Understanding Stomatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Stomatitis is the inflammation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity, resulting in symptoms like loss of appetite, salivation, and painful mastication. It can be caused by various factors such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, and irritants. Treatment involves hygiene measures, medical interventions like antiseptics, antibiotics, and supportive care to address associated symptoms like dehydration. For specific cases like palatitis in equines, additional procedures may be necessary. Proper care, including removal of causative factors, is essential for managing stomatitis effectively.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
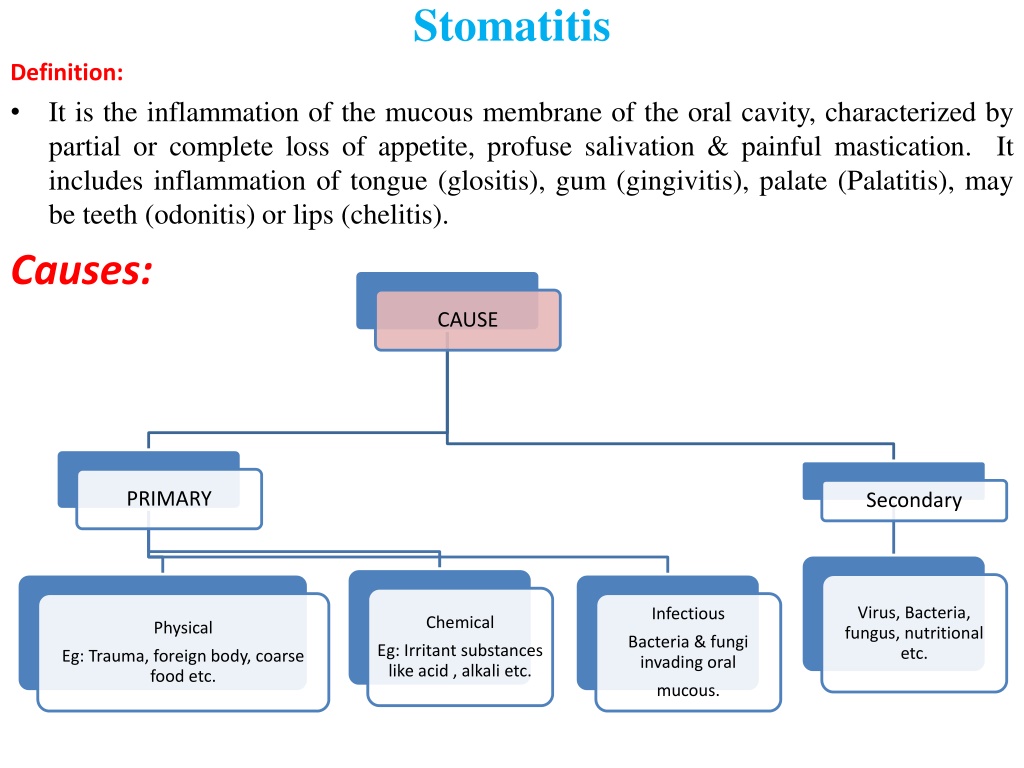
Stomatitis Definition: It is the inflammation of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, characterized by partial or complete loss of appetite, profuse salivation & painful mastication. It includes inflammation of tongue (glositis), gum (gingivitis), palate (Palatitis), may be teeth (odonitis) or lips (chelitis). Causes: CAUSE PRIMARY Secondary Virus, Bacteria, fungus, nutritional etc. Infectious Chemical Physical Bacteria & fungi invading oral Eg: Irritant substances like acid , alkali etc. Eg: Trauma, foreign body, coarse food etc. mucous.
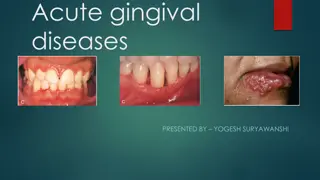
Symptoms: Partial or complete loss of appetite (Animal hesitate when taking food). Slow & painful mastication. Chewing movement are accompanied by salivation. Salivation either frothy & small or profuse & drooling and may contain pus or shreds of epithelial cells. A fetid odor from mouth in infections. Enlargement of local lymph nodes. Surrounding tissues, upper and lower lips may be affected. Toxemia and dehydration may be occur.
A. Medical treatment: (1)Wash or touch the mouth cavity or lesion with mild antiseptics, astringents & antiphlogistics such as one of the following: 2 % solution of copper sulfate 2 % suspension of borax 2 % gention violet 2 % alum solution 1: 4000 fresh solution of potassium permanganates. 1 -2 % Borax glycerine (over lesions). 1-3% iodo glycerine (over lesions). (2) Touch the ulcer with 0.5-1 % alcohlic Tr. Iodine or 0.5 to 1 0 % silver nitrate. (3) SC injection of atropine sulfate to control salivation. (4) Antihistaminic (Dexamethosone, 10-20 ml, for large animal) in allergic condition. (5) Antibiotics or sulfonamides to control infection. (6 ) Antifungal (Mycostatin 25 mg/ kg BW orally) in mycotic infection.
(7) In palatitis of equine, aspirate fluid under mucosa of palate by long sterile needle, then irrigate with antiseptic, then oral antiseptic wash, supportive treatment & antibiotic if fever present. (8) Supportive treatment: Glucose 10 - 40% IV in difficulty swallowing, vitamin A&C. (9) Surgical removal of granulomatous or gangrenous mass. B. Hygienic treatment: (1) Remove or treat the real cause (foreign bodies, sharp teeth). (2) Prevent animal to graze at pasture & isolation in infection diseases. (3) Easily digested palatable soft food as bran mashes for equine, green food for ruminants, milk rice or fine minced for dogs. (4) Give the animal clean water in enough amounts after each feeding before using oral antiseptic.