Understanding the Biosphere: Life on Earth
The biosphere encompasses all life on Earth, from individual organisms to ecosystems, biomes, and interactions between living and non-living components. Learn about the importance, components, and energy flow in the biosphere, highlighting its role in sustaining life on our planet.
Uploaded on Sep 27, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Biosphere Alissa Buford & Rahil Alhumaidi October/10/2013 B-2
What is Biosphere? The biosphere is the global sum of all ecosystems. Root word of Biosphere Bio means Life , sphere means Circle . The biosphere is all life on Earth. This includes all the things that are living as well as the remains of those that have died, but have not yet decomposed. The biosphere includes both life on land and in the oceans which adds up to 100% of the planet.
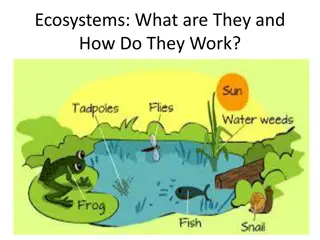
Parts of the Biosphere Individual: An organism who only interacts with species of his own kind. Population: sum of all individuals (species interacting with there environment only) that are living together as a group. Community: All the populations (All individuals of similar species) in a specific area. Ecosystem: more than a community (populations of organisms of diverse species) of living organisms. Biome: set of ecosystems (all living and non-living things interacting together) in a geographic area. Biosphere: the sum of all the biomes (blending of all ecosystems together) of humans, animals and plants, in their defined habitats.
How does matter and energy flow in a biosphere? Trophic Levels: producers (organisms that make their own food from sunlight and/or chemical energy from deep sea vents) are the base of every food chain. Primary consumers are animals that eat the producers. Secondary consumers eat primary consumers. They are carnivores (meat-eaters) and omnivores (animals that eat both animals and plants). Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers. Tertiary consumers die than decompose into earth. As rain falls, the decomposition grows into grass.
Biosphere Interactions The life supporting zone of the earth where atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere meet, interact and make life possible, is known as biosphere. The lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere are non- living components of the environment and are known as abiotic. The biotic or living components include plants, animals and microbes living on the earth. A constant interaction between the abiotic and biotic components of the biosphere results in the transfer of food and energy, which makes it a dynamic but stable system. The biosphere is the biggest biological system. It consists of smaller functional units known as ecosystems or ecological systems.
Biosphere Interesting Facts The biosphere is as important as life itself because it is our existence. Without the biosphere, the Earth would be a lifeless planet such as Mars or Venus. The biosphere is a system characterized by the continuous cycling of matter. This biosphere is generally believed to have evolved ~3.5B years ago. (which is the age of earth).
Life on Earth Video! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O- f5b98Uq8s Enjoy ..!