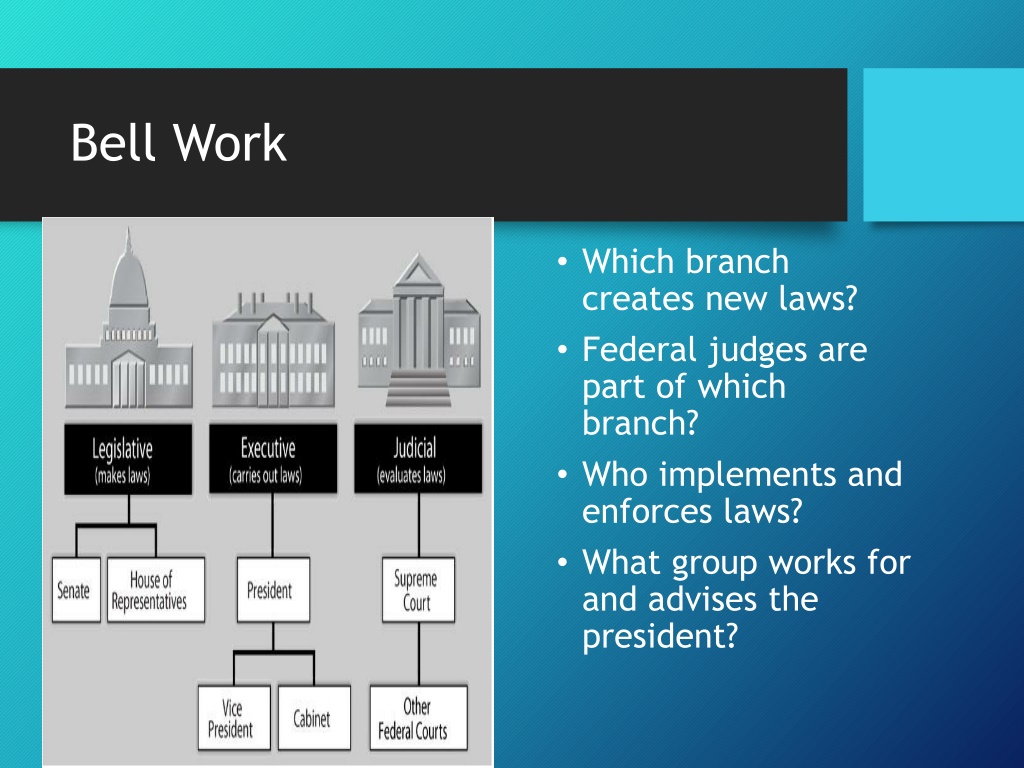
Bell Work Which branch creates new laws? Federal judges are part of which branch? Who implements and enforces laws? What group works for and advises the president?
In Lakech by Luis Valdez Tu eres me otro yo You are my other me If I do harm to you, Si te hago da o a ti, I do harm to myself Me hago da o a mi mismo If I love and respect you Si te amo y respeto I love and respect myself Me amo y respeto yo
Bell Work Which branch creates new laws? Federal judges are part of which branch? Who implements and enforces laws? What group works for and advises the president?
Test Results Overall Average: 80.7% Highest Average: This Class: 82.3% 77.8%
Which of these would be an example of a government providing economic security Funding a police force Negotiating a trade deal with another country Instituting a draft during wartime Creating a law against cell phone use while driving
Although Ohio is considered a state, it is different from a country such as Japan, which is also considered a state. What makes Ohio different from Japan? Ohio does not have its own organized government. Ohio is not characterized by a distinct ethnic group. Ohio is not in a defined geographic territory. Ohio is subject to laws from another entity.
In a truly democratic society, which of the following happens during an election? Citizens are required to vote for the candidate that belongs to their party. Citizens vote, but the winner is ultimately decided by a high court. The candidate that has been appointed by a political party takes power. The elected candidate takes office without violence from the rival party.
Shays Rebellion caused the new nation s leaders to realize that a stronger national government was needed. the Articles did an inadequate job of protecting individual rights. the Articles did an inadequate job of protecting states rights. the nation needed to outlaw slavery.
Under the Articles of Confederation, Congress could declare war, but it could not make treaties. establish post offices, but it could not levy taxes. force everyone to abide by the law, but it could not establish a court system. levy taxes, but it could not establish an executive branch.
