Understanding Supply and Demand: Key Concepts in Economics
Prices in markets are determined by the forces of supply and demand, where changes in one or both factors impact price levels. This concept is essential in economics to comprehend the dynamics of pricing, production, and resource allocation within an economy. The economy revolves around the efficient allocation of resources to meet the needs and wants of people, with economists studying these interactions to understand economic systems better.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
UOI Webinar 27thMarch
LOI : 2 The Role of Supply and Demand
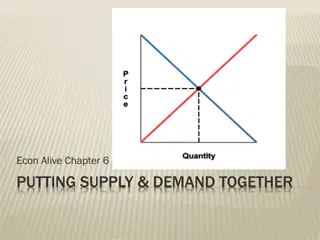
Price Change: Price may change when demand, supply, or both change. An increase in demand cause prices to increase. An increase in supply cause prices to decrease. If demand and supply both increase but the demand change is larger, price will increase it will act as if the only change had been a change in demand. If demand and supply both increase but the supply change is larger, price will decrease it will act as if the only change had been a change in supply. Ex. Suppose the government allowed a certain amount of imported steel to enter the economy. This would cut down on supply and result in a higher steel price. Also, if there was a decrease in potato prices it would suggest an increase in quantity demanded and a decrease in quantity supplied.
What makes prices rise and fall? Do candy makers have a meeting and decide how much they will charge for their candy? Or does the government command candy makers to lower their prices? Who determines the prices of the stuff we buy? It might seem like mysterious forces are at work, but that's not the case. Prices for most goods and services are determined in markets by what economists call supply and demand. Supply and demand work together to determine prices. In fact, supply and demand are among the most fundamental concepts in economics, so being familiar with these terms will help you better understand the economic world around you .
LOI 3: Production and exchange of goods and services of goods and services
What is an economy? An economy is a system for allocating resources to meet people's needs and wants. It determines how goods and services are made and exchanged. The study of the economy is called economics and a person who studies economics is called an economist.
The Economy You've probably heard people talk about "the economy." When people say this they are usually referring to the economy of the country where they live. A good economy is generally one where there are lots of good-paying jobs, businesses are making money, and the overall economy of the country is growing. A bad economy is one where people are losing their jobs, businesses are shutting down, and the overall economy isn't growing.
Webinar Unit of Inquiry 30.3.20
Micro vs. Macro Economics is often divided up into macroeconomics and microeconomics.
Microeconomics studies how individuals and businesses make decisions within the economy. Examples of microeconomics include: Why someone chooses to buy one product over another? How the supply and demand of products work together? What price a company charges for its product? Why different jobs make different amounts of money?
Macroeconomics looks at a bigger picture than microeconomics. It looks at the economy as a whole and not individuals or small businesses. Examples of macroeconomics include: The Gross National Product of a country Unemployment rates Net imports and exports for a country and how this affects jobs The current rate of inflation
Types of Economies Traditional - A traditional economy is typically based on bartering, trading, and farming. The economy is largely determined by how things have been done in the past with little change. People in traditional economies tend to do the same jobs as their parents. Market - A market economy (sometimes called a "free market") is one based on supply and demand. Consumers are free to buy whatever product they want. Companies can make whatever product they want. There is little government intervention allowing the economy to sort itself out through competition. Command or Planned - A command economy is one where the government closely controls the economy. The government determines what goods are manufactured, the price they will be sold, and who gets the profits. The government owns many of the major industries. Mixed - A mixed economy is a combination of a market and a command economy. Some industries are owned and controlled by the government, while other industries are allowed to be determined by the market. Mixed economies vary in how much control and regulations the government has
Basic factors of production https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-finance- domain/ap-macroeconomics/basic-economics- concepts-macro/introduction-to-the-economic-way- of-thinking-macro/v/four-factors-of-production https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/factors- production.asp ( see later after the webinar)
Produce the service or goods https://looka.com/blog/how-to- start-a-service-business/ Activity: What is your service business idea? or What is your product you would like to sale?
LOI 4 Our responsibility as consumers Producers and Consumers https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OA P_JlWLa4k https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PAb Bd0UjPzE (watch later at home)
Who is a Producer? A producer is someone who creates and supplies services. Producers combine labor and capital called factor inputs to create that is, to output something else. Business firms are the main examples of producers and are usually what economists have in mind when talking about producers. goods or
Difference between producers and consumers Producers Producers are the people who create the jobs opportunities and the benefits that others consume. Consumers not just people who go out and shop and buy, but even the jobs they have were someone else. "consumers consumers" of employment. They job and the Consumers are created They by are