Understanding Stock Valuation: Key Concepts and Approaches
Stock valuation is essential for investors to determine the intrinsic value of a stock compared to its market price. This process involves analyzing fundamental factors like revenue, dividends, and risk. Different models are used to calculate intrinsic value, guiding investment decisions based on whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
INVESTING IN STOCK MARKETS STOCK VALUATION PART - I Notes Compiled by: Dr. RUCHIKA KAURA Assistant Professor Department of Commerce
Important Questions 1. What do you mean by valuation of stock ? What are the objectives of stock valuation? 2. What do you mean by valuation of stock ? Discuss the main approaches used to calculate the intrinsic value of shares. 3. Discuss briefly the fundamental analysis approach for valuation of stock. 4. What is Price Earning ratio? How is this ratio different from PEG ratio?
Valuation of Stock - Meaning Valuation of stock means to calculate the fair market value or intrinsic value of stock by using some technique or model. This fair value or intrinsic value of the share is compared with its market price or traded price. If Intrinsic value < market price, it means share is overpriced. If Intrinsic value > market price, it means share is underpriced. Investments should not be made in overpriced shares. An investor should buy underpriced shares and sell overpriced shares.
Objectives of Valuation of Stock Most important objective is to calculate the intrinsic/fair value of the share/stock. So that the investor can compare it with its market price and decide whether to invest in these shares or not. Second objective is to make prediction of the future movement of price behaviour of shares. So that the investor can know whether the stock is worth investing/holding or not.
Approaches to Valuation of Stock There are basically two main approaches/ school of thoughts to valuation of stock or to calculate the intrinsic value of shares: 1. Fundamental Analysis Approach 2. Technical Analysis Approach (will be covered in next lecture)
Fundamental Analysis Approach Under this approach, valuation of stock is done on the basis of the fundamental factors related to a company like revenue, dividends, risk, earning capacity of company etc. Intrinsic value of share is calculated using various methods/techniques devised on the basis of any of these fundamental factors related to company/share. Such analysis is done to help the investor in taking investment decision.
Fundamental Analysis Approach Dividend based model Earning based model Revenue based model Zero growth model Constant growth model Variable growth model Price Earning ratio Price Earning to Growth ratio Price to Sales ratio Earning per Share (EPS) Dividend per Share (DPS) Dividend Payout Ratio (DP ratio) Price Revenue ratio
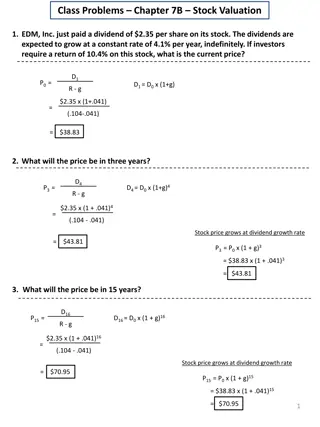
Dividend Based Model This model uses dividend paid by the company as the fundamental factor for stock valuation. Stock value can be computed using any of the following three formulas, depending upon whether the dividend paid by the company has no growth, constant growth or varying growth rate. Zero Growth model: When the company pays same amount of rupee dividend every year, the intrinsic value of share can be calculated as: P0=(D1/Ke) where P0 = Current market price of share D1 = Dividend to be paid by the company at the end of the year Ke = Cost of equity/Equity capitalization rate
Dividend Based Model Constant Growth model: When the dividend paid by the company grows annually at a constant rate, denoted as g , the intrinsic value of share is calculated as: P0=(D1/Ke- g) where P0 = Current market price of share D1 = Dividend to be paid by the company at the end of the year Ke = Cost of equity/Equity capitalization rate g = Constant rowth rate in dividend
Earning Based Model This model uses earning capacity of the company as the fundamental factor for stock valuation. Price Earning Ratio (P/E Ratio): P/E Ratio = This ratio indicates the relative value of a company s share in the stock market. A high P/E ratio implies that the market is optimistic about the growth of the company and a low P/E ratio implies that the market is pessimistic about the growth of the company. For eg. A company s share is currently traded at Rs. 120 and its EPS is Rs. 12. So, P/E ratio = 120/12 = 10. It means that for every one rupee of earning per share, the investor will have to pay ten rupees i.e. the share is traded at a multiple of 10.
Earning Based Model Price Earning to Growth Ratio (PEG Ratio): PEG ratio = This is the ratio of P/E to the expected growth rate of the company. This ratio is considered better than P/E ratio as it also considers company s growth rate and so, gives a complete picture. If PEG ratio is less than 100%, it is considered as desirable because it shows that the stock is undervalued, so, can be purchased for investment. If PEG ratio is more than 100%, it is considered as undesirable because it shows that the stock is overvalued, so, should not be considered for investment.
Revenue Based Model Price Revenue Ratio (P/R ratio): P/R ratio = or P/R ratio = (market capitalization= market price per share * no. of equity shares) This ratio measures the value of a company s share for every rupee of sales/revenues made by the company. Many investors consider this ratio as better than the P/E or PEG ratios because it considers revenues earned or sales made by the company instead of the earnings of the company as earnings are influenced by so many factors such as the management manipulations, accounting policies etc.
References Investing in stock markets by Dr. R.S. Bhardwaj and Bhamini Garg Investing in stock markets by Prof. (Dr.) Vanita Tripathi and Neeti Panwar Read these links from the net: https://www.thebalance.com/tools-of- fundamental-analysis-3140772 https://www.taxmann.com/bookstore/bookshop/ bookfiles/Investing%20in%20Stock%20MarketsVa nita%20Tripathichapter4.pdf