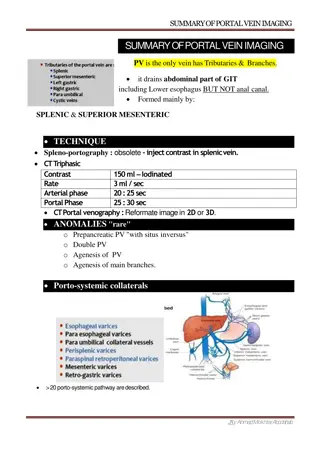
Vein and volcano stones in Troodos
Igneous rocks, formed from magma or lava, and metamorphic rocks, transformed through heat and pressure, are explored alongside calcite, a versatile mineral used in various industries. Discover the beauty and significance of these geological formations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Vein and volcano stones in Troodos Poland: Dominika Szwabowicz Agata Lech Cyprus: Rafaelia Koumoudiou Ionela Bulai
Igneous rock: Igneous rock or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses.
Metamorphic rock: Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock types, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The original rock is subjected to heat and pressure, causing profound physical or chemical change. The protolith may be a sedimentary, igneous, or existing metamorphic rock.They are classified by texture and by chemical and mineral assemblage. The study of metamorphic rocks provides information about the temperatures and pressures that occur at great depths within the Earth's crust. Some examples of metamorphic rocks are gneiss, slate, marble, schist, and quartzite.
Calcite: Calcite is a rock-forming mineral with a chemical formula of CaCO3. It is extremely common and found throughout the world in sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks. Some geologists consider it to be a "ubiquitous mineral" - one that is found everywhere. The properties of calcite make it one of the most widely used minerals. It is used as a construction material, abrasive, agricultural soil treatment, construction aggregate, pigment, pharmaceutical and more. It has more uses than almost any other mineral.

 undefined
undefined