Understanding the LARC Capability Maturity Model for Organizational Improvement
The LARC Capability Maturity Model (CMM) focuses on enhancing the viral load cascade, aiming to achieve better patient outcomes and improve institutional capabilities for viral load scale-up. Developed by Carnegie-Mellon University Software Engineering Institute in 1987, the CMM provides a structured approach to assess and improve organizational capabilities through defined stages of maturity. By implementing changes at various sites and enhancing service delivery, organizations can progress through the CMM stages, starting from an initial stage to optimized processes. The tool covers 5 phases in the viral load cascade, emphasizing key functions such as demand creation, specimen collection, laboratory testing, result reporting, interpretation, and client management. Utilizing the CMM can help organizations establish core functions, set clear paths for achieving maturity goals, and drive meaningful improvements in key functions.
- Capability Maturity Model
- Organizational Improvement
- Viral Load Cascade
- Carnegie-Mellon University
- CMM
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
LARC Capability Maturity Model
LARC Program Goals To strengthen the viral load cascade to achieve better patient result (i.e., viral load suppression) To improve institutional capability for viral load scale-up Measures Program Goals Did the changes implemented at each site improve service delivery? Was the institutional capability for viral load scale- up enhanced? Aims and metrics Capability Maturity Model (CMM)
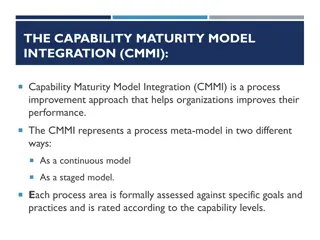
Capability Maturity Model Developed by Carnegie-Mellon University Software Engineering Institute (1987) Introduced a process for assessing software capability through a structured, sequential manner Described the maturation of each function according to a linear scale of increasing capability Can be adapted to evaluate an organization (or regional initiative) capability
CMM Stages Optimized Focus on process Stage 5 improvement Measured Processesare measured andcontrolled Stage 4 Stage 3 Defined Processes are defined and standardized for the organization Stage 2 Managed Processes are dependent on individuals and are not standardized Stage1 Initial - Processes are not repeatable, poorly controlled, andreactive
Organizational Assessment with CMM Establish core functions in which capability is required Based on the organizational goals, identifythe essentialfunctions Describe sequential stages of maturity of each function Progression is step-wise andlinear Characteristics that define each maturational stage Progress from one stage to the next reflects a meaningful improvement in a keyfunction Sets a clear path of achieving maturational goals
The LARC CMM tool covers 5 phases in the viral load cascade. Viral Load Cascade CMM CMM CMM CMM CMM Result Demand Creation for Testing Specimen Collection and Processing Sample Transport Laboratory Testing Result Reporting interpretation & Client Management Lab-Clinic Interface Lab-Clinic Interface 6
Demand Creation forTesting Stage1 Stage2 Stage3 Stage4 Stage5 Clinicians unawareof access to viral loadtesting and have not been educated on its rolein ARTmonitoring Increasedawareness of VL testing in clinicians, however minimal information is sharedwith clients Cliniciansroutinely educate clients aboutviral load testing andits benefits Organizationreviews routinely collected program data to measure performance in relationto standard operating procedures and national guidelines for clinician use of viral load testingand education ofclients Organization uses rigorous evaluation procedures and findings to demonstrate effectiveness andimprove the process of demand creation for viralload testing Clinicians routinely order viral load testingin- line with national guidelines Clinicians occasionally order viral load testing for clients Community leaders/CSOs unaware of access to viral loadtesting and have not been educated on its role in ARTmonitoring All stakeholders (e.g., clinicians, client groups, community leaders, etc.) play active role in community education about VL testing and promote campaigns forall individuals to know their VL Community leaders /CSOs have an increased awareness of viral load testing andits role in ARTmonitoring Community leaders /CSOs play an active role in educating their community about knowing their viralload status Clients unaware of access to viral loadtesting and have not been educated on its role in ARTmonitoring Clients have an increased awareness of viral load testing andits role in ARTmonitoring Clients are awareof and actively seek viral loadtesting No standard operating proceduresfor viral load testing and education Viral load testingand education standard operating procedures are established and implemented across the organization Standard operating procedures for viral load testing and educationare indevelopment
