Understanding the Carbon Cycle and Its Importance
Explore the carbon cycle, a vital process circulating carbon between living organisms and the environment. Discover the sources of carbon, types of carbon cycles, stages and processes involved, and the significance of photosynthesis. Dive into terrestrial and aquatic carbon cycles, delving into how carbon moves through different ecosystems.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CARBON CYCLE Sources of Carbon Carbon is a very important element found in every living things (human beings, plants and animals) on the surface of the earth. Apart from living things, carbon is also found in various food nutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats and oil and also exists in the earth's atmosphere which we normally called carbon dioxide gas (CO2).
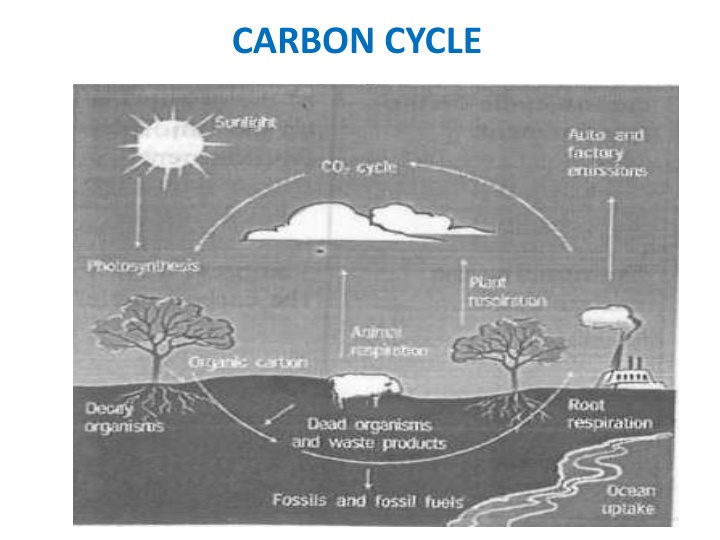
CARBON CYCLE What is carbon cycle? Carbon cycle is the organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again, or It is a complex series of processes through which all of the carbon atoms in existence circulates in the environment, or It shows how carbon rotates or circulates between living and dead organisms and the atmosphere.
CARBON CYCLE Types of Carbon Cycle Terrestrial carbon cycle(those that occur on land) Aquatic carbon cycle(those that occur in water).
CARBON CYCLE Carbon cycle that occurs on land is called terrestrial carboncycle. With the terrestrial carbon cycle, carbon moves through the ecosystem on the land. Carbon cycle that occurs in water bodies (sea, lakes, and rivers etc) is called aquatic carbon cycle.
CARBON CYCLE Carbon cycle that occurs on land is called terrestrial carboncycle. With the terrestrial carbon cycle, carbon moves through the ecosystem on the land. Carbon cycle that occurs in water bodies (sea, lakes, and rivers etc) is called aquatic carbon cycle.
CARBON CYCLE Stages and Processes involved in the Carbon Cycle 1. Photosynthesis 2. Respiration 3. Decomposition /decay 4. Combustion (burning)
CARBON CYCLE Photosynthesis(This is the first stage in the cycle) Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants prepare their own food using carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, water and mineral salts from the soil and energy from the sun.
CARBON CYCLE In this stage of carbon cycle, plants remove carbon from the atmosphere by using the energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide into carbon compounds (glucose). The carbon compounds in plants are transferred to animals when the animals eat the plants. In the process, oxygen gas is released. The overall photosynthesis reaction is: carbon dioxide + water + sunlight -> glucose + oxygen.
CARBON CYCLE Respiration(the second stage in the carbon cycle) Respiration is the process by which energy is obtained from food in the body of living organisms with or without the use of oxygen. The oxygen gas produced during photosynthesis is used by plants and animals to break down the food to release energy for metabolic activities. In the process, plants and animals released carbon atom back into the atmosphere in a form of carbon dioxide gas and the energy remaining is used to build tissues. The overall reaction of respiration is: C6Hl206+ 602 -* 6C02 + H20 + energy
CARBON CYCLE Decomposition /decay: (third stage of the process) Decomposition is the breakdown of dead organic matter by micro-organisms found in the soil. The organisms that break down (decompose) the dead organic matter are known as decomposers. When animals and plants die and decayed or decomposed (rot), the carbon atoms which are stored in their body are released back into the soil which serves as nutrients in the soil which may be used to grow new plants or small micro-organisms in both terrestrial and aquatic habitats.In the process carbon dioxide is released back into the atmosphere.
