Understanding the Anatomy of the Urogenital Triangle in Perineum - Part 2
The urogenital triangle, part of the perineum, is crucial in male and female anatomy. It consists of specific boundaries, layers of fascia, and pouches, each serving distinct purposes. The superficial perineal pouch is significant, housing structures like the root of the penis in males and the bulb of the vestibule in females. In addition, muscles such as the transverse perineal muscle, bulbospongiosus, and ischiocavernosus play important roles in this region.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Perineum Part 2 Anatomy lab Urogenital Triangle Ass.Lic.Reham saad kadhum
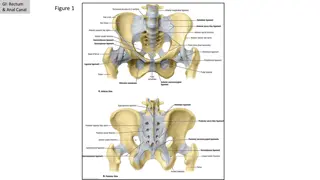
Urogenital Triangle Boundaries Contents (male=penis and scrotum , Female =external genitelia + orifices of urethra, and vagina ) The urogenital triangle is bounded in front by the pubic arch and laterally by the ischial tuberosity's
Superficial Fascia The superficial fascia of the urogenital triangle can be divided into a fatty layer and a membranous layer. The fatty layer (fascia of Camper) is continuous with the fat of the ischiorectal fossa and the superficial fascia of the thighs. In the scrotum, the fat is replaced by smooth muscle, the dartos muscle. The dartos muscle contracts in response to cold and reduces the surface area of the scrotal skin . The membranous layer (Colles fascia) is attached posteriorly to the posterior border of the urogenital diaphragm, laterally to the margin of pubic arch; anteriorly it is continuous with the membranous layer of superficial fascia of the anterior abdominal wall (Scarpa s fascia). The fascia is continued over the penis (or clitoris) as a tubular sheath
Note The urogenital triangle contain 3 membranes 1. Membranous layer of superficial fascia (superficial ) 2. Perineal membrane in the middle (middle ) 3. Pelvic fascia (deep) The urogenital triangle contain 2 pouches 1. superficial perineal pouch located between (membranous layer of perineum + perineal membrane ) 2. deep perineal pouch between ( perineal membrane + pelvic fascia )
Superficial perineal pouch Boundaries Superior : membranous layer of super fascial fascia Inferior : perineal membrane Laterally ; pubic arch Contents of Superficial perineal pouch Male : Root of penis ( bulb and 2 crura ) + superficial perineal muscles Female : Bulb of vestibule & crura of clitoris = superficial perineal muscles
The super fascial perineal muscles are Transverse perineal muscle Bulbospangiosus Ischiocavernosus
Deep perineal muscle Ishio.cavernosus m Clitoris Transvers. Perineal M Anococcygeal body ( ligament ) Bulbo.spangiosus
Deep perineal pouch It is completely closed space , Boundaries Sup: Perineal membrane Inf; pelvic fascia Lateral; Pubic arches
Note about the last modules the perineal membrane not present in the models it s the perineal body , either male or female Also the cremaster fascia is the second layer or middle layer in the scrotum of male not that which pointed in models Internal spermatic fascia is the inner layer of the spermatic cord located inside together with cremastric muscle