Understanding the Causes and Impact of the Cold War
The Cold War was fueled by post-WWII tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union, driven by conflicting ideologies and geopolitical ambitions. The spread of communism, arms race, space race, and even sports rivalry characterized this conflict, lasting about 45 years. The competition for global influence and power shaped international relations during this period, leaving a lasting impact on the world.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
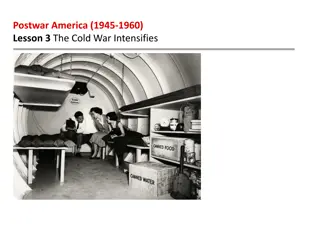
The Cold War Outcome: Why a Cold War?
Why a cold war? 1. Setting the stage: During and After WWII a. The U.S. and Soviet Union were allies during WWII b. Both counties spied on each other during WWII c. Both wanted to share as little as possible in the victory over the axis powers d. Communism was spreading i. Stalin took over Eastern Europe ---> The Iron Curtain ii. Mao Zedong created the People s Republic of China in 1949 iii. North Korea iv. Vietnam
Why a cold war? 2. Five W s & How: a. What was it and who fought it? i. Hostility between post-WWII superpowers: The U.S. (Free World) versus USSR (Communist World) ii. Would last about 45 years iii. Neither country directly fought one another
Why a cold war? b. Where was it fought? i. Wherever Communism threatened globally
Why a cold war? c. How was it fought? i. Arms Race (each side built up huge nuclear arsenals) 1. 1949 USSR achieved an Atomic Explosion 2. Technology on both sides led to advanced: a. Destructive power b. Numbers of weapons (Mutually Assured Destruction) c. Methods of delivery Goal: Maintain the balance of power or if possible, gain the advantage
Why a cold war? ii. Space Race (1957-1969) 1. Launching satellites (sputnik 1957; Soviet victory) 2. Race to the moon (U.S. victory)
Why a cold war? iii. Sports and Movies 1. Olympic Games served as a Cold War battlefield
1980 Winter olympics US team coached by Herb Brooks Soviet Union won the gold medal in hockey in 1956, 1964, 1968, 1972, & 1976 US team was made up of college amateurs US won semi-final game US would go on to win gold Seen as more than a hockey game Considered greatest sports moment in history (for US)
Why a cold war? iii. Sports and Movies 1. Olympic Games served as a Cold War battlefield 2. Stereotypes: a. We portrayed the Soviets as cold & ruthless b. They portrayed Americans as spoiled & undisciplined Goal: To prove physical superiority iv. A Race for World Influence Goal: To outnumber the opponent (U.S. Goal = Containment)
Why a cold war? d. Why did the U.S. win the Cold War? i. In the long run, USSR s weaker Communist system could not keep up the race; economic collapse ii. Mikhail Gorbachev was elected in USSR in 1985 (introduced democratic reforms) iii. Soviet Union collapsed in 1991