CARBON CYCLE Combustion (burning): (final stage ) Combustion or burning occurs when fuel reacts with oxygen to produce energy usually heat, carbon dioxide and water. When animals and plants die in the soil, some decay or get rotten in the soil immediately whilst some still remains, accumulate and get locked up in the soil. As they get locked up in the soil for years or decades, they form what we call fossil fuel (coal, petrol, and natural gases).When these fossil fuels are mined and burnt in the industries or in the environment, they contain carbon atoms which are released back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
CARBON CYCLE Importance of the carbon cycle 1. Through the carbon cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is made available to plants to manufacture their own food for animals through a process called photosynthesis. 2. Through the carbon cycle, oxygen is released which is needed by living organisms for reproduction. 3. The surface of the earth would have been too cold to live on if there were not to be presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.Because carbon dioxide serves as blanket over the planet earth which traps some of the sun's energy that falls on the ground from escaping.
CARBON CYCLE Ways by which the carbon cycle is disrupted Today as a result of indiscriminate human activities, the rate at which carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere is more than the rate at which it is being absorbed from the atmosphere. As a result, the carbon cycle has been greatly disrupted causing global warming on the surface of the earth as a whole. Below are some human activities that have disrupted the carbon cycle.
CARBON CYCLE Ways by which the carbon cycle is disrupted Indiscriminate cutting down of trees (deforestation): The forest as we all know play a very important role in our environment. Forest absorbs carbon dioxide being produced into the environment. In other words, forest serves as carbon sink. As a result of human activities such as mining, farming, construction of roads, most trees have been felled down without replacing them. As a result, only some few trees are left behind to absorb small percentage of the carbon dioxide produced which is not sufficient.
CARBON CYCLE Ways by which the carbon cycle is disrupted Industrialization/Excessive release of carbon (IV) oxide from industries such as VALCO, Tema steel, Tema oil refinery and exhaust fumes from cars into the atmosphere is disrupting the carbon cycle which needs to be checked. Pollution: Introduction of dangerous chemicals onto the land and in water bodies kill a lot of living organisms increasing the rate of decomposition of dead organic matter. This dead organic matter (dead plants and animals) releases more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and as result disrupting the carbon cycle.
CARBON CYCLE Effects of disruption of the carbon cycle on the environment. The disruption of carbon cycle results in the following: 1. Green house effect or global warming. 2. Increase in carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere. 3. Depletion of the ozone layer.
CARBON CYCLE Effects of disruption of the carbon cycle on the environment. The disruption of carbon cycle results in the following: 1. Green house effect or global warming. 2. Increase in carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere. 3. Depletion of the ozone layer.
CARBON CYCLE What is green house effect and global warming? Carbon dioxide as we all know is a green house gas. There are other natural green house gases such as methane, ozone and watervapour. These gases are very important to the survival of man and other living things on the surface of the earth. Because they serve as heat trapping gases or act as insulators (substances that does not allow heat to pass through them) around the earth and prevent infrared radiation escaping from the surface of the earth and in the process keep the earth's surface warm.
CARBON CYCLE Without them the earth would be a frozen world. However, too much of these gases can cause a build up for the average temperature of the earth s surface to rise and as a result making the surface of the earth become gradually warmer. The term used to describe the gradual warming of the atmosphere caused by increase in the amount of some gases in the air is what we called green house effect.
CARBON CYCLE Global warming Global warming refers to the increase in the temperature of the atmosphere surrounding the earth surface caused by increases in green house effect.
CARBON CYCLE Causes of global warming 1. Bush fires: Bush fires which results in the burning down of trees and vegetation releases high amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane into the atmosphere. 2. Industrialization (burning of coal, oil) results in the production of high amount of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. 3. Deforestation: It reduces amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 4. Use of CFC's (chlorofluoro carbons) gases in refrigerators, air condition system and in the production of plastic foams also destroys the ozone layer.
CARBON CYCLE Damaging effects of global warming. 1. Increase in the incidence of bush fires. 2. Rise in sea level which leads to flooding of low lying and coastal areas. 3. Reduction in atmospheric humidity and soil moisture leading to poor and low agricultural production. 4. Melting of icebergs. 5. Increase in atmospheric temperatures.
CARBON CYCLE Ways of maintaining the carbon cycle 1. Reforestation: Replanting of trees to replace those that have been felled down. 2. Afforestation: Planting more trees which would absorb carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 3. The use of renewable sources of energy other than fossil fuels. 4. Planting of cover plants on bare soils. 5. Avoid indiscriminate cutting down of trees (Deforestation). 6. Preventing the environment from being polluted.
CARBON CYCLE Ways of maintaining the carbon cycle 1. Reforestation: Replanting of trees to replace those that have been felled down. 2. Afforestation: Planting more trees which would absorb carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 3. The use of renewable sources of energy other than fossil fuels. 4. Planting of cover plants on bare soils. 5. Avoid indiscriminate cutting down of trees (Deforestation). 6. Preventing the environment from being polluted.