Understanding the Splicing Process in Botany: Mechanism and Types
Splicing is a crucial process in genetics where non-coding regions (introns) are removed from messenger RNA to generate mature RNA for protein synthesis. This process involves joining coding regions (exons) to produce functional mRNA templates. The mechanism, types, and importance of splicing, including alternative splicing for diverse protein functions, are explored in detail.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
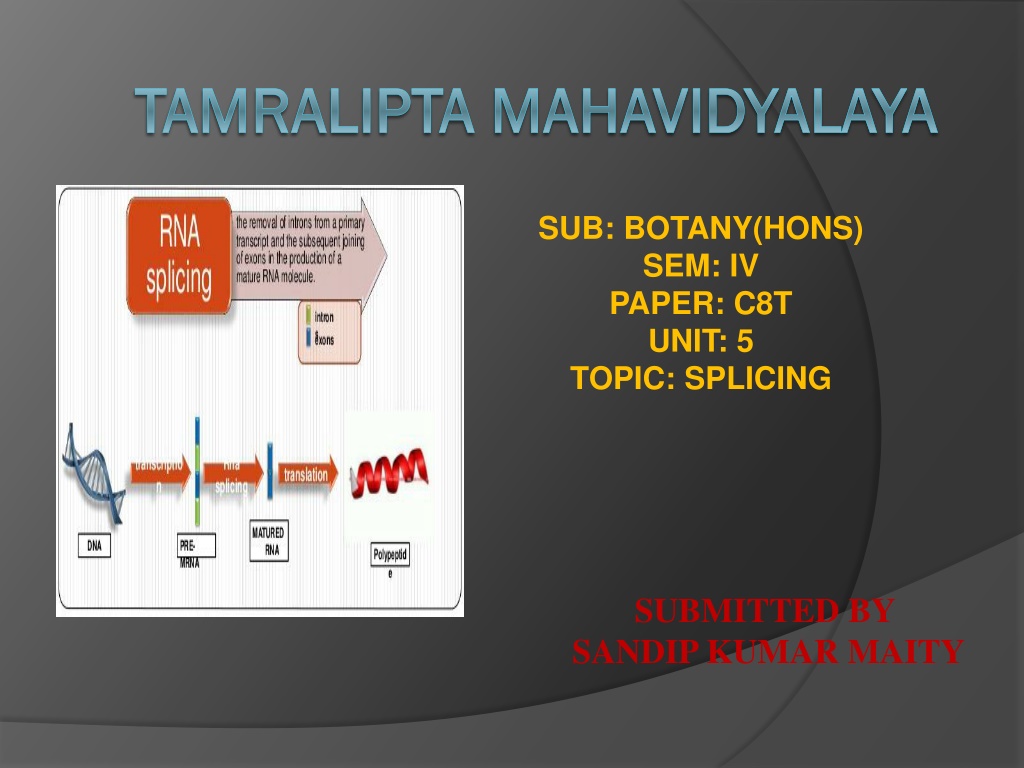
TAMRALIPTA MAHAVIDYALAYA TAMRALIPTA MAHAVIDYALAYA SUB: BOTANY(HONS) SEM: IV PAPER: C8T UNIT: 5 TOPIC: SPLICING SUBMITTED BY SANDIP KUMAR MAITY
WHAT IS SPLICING? The process by which introns( the non-coding regions of genes) are excised out of the primary messenger RNA transcript, and the exons (coding regions) are joined together to generate mature messenger RNA. The latter serves as the template for synthesis of a specific protein.
Mechanism of splicing Exercised intron has 3 -OH P between 2 exons in spliced product comes from 3 - splice site. Intermediate and spliced intron contain branched nucleotide. Branch involves 5 end of intron(G) binding to A within intron.
Alternative splicing It It is is a a process process that different different protein functions functions or or properties exon exon elements elements that sequence sequence that enables enables a a messenger protein variants variants ( (isoforms properties. . It It occurs that are are joined messenger RNA isoforms) ) that occurs by by rearranging rearranging the joined by by splicing splicing to to alter RNA (mRNA) (mRNA) to to direct that may may have the pattern alter the direct synthesis synthesis of of have different different cellular pattern of of intron the mRNA mRNA coding cellular intron and coding and
cissplicing: It is an intra molecular mechanism in which intervening sequences in eukaryotic pre mRNAs are removed. Trans Trans- -splicing splicing: : T Trans-splicing multiple separate pre-mRNAs. This phenomenon can be exploited for molecular therapy to address mutated gene products. splicing generates a single RNA transcript from