Specimen Collection and Processing Stage1 Stage2 Stage3 Stage4 Stage5 No client accessto viral load testing /specimen collection Viral loadspecimens are collectedoccasionally and only on certain days, limiting client access to testing and increasing burden for clients to return for VLsample collection Viral loadspecimens are collectedroutinely with few barriersfor clients Organizationreviews routinely collected program data to measure performance in relationto standard operating procedures and national guidelines forspecimen and collectionpreparation Organization uses rigorous evaluation procedures and findings to demonstrate effectiveness andimprove the process ofspecimen collection andpreparation Standardized supply chain system forspecimen collectioncommodities No standard supply chain system forspecimen collection commodities (e.g., DBS bundles) so supplies limit ability to collectspecimens Increased capacityfor supply chain system for specimen collection commodities, however notstandardized All stakeholders(e.g., clinicians, personnel, clients, etc.) play active role in appropriate viral load specimen collection and preparation to facilitate clients to know theirVL Clinicians/personnel complete specimen requisition forms accurately andcompletely Clinicians/personnel not trained to complete specimen requisition forms Viral load specimen collection and preparation standard operating procedures are established and implemented across the organization Increased awareness in clinicians/personnelfor properly completing requisitionforms No standard operating proceduresfor appropriate viral load specimen collection and preparation Standard operating procedures for appropriate viral load specimen collectionand preparation are in development Clinic-Lab Interface
LaboratoryTesting Stage1 Stage2 Stage3 Stage4 Stage5 Inadequatelab infrastructure for viral load testing (i.e. space/storage/ equipment/reagents/kits for viral loadtesting) Improvedlaboratory infrastructure, however, laboratory is only able to receive and test viral load specimens occasionallyor must refer toanother laboratory Laboratory is ableto regularly receive andtest viral load specimensin timelymanner Organization reviews routinely collected program data to measure performance in relationto standard operating procedures and national guidelines for viralload specimentesting Organization uses rigorous evaluation procedures and findings to demonstrate effectiveness andimprove the process of laboratory viral loadspecimen testing Laboratory has appropriately trained and competentstaff Laboratory staffare not properly trained nor competent to test viral loadspecimens Laboratory staff are trained, however, competencies areminimal Laboratory isworking at capacity and viral load testing is completed in a timelymanner Laboratory haslittle or no capacity for viral loadtesting Laboratory is has minimal capacity and viral load testing isoccasionally completed in a timely manner Laboratory viral load testing standardoperating procedures and competency standardsare established and implemented across the organization No standard operating procedures or competency standardsfor laboratory viral load testing Standard operating procedures and competency standardsfor laboratory viral load testing are in development
ResultsReporting Stage1 Stage2 Stage3 Stage4 Stage5 Results arenot received in a timely manner at theclinic from thelaboratory Resultsare occasionally receivedin a timely manner by the clinic from the laboratory Resultsare regularly receivedby the clinic in a timely manner from the laboratory Organization reviews routinely collected program data to measure performance in relation to standard operating procedures andnational guidelines for results reporting Organization uses rigorous evaluation procedures andfindings to demonstrate effectiveness and improve the process for resultsreporting Results are not recorded in theclient s chart in a timely manner Results are occasionally recorded in the client s chart in a timely manner but often not returned to clients Results are regularly recorded in the client s chart in a timely manner and returned to theclient regularly No standard operating procedures for results reportingand documenting results in the client schart Clinic ensures a facility-based person is accountable for timely recording of VL results in client charts and notification of clients with VL>1000 to return to clinic prior to scheduledappointment Standardoperating procedures for results reporting and documenting results in the client s chart are in development Results reporting and chart documentation standard operating procedures are established and implemented across the organization