Any powers not specifically stated in the Articles of Confederation could not be exercised by either the central or state governments. were given to the central government. were given to the states. were shared by the central government and the states.
Which of the following was a positive achievement under the Articles of Confederation? establishing an executive branch signing a peace treaty with Britain levying and collecting taxes stopping states from coining their own money
The Federalist papers were successful primarily because they clearly explained the principles of American constitutional government. limited the power of the executive branch. presented a way of solving the dilemma between the large and small states. set up a clear way of separating the powers of the three governmental branches.
The National Government To become law, the Constitution had to be ratified by nine of the thirteen states. In The Federalist Papers, James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, and John Jay argued in support of the Constitution. A key argument was that the division of power made it impossible for one person to have absolute power. The government was limited by assigning different powers to each branch and providing each with checks over the power of the others.
Legislative Branch The enumerated powers of Congress are listed in Article 1, Section 8 of the Constitution, which explains what kinds of laws Congress can make. The final clause gives Congress authority to make whatever laws are necessary and proper to carry out its other powers. Congress has used this elastic clause in many ways.
Executive Branch The president heads the executive branch, which includes the departments that enforce the laws passed by Congress. The executive branch includes federal agencies, commissions, government corporations, and boards that carry out specific duties. The president is empowered to grant pardons, make treaties, appoint key officials, and serve as commander in chief of the military.
Judicial Branch Article III establishes the federal court system, consisting of a Supreme Court and the lower courts. The federal court system hears cases about the Constitution and other federal issues. The judicial branch s power comes from judicial review, the court s ability to interpret the Constitution and overturn laws that violate it. This power gives the judicial branch a status equal to the other two branches of government.
American Government: Then and Now President Washington had relatively little to do, while modern presidents have full and tightly organized schedules. The first Congress members introduced fewer than 200 bills and worked part time, but today Congress members introduce about 10,000 bills each year and work almost year-round. Early Supreme Court justices heard almost no cases and traveled to district courts to hear appeals when the Supreme Court was not in session.
Relations Among the Branches The division of power among three branches requires that the branches cooperate with one another. Executive powers that require cooperation between the president and Congress serve as limits on presidential power. Checks and balances, political parties, and the different kinds of power held by each branch are sources of conflict.
3 Branches Activity Working with your partner, use the diagram to answer the questions on the back
Translate the Constitution The Constitution of the United States is in your text from pages 797 through 815 Rewrite the Preamble, all 7 Articles and 27 Amendments so that it has meaning for a high school student Use dictionaries, a thesaurus, and your textbook (including the notations in the margins of the Constitution) to help you. Your final product will be due February 28 and will be counted as a unit assessment.
What are the three branches of the national government? A.legislative, executive, and judicial B.federal, state, and local C.Army, Navy, and Air Force D.Internal Revenue Service, Federal Bureau of Investigations, and Health and Human Services
What are the powers listed in the Constitution for Congress called? A.executive powers B.enumerated powers C.provisional powers D.absolute powers
Which branch of government has the civilian commander for the military? A.legislative branch B.the military is an independent branch of government C.judicial branch D.executive branch
What is the power to overturn laws that violate the Constitution? A.veto power B.impeachment C.judicial review D.enumerated power
Which of the following best describes how government has changed over time? A.The president no longer oversees most federal bureaucracies. B.The legislature is no longer involved in matters of foreign policy. C.The Supreme Court reviews fewer cases today than when the Constitution was first adopted. D.All branches are more busy today than early U.S. government.
Which branch of government has the power to appoint federal judges? A.legislative branch B.executive branch C.judicial branch D.state governors
What is the statement "make all laws which shall be necessary and proper" that applies to the legislative branch sometimes called? A.judicial review B.unlimited government C.the Elastic Clause D.federalism
Which branch of government has the responsibility to carry out laws passed by the federal government? A.legislative branch B.executive branch C.judicial branch D.state branch
The executive power to negotiate treaties and the legislative power to ratify treaties an example of A.shared powers. B.judicial review. C.impeachment powers. D.federalism.
What is an enumerated power of the legislative branch? A.the power to command the military B.the power to carry out education policy C.the power to collect and appropriate funds D.the power to pardon people convicted of federal crimes
Reflection How do the 3 branches of government share, check and balance power?