Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms in Biology
Explore the basic differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms, including the distinctions between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Unicellular organisms, such as bacteria and amoeba, consist of a single cell and are often microscopic. Examples of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic unicellular organisms are provided. In contrast, multicellular organisms are composed of multiple cells and include vertebrates, invertebrates, and plants. Discover the fascinating world of these fundamental life forms.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PRINCIPLES OF LIFE-II 3(2+1) BS SEMESTER 2 SESSION 2019-23 Course Tutor: Dr Moneeza Abbas
unicellular and multicellular organisms
The basic distinction among organisms is between unicellular multicellular organisms. Among the unicellular organisms, there is another fundamental distinction: between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes are relatively primitive unicellular organisms in which the protoplasm and the genetic material are encased within a cell wall of some kind but the genetic material is not located within a nucleus. organisms and
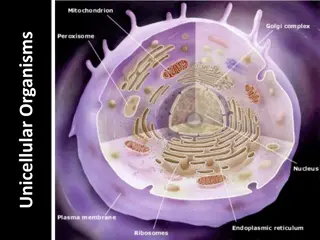
Eukaryotes are relatively advanced unicellular organisms in which the genetic material is enclosed in a special nucleus within the cell. Prokaryotes reproduce asexually, whereas eukaryotes reproduce sexually. The earliest fossils are believed to be prokaryotic; eukaryotic organisms evolved in the course of the Proterozoic.
Unicellular Organisms As the name implies, unicellular organisms are made up of a single cell. They are the oldest form of life, with fossil records dating back to about 3.8 million years ago. Bacteria, amoeba, Paramecium, archaea, protozoa, unicellular fungi are examples of unicellular organisms. These unicellular mostly invisible to the naked eye, hence, they are also referred to as microscopic organisms. Most of the unicellular organisms are also prokaryotes unicellular algae, and organisms are
Examples of Unicellular Organisms Some of the examples of unicellular organisms are: Amoeba Euglena Paramecium Plasmodium Nostoc, Salmonella ( Prokaryotic unicellular organisms) Protozoans, Fungi, Algae ( Eukaryotic unicellular organisms)
Multicellular Organisms Organisms that are composed of more than one cell are called multicellular organisms. Multicellular organisms are almost always eukaryotes. However, bacteria can form large interlinked strcutures such as colonies or biofilms but these can t be classified as multicellular organisms.
Multicellular Organisms Examples Some of the examples of multicellular organisms are listed below: All vertebrates and invertebrates All angiosperms, gymnosperms and higher land plants
Difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Unicellular organisms: An unicellular organisms is representedby a single cell. All activities of the organisms are performed by a single cell. There is no division of labour as the single cell performsall life activities. Reproduction consumes a single cell. The life span of an individual is short. Multicellular organisms: A multicellular organisms consists of largenumber of cells. A single cell performs one or few activities of the organisms. Cells are specialized to perform different functions of the body so that there is a division of labour within cells. Only some cells if the body called germ cells take part in reproduction. Other cells(somatic cells) remain intact. The life span of an individual is long