Results Interpretation and Client Management Stage1 Stage2 Stage3 Stage4 Stage5 Viral load results are difficult to read and interpret and requireslaboratory assistance Viral load results are occasionally readable and interpretable and requires minimallaboratory assistance Viral load results are consistently readableand interpretable byclinicians Organization reviews routinely collected program data to measure performance in relation to standard operating procedures and national guidelines forclient management Organization uses rigorous evaluation procedures and findings to demonstrate effectiveness and improve the processof clientmanagement Clinicians are adequately trained in viral load result interpretation Clinicians are not properly trained to interpret viral loadresults Increased awarenessof result interpretation by clinicians Cliniciansregularly discuss VL results with clients All stakeholders (e.g., clinicians, personnel, clients, etc.) play active role in client management and their viral load Clinicians are uncomfortable integrating viral load results into ART care Few clinicians are comfortable integrating viral load results into ARTcare Clients understand their viral load results and can repeat their understanding back to theclinician Clients have a limited understanding of their viral loadresults Clients do not understand their viral load results Clinic has ability to identify missed opportunities for ensuring VL results are integrated with client management Standardized system in which all providers have a designated POC/referral system in place to consult for management of VL results and switch to 2ndline Intermittent availability of consultation for 2nd line treatment Clinicians have no backup person to call to discuss difficult cases or clients who require 2nd line treatment Standard operating procedures for result interpretation and client management are in development Result interpretation and client management standard operating procedures are established and implemented across the organization No standardoperating procedures for result interpretation and client management
How to Use the CMM Select the appropriate CMM tools Coach audits each facility to determine the grade (with facility LARC team participation) Two scores per CMM: Before LARC (baseline) - by November 15th,2020 At the end of LARC TBD
ResultsReporting Score = 2 Stage1 Stage2 Stage3 Stage4 Stage5 Results arenot received in a timely manner at theclinic from thelaboratory Resultsare occasionally receivedin a timely manner by the clinic from the laboratory Resultsare regularly receivedby the clinic in a timely manner from the laboratory Organization reviews routinely collected program data to measure performance in relation to standard operating procedures andnational guidelines for results reporting Organization uses rigorous evaluation procedures andfindings to demonstrate effectiveness and improve the process for resultsreporting X Results are not recorded in theclient s chart in a timely manner Results are occasionally recorded in the client s chart in a timely manner but often not returned to clients Results are regularly recorded in the client s chart in a timely manner and returned to theclient regularly X No standard operating procedures for results reportingand documenting results in the client schart Clinic ensures a facility-based person is accountable for timely recording of VL results in client charts and notification of clients with VL>1000 to return to clinic prior to scheduledappointment Standardoperating procedures for results reporting and documenting results in the client s chart are in development X Results reporting and chart documentation standard operating procedures are established and implemented across the organization
ResultsReporting Score = 1 Stage1 Stage2 Stage3 Stage4 Stage5 Results arenot received in a timely manner at theclinic from thelaboratory Resultsare occasionally receivedin a timely manner by the clinic from the laboratory Resultsare regularly receivedby the clinic in a timely manner from the laboratory Organization reviews routinely collected program data to measure performance in relation to standard operating procedures andnational guidelines for results reporting Organization uses rigorous evaluation procedures andfindings to demonstrate effectiveness and improve the process for resultsreporting X Results are not recorded in theclient s chart in a timely manner Results are occasionally recorded in the client s chart in a timely manner but often not returned to clients Results are regularly recorded in the client s chart in a timely manner and returned to theclient regularly X No standard operating procedures for results reportingand documenting results in the client schart X Clinic ensures a facility-based person is accountable for timely recording of VL results in client charts and notification of clients with VL>1000 to return to clinic prior to scheduledappointment Standardoperating procedures for results reporting and documenting results in the client s chart are in development Results reporting and chart documentation standard operating procedures are established and implemented across the organization