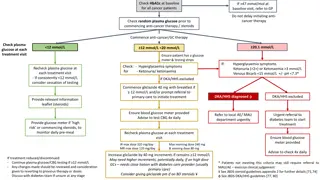
Uses and Conversions of Glucose and Fructose in Chemistry
Glucose and fructose have various uses, including as food for patients and in confectionery. Glucose is also used in silvering mirrors, processing tobacco, and starting material for vitamin C synthesis. Fructose is a sweetening agent and a sugar substitute. Glucose can be converted into fructose through a series of chemical reactions involving osazone formation and reduction. Additionally, Haworth's structure elucidates the arrangement of glucose molecules in a ring-like structure. The process of drawing Haworth representations is explained.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Haworth Structure of Glucose, Interconversion and Uses of Monosaccharides Class :I Zoology Sub: Organic, Inorganic and Physical Chemistry 1 Dr. S. SIVAKUMAR Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry Hajee Karutha Rowther Howdia College Uthamapalayam 1
Uses of Glucose and Fructose: Glucose is used As a food for patients, growing babies and weak persons. As a sweetening agent in confectionery and in the preparation of sweets, candies and syrups. As a reducing agent in silvering of mirrors and vat-dyeing. As a intravenous injection to the patients with lower glucose content in blood. 2
In the processing of tobacco. As a starting material in the synthesis of vitamin C. In the preparation of glycerol. In fruit preservation and in making jams and jellies. Fructose is used As a sweetening agent in confectionery. It is also used as a substitute of cane sugar for patients suffering from diabetes. 3
Haworths structure of Glucose: Haworth (1926) related the carbohydrates to the heterocyclic compound pyran. He proposed the pyranose structure to denote the carbohydrates. The following figures show how Fischer Projection Formula can be translated into Haworth s representation 4
How to draw Haworths representations. Draw a hexagon as shown in the figure and write O at the top right-hand corner. Draw vertical lines through the remaining five corners as shown in the figure. Number the ring carbon atoms starting from the corner next to O in the clockwise direction. Write CH2OH on the top left hand corner. Now, attach the substituent s i.e., H and OH to the respective carbon atoms such that those present on the left-hand side of Fischer Projection Formula are above the plane of the ring while those on the right are shown below the plane of the ring. 7
Conversion of Glucose into Fructose: Glucose is warmed with excess of phenyl hydrazine to get osazone. The osazone on warming with hydrochloric acid forms osone. This on reduction with zinc and acetic acid gives fructose. 8
Conversion of Fructose into Glucose: Fructose is reduced to the corresponding polyhydric alcohol with hydrogen in presence of nickel. This product on oxidation with nitric acid gives an acid. This acid on warming gives -lactone. When the lactone is reduced with sodium amalgam in acid medium, glucose is formed. 9
Mutarotation Mutarotation is the change in the optical rotation because of the change in the equilibrium between two anomers, when the corresponding stereocenters interconvert. Cyclic sugars show mutarotation as and anomeric forms interconvert. The optical rotation of the solution depends on the optical rotation of each anomer and their ratio in the solution. 10